Section 9.1 to 9.3
advertisement
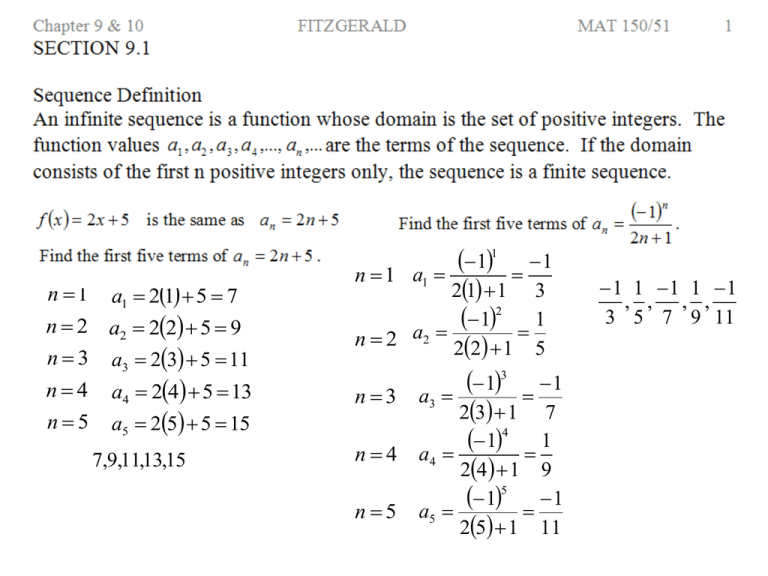
n 1 a1 21 5 7 n 2 a2 22 5 9 n 3 a3 23 5 11 n 4 a4 24 5 13 n5 a5 25 5 15 7,9,11,13,15 n 1 n2 n3 n4 n5 1 1 1 a1 21 1 3 2 1 1 a2 22 1 5 3 1 1 a3 23 1 7 4 1 1 a4 24 1 9 5 1 1 a5 25 1 11 1 1 1 1 1 , , , , 3 5 7 9 11 Alternating signs means we have (-1)n-1 power. Make a T-chart and find a pattern with the difference tests. n an 1 1 2 3 3 5 4 7 an 2 n 1 n an 2 1 1 4 1 3 1 2 2 5 6 1 5 8 1 7 3 10 2 2 2 1st level Difference Test. Linear equation with a slope of 2. What needs to be done to 2, 4, 6, 8 to get 1, 3, 5, 7? an 2 n 1 4 17 an n 2 1 1 1 2 2 4 1 5 2 9 1 10 3 5 7 16 1 17 2nd level Difference What needs to be done to 1, 4, 9, 16 Test. Quadratic to get 2, 5, 10, 17? equation an 1 n 1 n 2 1 a0 1 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21,... a1 1 n 2 a2 a22 a21 a0 a1 1 1 2 n 3 a3 a32 a31 a1 a2 1 2 3 n 4 a4 a42 a41 a2 a3 2 3 5 Do you see a pattern? 0! 1 1! 1 2! 2 1 2 3! 3 2 1 6 4! 4 3 2 1 24 5! 5 4 3 2 1 120 6! 6 5 4 3 2 1 720 20 1 a0 1 0! 1 21 2 a1 2 1! 1 22 4 a2 2 2! 2 23 8 4 a3 3! 6 3 2 4 16 2 a4 4! 24 3 4 8! 8 7 6! 2!6! 2 1 6! 47 28 1 2 2!6! 2!6 5! 3!5! 3 2!5! 2 2 1 n! n n 1! n 1! n 1! n n 1 31 32 33 34 35 3 6 9 12 15 45 4 n k 1 2 3 9 k k 1 1 32 1 42 1 52 1 62 10 17 26 37 90 n 2 1 1 2 3 2 0 2 2 2 2 k 1 1 k 1 The k values are 1 bigger than the powers on the 2. Notice that all the properties creates summations that all start at k = 1 and ends with n. Find each sum. Property #2 and #6. n= 1010 1 3 511 165 k 3 3k 3 2 k 1 k 1 10 10 Property #3. 8 k 1 Property #8. 4 Property #1. 88 1 88 1 k 1 k 1 1 18 2 k 1 2 k 1 k 1 n= 5 3 8 8 2 8 3 2 2 49 8 36 8 1296 8 1304 2 Property #2, #3, and #4. n= k 24 k 1 7k 2 k 7 k 2 24 2 24 24 k 1 k 1 2 k 1 4 Property #7, #6, and #1. 12 2424 1224 1 2424 1 7 224 6 2 42549 71225 224 2848 Property #2. 4k n = 20 k 6 2 Property #5. 20 2 5 2 4 k 4 k k k 6 k 1 k 1 Not k = 1, Property #5 20 2 2020 1220 1 55 125 1 4 6 6 10 7 202141 5611 4 6 6 4 10741 511 11260 1st level difference test. n = 40 a1 = 2 +4 +4 +4 +4 d=4 a40 = 2 + 4(40 – 1) a40 = 2 + 4(39) = 158 Treat the terms like points, as we did in Sect. 9.1, ( 4, 20 ) and ( 13, 65 ). The difference, d, is the same as the slope. Find the slope between the 2 points. 65 20 45 d 5 Find a1, use ( 4, 20 ) and ( 1, a1 ) with the slope formula. 