Jon Wigley
advertisement

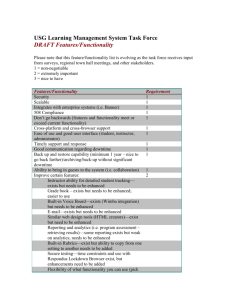
“Benchmarking an Organisation” Presentation by Jon Wigley IPPA Conference Harrogate, September 14th 2013 Agenda Setting Expectations “How MO`s measure up against their journey towards advance development and compare to other MO`s working towards the same objective” Benchmarking process - Frameworks Not-for-Profit v For-Profit Similarities and differences Agenda What are we benchmarking? Organisational excellence In whose eyes? Who matters? Members, Peers, Service Partners, Industry, Clients, Employees, Volunteers…..Others? Agenda Against whom are we benchmarking? MO`s - Each Other? Other not-for-profit in the Health Industry? Other not-for-profit? For profit? Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs)? Agenda Benchmarking based on what criteria? Deliverables (kpi`s) + Set + Monitored + Reviewed + Revised Objective v Subjective + Deliverables v Feelings Agenda Why are we benchmarking? Why is it important (to you)? + Excellence + Better + Challenge + Change + Positive Energy Agenda Setting expectations (yours)? What would you like to get out of this day? Why? Introduction – Jon Wigley Jon Wigley – Background A Business Coach Coaching v Consulting SMEs focus Industries – Finance, Legal, Media, Technology, Entertainment, etc Private Practice – Physiotherapy First hand experience! General Introduction Rapidly changing world and more demanding pressures – drivers and impact…and opportunities! Social trends: expectations and demands Technology & Social Networks: Communication Mobility: Loyalty Aspiration: Consumerism Recession: Cost/Value Dynamics of a NFP The prevailing dynamics of a Not-for-Profit Honorary functions filled by dedicated insider practitioners, often for many years, even decades! Passionately care about what they do xxx Day-to-day patterns of behaviour permeate their voluntary contribution + TRUST(ee) + COMMITMENT + LOYAL(ty) Similarity of NFPs to SMEs Not-for-Profit entities and the similarity to SMEs The emotional pull of the small business The passion that create and drives an SME The challenge of managing a small business Working “IN” v Working “ON” Time – A most precious resource Core skills and experience Is business evolution predictable? The evolution of a small business Is there a typical mode of progression? Anchor for our benchmarking – to know where we are up to, we need to reflect where we have come from! How do we typically measure our progress? Measuring objective progress How do we typically measure our progress? Objective measures? Increase in: Turnover Profit Number of clients Increase in pricing Number of staff Amount/size of equipment, premises, etc Measuring subjective progress How do we typically measure our progress? Subjective measures? Feelings?! +/Feelings drive behaviour and have significant impact but often unconscious Feelings can, and do, shift over time Behaviour is managed with, and through, a defined business culture Stages - Feelings The “Stages” Framework The major significance of feelings How they significantly and silently impact over time on a business, a team, and every individual How they shift over time The Stages Framework - Presented Functionality – The Key Skill Functionality – The Key Skill Set to benchmark Being Functional – What does it mean? “To serve a PURPOSE for which it was designed” “Fit for purpose” Efficiency – minimum expenditure of time & effort “The purposeful use of resources to achieve a desired outcome” Functionality – benefits? Functionality – What will it achieve? Clear management reporting Motivated staff Lack of duplication Management focus that maximises skills Time released Functionality - Avoids Functionality – What will it avoid? Duplication of effort Management time lost Bottlenecks “Work-arounds” (The Rock in the Stream) Staff frustration Miss-match of skills No direct, clear communication Functionality – 7 x key objectives 1. PROFITABILITY (RESOURCES ALLOCATION) Subjective: Objective Qualitative: Quantitative People: Infrastructure Functionality – 7 x key objectives 2. PRODUCTIVITY (EFFICIENCY) Processes Methodology Formality Discipline Precision Management Tools Functionality – 7 x key objectives 3. Building a STRONG FOUNDATION Upon which to (GROW) Planning Scheduling Managing Monitoring Reviewing Revising Functionality – 7 x key objectives 4. POSITIVE ENERGY (People and Roles) Define the “right” roles Define the “right” people Put the right