Lab: Uniform Motion Objectives

Lab: Uniform Motion
Objectives:
To determine the time interval for an object to travel different distances.
To determine the average velocity of the object for different time intervals.
To graph a position versus time graph for the object.
To determine whether or not the object moves with uniform motion
Theory:
Uniform motion requires movement at a constant speed in a straight line. The only situation in which distance travelled and displacement have the same value is for an object oving in a straight line.
The average velocity of an object can be found from its displacement (Δd) during a time interval (Δt), according to the equation: v ave
d t
d t
2
2
t d
1
1
The average velocity can also be found graphically from the slope of a position-time graph.
Materials
: stopwatch measuring device moving object launch materials
Specify materials used. Do NOT include pen, paper, calculator unless they were part of the apparatus.
Procedure:
Prepare launch system
As a group, design a method that will launching the object the same way every time at what appears to be the same starting speed and the same direction.
Longest trial
Determine the longest straight-line distance (displacement) that the object can travel.
Measure a distance slightly shorter than that maximum to ensure that the object reaches there three times.
Using a stopwatch, measure the time interval for the object to travel that distance.
Repeat the measurement for the time interval until your group has three similar values.
Record the distance and time intervals in the table (Table 1).
Describe the motion of the object.
Shorter trials
As a group, select three shorter distances.
Measure and record the time intervals to travel each distance as above.
Processing Data
Complete Table 1
Calculate the average time interval for each distance.
Calculate the average velocity of the object for each distance.
Calculate the sample standard deviation for each set of trials; this is the absolute uncertainty for time
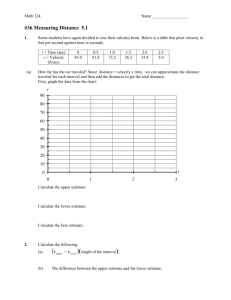
Construct a position (y) versus time (x) graph
Plot the data points in Table 1 including point (0 m, 0 s).
Construct a line of best fit (ONE straight line through the scattered data points)
Determine the slope of the line of best fit using (0m, 0s) and a point beyond the data for the longest trial.
Show a sample calculation for each type of calculation using the first set of data and the line of best fit. include: formula, substitution of experimental values, solve.
Table 1 Time intervals for different straight line distances travelled by the object.
Distance, ∆ d / m Time Interval, t / s Average Velocity, v / m s -1 mesure to 2 decimal places eg. 1.00, 2.34 one trial time another trial time a thrid trial time the average of the three similar trial times for that distance use the distance and the average time interval
0 0 0 –
Conclusion and Evaluation
Conclusion
State the average velocity from the line of best fit of the position-time graph.
State the highest and lowest values and their corresponding distances for the average velocity from Table 1.
Identify any relationship between distance travelled and any changes in average velocity.
Conclude whether or not you believe that your object had uniform motion for the distances investigated.
Explain your conclusion based on your results.
Evaluation
Identify any weaknesses of the experiment itself (not the group members themselves).
Identify how these weaknesses could be minimized or eliminated in a future experiment.
Identify other ways to improve this experiment.