13 4 9 20 a1 20 a1 20 a1 15 a1 5 5 5 4 1 3 an 5 5n 1 This is a visual approach to solving this problem. Make consecutive blanks for each term. d d d d d d d d d a1 5 ____, 10 ____, 15 ____, 20 ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____ 65 ____, 5 5 5 Make an equation from 20 to 65 with the 9 d’s. Now subtract the d value backwards for the 1st term. an 5 5n 1 20 9d 65 9d 45 d 5 n a1 an 101 a1 an n an a1 d n 1 a1 d = -50 Solve for n. Build the formula. Where did the numbers come from? n These two formulas S n a1 an go hand in hand. 2 n S n a1 an +11 +11 +11 2 150 5 1644 751649 123,675 S150 2 a1 n S n a1 an 2 101 times how many groups? 101 ( 50 ) = 5050 n 2 +11 a150 = ? d = 11 a150 5 11150 1 a150 1644 an n=? an a1 d n 1 250 1000 50n 1 750 50n 1 16 n Find these values. 15 n 1 16 1000 250 2 16 1250 81250 2 S16 10,000 S16 a1 n = 10 *3 *3 *3 *r *r r=3 an a1r n 1 a10 2 3101 2 39 39,366 36r 2 16 16 4 2 r 2 3 36 9 or With two r values gives us 2 equations. 3 2 2 r n 1 n 1 2 3 2 a 81 an 81 n 3 3 Make an equation from 81 ____, 54 ____, 36 ____, ____ 16 36 to 16 with the 2 r’s. ____, 2 3 or 3 2 Multiply both sides by a –r. This creates opposite terms. S n a1 a1r a1r 2 a1r 3 ... a1r n 2 a1r n 1 rS n a1r a1r 2 a1r 3 ... a1r n 2 a1r n 1 a1r n Add the equations together and cancel terms. Factor out the S. S n rS n a1 a1r n a1 1 r n Sn 1 r Divide by (1 – r). n = 10 a1 1 r n Sn 1 r a1 = 5 S n 1 r a1 1 r r =2 n Factor out the a1 5 1 210 51 1024 5 1023 5115 S10 1 1 1 2 ? n ? a1 1000 r )oo (½ will continue to get smaller until it is zero! 1 10001 2 S 1 1 2 1 2 10001 0 10002 2000 1 Dividing by ( ½ ) is the same as 2 multiplying by the reciprocal of 2. 0.9 0.9 0.09 0.009 0.0009 ... 9 9 9 9 ... 10 100 1000 10000 n 1 9 a1 r 10 10 1 0 10 S 9 1 1 10 10 1 1 10 9 10 1 9 10 0.9 1 Determine when a series diverge or converge. If a finite sum S n approaches a number L as n , we say the k 1 a r infinite geometric series 1 converges. A series k 1 diverges when the sum is . An infinite geometric series will always converge when 0 r 1 . This gives us two formulas for geometric series. a1 a1 1 r n S Sn 1 r 1 r An infinite geometric series will always diverge when r 1. 2nd STAT – OPS #5 is the sequence formula. seq(function,variable,starting value,ending value) Find the first 5 terms of an 3n 5n 4 2 2nd STAT – MATH #5 is the sum formula. Used for Series questions. sum(seq(function,variable,starting value,ending value)) 5 Find 2 3 n 5n 4 n 1











