BCH 3000-REVISION QUESTIONS Which vegetable is not a starchy
advertisement

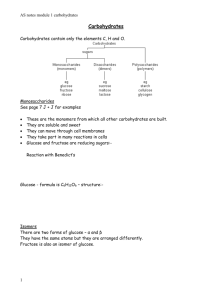
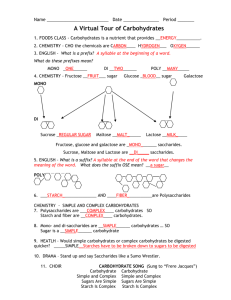
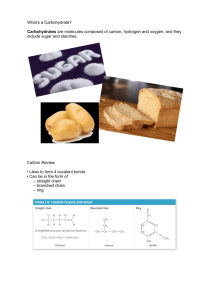
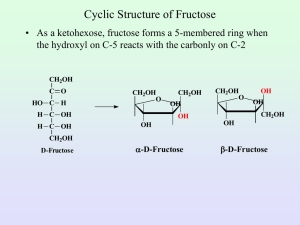
1 BCH 3000-REVISION QUESTIONS 1. Which vegetable is not a starchy vegetable? a) Spinach, b) Potatoes c) Carrots d) Peas ________________ 2 Which complex carbohydrate is a storage form of energy in plants? Cellulose b) Starch c) Glycogen d) All of the above __________________ 3 Glucose is a ________________________________________ 4. All carbohydrates have how many calories per gram? _________________ 5. Which macronutrient does the body prefer as a source of energy? ___________________ 6. Starch requires which digestive enzyme to break it down into individual glucose units? _____________________ 7. Which simple sugar is found in milk? ___________________________ 8. Which complex carbohydrate helps plants keep their shape? __________________________ 9. Complex carbohydrates include __________________, ________________ and ____________________ 10. If half of your calories should come from carbohydrates, how many grams of carbohydrates should you consume on a 1500 calorie per day diet? _______________________ 11. Table sugar, or sucrose, is made up of which two single sugar units? ____________________________ 12. Starches, Sugars and Fibers are all types of carbohydrates (True/False) ________________________________ 13. Fruits and vegetables are carbohydrates (True/False) _____________________ 2 14. Table sugar is a complex carbohydrate (True/False). _______________________. 15. Most carbohydrate foods come from plants. ____________________________ Carbohydrate foods should be eliminated from your diet if you want to lose weight (True/False) _______________________ 16. 17. 18. Which vegetable is not a starchy vegetable? Spinach, Potatoes, Carrrots, peas Co rrect Which complex carbohydrate is a storage form of energy in plants? _______________________ 19. What bond links the monosaccharides units ____________________ 20. Glucose has which functional group? ______________________ 21. Maltose is formed from __________________ 22 Lactose, sucrose, and maltose are all examples of __________________ 23. What monosaccharides make up a sucrose (table sugar) molecule? __________________ 24. Two sugars which differ from one another only in configuration around a single carbon atom are termed ___________________________ 25. The most important epimer of glucose is ____________________ 26. α-D-glucose and β -D-glucose are __________________ 27. Compounds having the same structural formula but differing in spatial configuration are known as ___________________ 28. In glucose the orientation of the —H and —OH groups around the carbon atom 5 adjacent to the terminal primary alcohol carbon determines __________________ 29. A sugar alcohol is ________________ 30. he sugar found in DNA is __________________ 31. Keratan sulphate is found in abundance in ________________ 3 32. Glucose on oxidation does not give (A) Glycoside (B) Glucosaccharic acid(C) Gluconic acid (D) Glucuronic acid 33. A positive Benedict’s test is not given by (A) Sucrose, (B) Lactose(C) Maltose(D) Glucose 34. An aldehyde and alcohol can react to form a A) hemiaketal. B) hemiketal C) hemiacetal D) All of the above. E) None of the above. 35. A dissaccharide linked by α-1-4 Glycosideic linkages is (A) Lactose (B) Sucrose (C) Cellulose (D) Maltose 36. The stable ring formation in D-Glucose involves (A) C-1 and C-4 (B) C-1 and C-2 (C) C-1 and C-5 (D) C-2 and C-5 37. α−D-Glucose and β−D-glucose are related as (A) Epimers (B) Anomers (C) Multirotation (D) Ketoenol pair 38. The polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of invertebrates is /(A) Pectin (B) Chitin (C) Cellulose (D) Chondroitin sulphate 39. Compounds having the same structural formula but differing in spatial configuration are known is (A) Stereoisomers (B) Anomers (C) Optical isomers (D) Epimers 40. On boiling Benedict’s solution is not reduced by(A) Sucrose (B) Lactose(C) Maltose (D) Fructose