people in the right roles (Remove the wrong people!) Functionality – 7 x key objectives 5. SELF RESPONSIBILITY A (No Blame) Culture Responsibilities: Understood Taken ……Fully! Functionality – 7 x key objectives 6. OWNERSHIP (Value) To own To possess To value The endowment effect – care, commit, contribute Functionality – 7 x key objectives 7. EMPOWERED WORKFORCE (Power) Giving power Giving authority ……to THINK ……to ACT Leads to effective SUCCESSION! The Functionality Cycle Against which we can benchmark ourselves as we go through the cycle Positive – Happy with current status Average – OK but could do with some work Poor – Definitely needs work The Functionality Cycle INTENT Our fundamental purpose – Why do we exist? Focused, conscious, and clear – gives context to everything we do or think to do Objectives set, unified and communicated You Others The Business Are You? The Functionality Cycle RESOURCES Lead: Manage People: Infrastructure Character: Facilities Talents: Equipment Skills: Systems Wisdom: Knowledge Potential: Actual Do You use well? The Functionality Cycle STRUCTURE Clearly define the required outcomes Create a structure that reflects the full range of necessary tasks (see Workflow - next) Delegate responsibility, but be accountable Distribute power and authority Empower a sense of ownership Roles and responsibilities understood and taken Do you have? The Functionality Cycle WORKFLOW Create an effective interface and balance between: + Strategic Operations (Long-term planning) + Business Operations (The day-to-day work) + Support Operations (The essential back office) The Functionality Cycle WORKFLOW (cont`d) The efficient workflow is based upon the clear definition and understanding of: Structure, Roles & Responsibilities, Reporting Lines, Policies & procedures, Communication, KPIs, Monitoring, Evaluation, Feedback, and Training…….. All supported by quality management tools Do you have? The Functionality Cycle EFFICIENCY/TIME Efficiency – “The minimum expenditure of time and effort” Processes, Methodology, Formality, Discipline, Precision, Management Tools Time – Time released v Management Time Lost Awareness of value, allocation of usage, and effective delegation Are you? The Functionality Cycle CAPACITY The full and conscious leverage of existing resources – today? Planning for future growth and the necessary increase in resources – tomorrow? Investment Planning? Right People: Right Roles Do You? The Functionality Cycle Support Operations Most SMEs completely under-value/estimate the importance of the following functions and as a consequence do not invest sufficiently in their proper management: IT, Finance, Legal, Administration, Secretarial, HR, Premises, Compliance, etc Do You? The Functionality Cycle • PERFORMANCE The importance of high performance Leveraging potential Setting objectives Reviewing performance – feedback Acknowledgement Value(d) Do You? The Functionality Cycle QUALITY Quality is a state of mind Product (what) AND Service (How) Always add value to what we do and how we do it Reflects a chosen and sustained Position Enhances brand and reputation Attracts – clients, referrals, employees, etc How aware are you? The Functionality Cycle CREATIVITY Why is it important to encourage creativity? Fresh Challenge Positive Energy Change Open Are You? The Functionality Cycle FLEXIBILITY Why is it important to maintain flexibility? Speed Choice and change Individual needs Bespoke Dynamic Are You? The Functionality Cycle The Business Culture & Soft Skills Culture = Behaviour (expected) Articulated and aligned values Processes – Recruitment, Induction, Delegation, Performance, Mentoring, etc Communication, Relationships, Issues Encouragement, Motivation and Incentives How aware are you? Summary Benchmarking – What, Against Whom, How and Why A rapidly changing world – drivers and impact The prevailing dynamics of a not-for-profit Similarities with SMEs Core Observations on SMEs The typical evolution of an SME – Stages Functionality & its 7 x Key Objectives The Functionality Cycle Benchmarking Stages – Where are you as an MO; Where are You? 7 x key Objectives – Profitability, Productivity, Strong Foundation, Positive Energy, Self Responsibility, Ownership, Empowered Workforce Functionality Cycle – Intent, Resources, Structure, Workflow, Efficiency, Capacity, Support Ops, Performance, Quality, Creativity, Flexibility, Culture & Soft Skills Did you get what you wanted from the day?