Stranger in a Strange Land: Implementation Science for Behavior

Stranger in a Strange Land: Implementation
Science for Behavior Analysis
Ronnie Detrich
Wing Institute
ABAI, 2014
Talking Points
• Provide an example of successful culture change.
• Describe principles of effective dissemination.
• Behavior Analyst as cultural anthropologist.
Large Scale Change
• Efforts typically have relied on rational discourse to persuade others to change.
• Generally a weak model for change.
Not everyone shares the assumptions necessary for argument to be persuasive.
Not everyone is influenced by data.
• Alternative strategies are necessary.
Texas Cleans Up
• In the mid-1980s Texas was spending $20 million to clean up roadside litter.
• Various campaigns had been ineffective
Keep America (Texas) Beautiful (Lady Bird Johnson)
What Did They Do?
• Target audience: Males between 18-35
• Series of public service announcements by iconic
Texans including:
Willie Nelson
Joe Ely
Texas Tornados
Fabulous Thunderbirds
No One More Iconic than SRV
Effects of Don’t Mess with Texas
• Reduced roadside litter by 72% between 1986-1990.
• Effects are maintaining.
• Considered the most successful anti-littering campaign in history.
• Phrase has become part of the culture of Texas extends well beyond littering.
Science of Implementation
• Identifies variables that result in broad scale adoption of new practices.
Influencing Dissemination
• Rogers (2003): Diffusion of innovation is a social process, even more than a technical matter .
• The adoption rate of innovation is a function of:
its compatibility with the values
beliefs
past experiences of the individuals in the social system.
Principles for Effective Dissemination:
Improving the Odds
(Rogers, 2003)
• Innovation has to solve a problem that is important for the “client.”
• Innovation must have a relative advantage over current practice.
• It is necessary to gain support of the opinion leaders if adoption is to reach critical mass and become selfsustaining.
• Innovation must be compatible with existing values, experiences and needs of the community.
Stranger in Strange Land: Behavior Analyst as
Cultural Anthropologist
• Anthropologist identifies values and behaviors that define a culture.
Values=reinforcers within the culture.
Behaviors=maintained by those reinforcers.
• Assessing culture:
Identifies important cultural practices and maintaining reinforcers.
Identifies potential obstacles to culture change
Suggests strategies for change.
Defining Cultural Practice
• Cultural practice: behavior that most members of the defined culture do.
Both overt and verbal behavior.
Can be measured via direct observation and surveys.
Measurement method depends on behavior of interest.
e. g. Aarons-Evidence-based Practice Attitude Scale
Metrics for Measuring Cultural Practice
• Incidence rates:
frequency that specific behaviors occur within a period of time.
• Prevalence:
percent of population that engages in behavior.
Some Assumptions
• High incidence rates + widespread prevalence = contingencies supporting practice .
• Changing cultural practices requires changing the relevant contingencies.
Possible Interactions
High
Incidence
Low
Cultural Practice Cultural Practice
•
Inadequate Frequency
Not Cultural Practice
• Subset of population engages in behavior
• Effective contingencies in place for this subset of culture
Not Cultural Practice
• No contingencies to support behavior
Analytical Task
High
Incidence
What contingencies support practices?
Low
Barriers to higher frequencies?
•
Lack of time?
• Lack of resources?
•
Unclear expectations?
Differences between high/low performers?
• Training?
• Experience?
• Peer group?
Barriers to greater prevalence/incidence?
• Verbal repertoires?
• Training?
• Unclear expectations?
Closing Thoughts
• Not everyone is persuaded by data and scientific explanation.
• To be effective, it is necessary to attend to audience variables and “make the case” in the most effective way.
• Behavior analysts should behave like cultural anthropologists.
Thank you.
Slides available at winginstitute.org
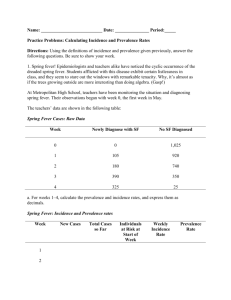
Example
• Incidence
Example: CBM probes completed = 10 per 2 weeks.
Goal: 20 students x 20 teachers x 2 weeks = 800 probes.
• Prevalence
20% (4/20) of teachers completed at least one CBM probe in 2 week period.
Goal: 100% (20/20) of teachers complete CBM probes every 2 week.
Possible Interactions
High
Incidence
Low
Cultural Practice Cultural Practice
• Inadequate Frequency
Not Cultural Practice
• Subset of population engages in behavior effective
• Contingencies in place for this subset of culture
Not Cultural Practice
• No contingencies to support behavior
Measuring Verbal Behavior
• Some occasions prevalence more important measure than frequency.
Verbal behavior measures
Example: “attitudes” toward data-based decision making.
Task is to identify breadth and depth of “attitude.”
– Example: Aarons (2005) measured attitude toward EBP among mental health workers.
Verbal behavior does not always correspond to overt behavior.
Important to measure all behavior not just verbal.
– Ferster (1967) what people do more important than what they say.