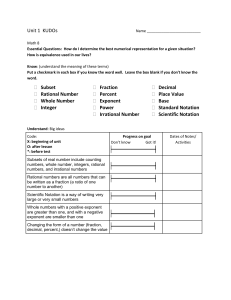
8th Math LF Aug 27
advertisement
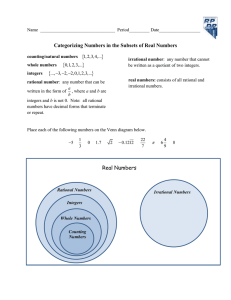
FRAME THE LESSON Student Expectations Bundled in Lesson Noun=Underline Verb=Italicize Readiness TEKS: 8.2D: Order a set of real numbers arising from mathematical and real-world contexts. TEACHER: Unit 1: Rational Numbers Engage: Explore: Supporting TEKS: 8.2A: Extend previous knowledge of sets and subsets using a visual representation to describe relationships between sets of real numbers. 8.2C: Convert between standard decimal notation and scientific notation. 8.2(B) approximate the value of an irrational number, including and square roots of numbers less than 225, and locate that rational number approximation on a number line Explain: Elaborate: Process TEKS: CLASS: 8th Math LESSON DATE: August 27 1 st 6 Week Period Objective/Key Understanding: Approximate value of irrational numbers by using number line. The student will learn about relationships between sets of real numbers, ordering irrational and rational numbers and scientific notation. Scientific notation is used to write very large or very small numbers. What is the process for converting between standard decimal notation and scientific notation? What is the process for converting between scientific notation and standard decimal notation? Closing Product/ Question/ Informal Assessment: Numbers are interrelated. Vocabulary: How are different sets and subsets of numbers related? Base, counting (natural) numbers, Decimal notation, E, Integers, and Order numbers, Place value, Powers, Rational numbers, Scientific notation, Whole numbers What relationships exist within our number system, and how are they used? Week 1 Teaching Points & Activities: Engage: Spiral review # 3 Do not allow students to open their Go Math: Grade 8 Student Edition. Use the numbers on page 15 from Lesson 1.2 and write them on sticky notes. Give each group a set of sticky notes with mixed up numbers on it. Give each group of students a large Post It with a blank “Real Number System.” I have an example saved for you titled “Real Number Graphic Organizer” and it can be located in First Six Weeks Resources. Challenge students to remember the classifications and place the post it notes in the correct set of numbers. Go over “Example 1” with students from page 16 in your Go Math: Teacher Edition (TE). Explore: Have students go over pages 16 and 17 from Lesson 1.2 by using “Think, Pair, Share.” Strategies for “Think, Pair, Share” can be found here: http://www.readwritethink.org/professional-development/strategy-guides/using-think-pairshare-30626.html Explain: Create four groups in your class. Assign each group a Real Number Classification. o Group 1: Rational Numbers o Group 2: Integers o Group 3: Whole Numbers o Group 4: Irrational Numbers o These groups can be tiered by level of learner to facilitate success, scaffolding, and differentiation with this activity. Using the Guided Practice from Lesson 1.2, call out or use your Mimio Capture to show students the numbers. Have the classroom debate why or why not the number is or is not in their classification. Set academic discourse and debate rules. Encourage the use of academic vocabulary. Examples: Introduce “UPS Check” strategy again. Tell students your expectations for using the strategy. Challenge students to outdo one another using “UPS Check” on “1.2 Independent Practice” in pairs. Any questions they do not finish in class will be homework. 8.1A: Apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace. Evaluate: 8.1C: Select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation and number sense as appropriate, Stop & Check for Understanding—High Level Questions to solve problems. The base-10 place value system is an efficient way to represent numbers and numeric relationships. 8.1D: Communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, Why is the base-10 place value system an efficient way to represent numbers? diagrams, graphic and language as appropriate. Why is it important to understand the value of numbers? 8.1E: Create and use representations to organize, record, and What relationships exist within our number system and how are they used? communicate mathematical ideas. How are numbers, large or small, represented and communicated using the base-10 place value 8.1F: Analyze mathematical relationships to connect and system? communicate mathematical ideas. 8.1G: Display, explain, and justify mathematical ideas and arguments using precise mathematical language in written or oral communication. Small Group Purposeful Talk Question Stems: ELPS: c.1.A, c.1.D, c.2.I, c.4.D M T W TH F Resources/ Materials: Go Math Post It Mimio Capture Critical Writing Prompt: *How are counting (natural) numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers related? *What types of visual representations can be used to represent the relationships between sets and subsets of numbers *How can a number belong to the same set of numbers but not necessarily the same subset of numbers? Rigor & Relevance: Real World Connection: a) Create a visual representation to organize and display the relationship between the sets and subsets of numbers: counting (natural) numbers integers rational numbers whole numbers b) Place the numbers in the correct set or subset within the visual representation. c) Record two additional numbers that belong in each set of counting (natural) numbers, integers, and rational numbers within the visual representation. d) Place all of the numbers recorded within the visual representation in ascending order and verify the order using a calculator.