Human Systems: Circulatory System
advertisement

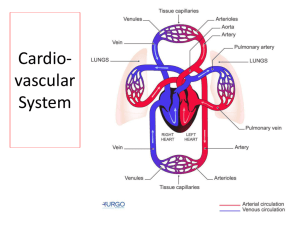
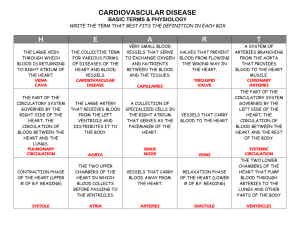
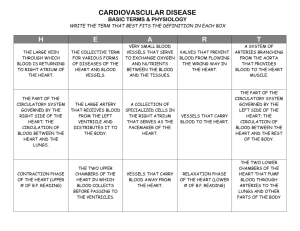
HUMAN SYSTEMS: Circulatory System BLOOD BLOOD Fluid connective tissue Circulates About Blood various substances 5L of blood in human adults is a part of the cardiovascular system (other include the heart and blood vessels) COMPONENTS OF BLOOD Blood contains Plasma plasma (fluid component) Blood cells (suspended component) Contains dissolved substances (water, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, other complexes, etc.) Blood cells RBC - Red blood cells (hemoglobin – transport of gases) WBC - White blood cells (immune system – defense against infections) Platelets (involved in blood clotting) BLOOD CELLS Red blood cells Transport oxygen Contain hemoglobin Most abundant cell type BLOOD CELLS Platelets Small in size, pieces of larger cells found in bone marrow Remain in circulation for 5-10 days Role in blood clotting BLOOD CELLS White blood cells Destroy pathogens Help in wound cleaning Modes of action Some search tissues for pathogens Some WBCs produce antibodies Some WBCs produce other chemicals against pathogens Other eliminate dead or damaged body cells FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD Transport of oxygen Transport of nutrients and minerals Transport hormones and other substances Regulation of body temperature BLOOD PRESSURE When heart contracts, blood is pushed out The force blood exerts on the walls of arteries is known as blood pressure Expressed in terms of millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) Blood pressure is expressed by two numbers - systolic and diastolic Systolic pressure – pressure in arteries when heart contracts Diastolic pressure - pressure in arteries when heart relaxes Healthy blood pressure: systolic 120 mm Hg, diastolic 80 mm Hg Pulse – rhythmic throbbing of arteries when blood is pumped by heart (around 60 - 70 per minute) BLOOD TYPES ABO system A, B, AB or O Depends on the type of antigens on RBC Blood groups and transfusion BLOOD TYPES Rh System Another type of antigen on RBC If antigen if present then Rh+ If absent then the individual is Rh- Rh system and transfusion BLOOD DISORDERS Hemophilia Leukemia Problem in blood clotting Protein required for clotting is missing Blood cancer Healthy blood cells are not produced Sickle cell anemia Mutation in hemoglobin Results is deformed RBCs CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Circulatory fluid (blood) Channels / tubes (blood vessels) Pumping device (heart) Transport of substances Regulation of body temperature Maintenance of homeostasis THE HEART Muscular organ Divided into four compartments (chambers) Upper chambers: Atrium Lower chambers: Ventricles Left and right sides of the heart are separated by wall Valves prevent back flow of blood Repeated opening and closing of valves produce heart beat BLOOD VESSELS Hollow tubes for flow of blood Some contain valve to prevent backward blood flow Three types Arteries Carries blood away from the heart Pulse is caused by flow of blood into arteries Capillaries Narrow blood vessels Allows exchange between body cells and blood Veins Blood enters from arteries to veins Carry blood towards heart BLOOD VESSELS TYPES OF CIRCULATION 1. 2. Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation CARDIOVASCULAR PROBLEMS Atherosclerosis Cholesterol and lipids accumulate in blood vessels This causes narrowing of vessels and decrease in elasticity High blood pressure Hypertension Narrowing or constriction of blood vessels increases pressure Stroke - blockage or rupture of blood vessels in brain CARDIOVASCULAR PROBLEMS CARDIOVASCULAR PROBLEMS Heart attack and failure Heart attack - when heart muscle cells do not get enough food Damage to heart cells If damage is excessive, heart may stop Heart failure occurs when heart is too weak to pump sufficient blood to meet body’s need Organs such as lungs, brain or kidneys may get damage