Ohm-law - Electricalcourses
advertisement

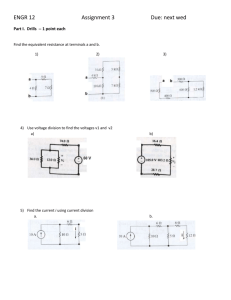
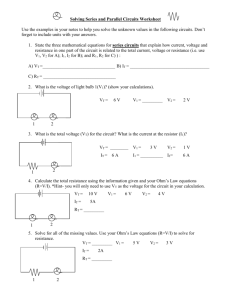
Module-1 Ohm’s law 1 By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: 1-Use prefixes to convert electrical quantities. 2-State Ohm's Law and define the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance. 3-Use Ohm's Law to solve unknown quantities of current, resistance, or voltage. 4-Apply the power formula to calculate the power in a circuit. 2 1- Introduction to Ohm's Law. 2-Investigations of Ohm's Law using Edison Version 4 simulator. 3-Electrical Units and Prefixes. 4-Electrical Power. 3 It states that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference (i.e. voltage drop or voltage) across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance between them, at a constant temperature. 4 5 6 Mathematical Equation is V I R Ohm's Law Formulas Find Current I V R Current equals voltage divided by resistance Find Voltage Find Resistance V R I V= I x R Voltage equals current multiplied by resistance 7 Resistance equals voltage divided by current Screen layout 8 Circuit connection 9 Voltage and current measurement 10 Suppose a 10KΩ carbon resistor is connected to a 12V battery .Calculate the current flow. I=V/R I= 12/10000= 1.2 mA. Suppose a solar cell provides a current of 2.5 mA to a 500 ohm load. Calculate the output voltage of the solar cell: V= I X R V= 2.5mA X 500 ohm V= 1.25 V 11 Quantity Name Unit of Measure Symbol Name Voltage U V Emf Current Resistance Function Symbo l Volt V Voltage is the electromotive force or pressure which makes current flow in a circuit I Ampere A Current is the flow of electrons through a circuit R Ohm Ω Resistance is the opposition to current flow offered by electric devices in a circuit 12 Metric prefixes table Number Power of Ten Prefix Symbol One billion 1,000,000,000 109 giga G One million 1,000,000 106 mega M One thousand 1,000 103 kilo K One 1 100 --- --- One thousandth 0.001 10-3 milli M One million 0.000001 10-6 micro μ One billionth 0.000000001 10-9 nano n One trillion 0.000000000001 10-12 pico p 13 Electrical power is defined as the potential energy or voltage times the current passing through the device. P = VI Where: P = electrical power in Watt (W) V = voltage used in Volt (V) I = current in Amperes (A) 14 Suppose an electric heater draws a current of 8A when connected to its rated voltage of 235V. The power rating of the heater is : P = VI=235x8=1880W=1.88 KW Suppose a current of 30A is being supplied to an electric load. The total resistance of the wire used to supply this current is 0.1 Ω. The power that lost in the wire is: P = I2 x R = (30)2 X 0.1 = 90 W 15 16