iLEAP Study Guide-Social Studies
Major purposes of government (PREAMBLE)
1. To form a more perfect union (to join together the colonies)
2. To establish justice (define and protect the rule of law)
3. To insure domestic tranquility (to prevent conflicts within or between the states)
4. To provide for the common defense (a united power opposing any attacks)
5. To promote the general welfare (human rights and a stable society)
6. To secure the blessings of liberty (insure that the concept of freedom endures)
Key Terms
Federalism- distribution of power into federal and state governments
Absolute or constitutional monarchy- ruled by a King or Queen
Direct democracy- people decide and vote on officials/laws (NO ELECTORAL COLLEGE)
Republic- power is exercised by the public at large
Representative democracy- elected officials represent the people
Autocracy- a form of government in which a country is ruled by a person or group with total power
Dictatorship- absolute and total control by one person usually by force
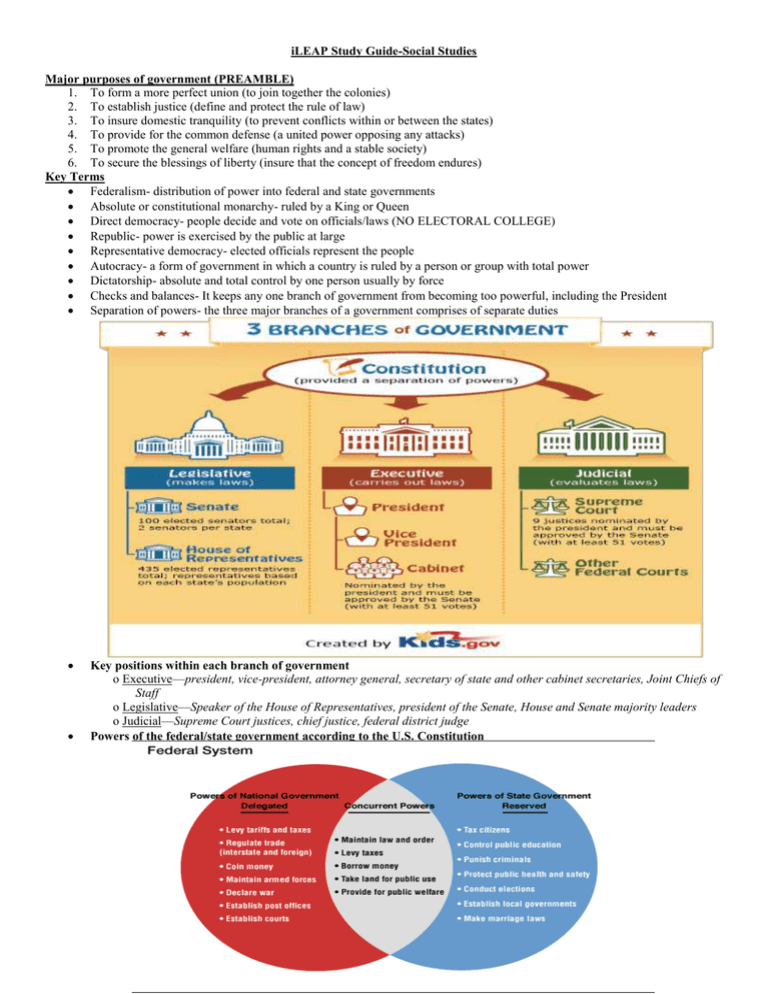
Checks and balances- It keeps any one branch of government from becoming too powerful, including the President
Separation of powers- the three major branches of a government comprises of separate duties
Key positions within each branch of government
o Executive—president, vice-president, attorney general, secretary of state and other cabinet secretaries, Joint Chiefs of
Staff
o Legislative—Speaker of the House of Representatives, president of the Senate, House and Senate majority leaders
o Judicial—Supreme Court justices, chief justice, federal district judge
Powers of the federal/state government according to the U.S. Constitution
Qualifications, terms of office, responsibilities, and limits of power for elected officials at the national level
Congress (HOR) (Senate)
President
Supreme Court
Natural Born Citizen (born in US)
No Constitutional Requirements
25 years old
35 years old
U.S. Citizen for 7 years
14 year resident of the Country
Live in the area they want to
represent
30 years old
U.S. Citizen for 9 years
Live in the area they want to represent
How a bill becomes a law at the federal level
The Senate and the House debate and vote the bill.
Electoral College
A candidate needs 270 electoral votes to win a presidential election
The number of electoral votes each state has is based on the number of representative and senators in the state
Foundations of the American Political System
•Similarities and differences of the Articles of Confederation and the U.S. Constitution
• Great Compromise
Roles of the Citizen
Qualifications and requirements for U.S. citizenship- birth in the U.S., birth to American parents abroad, or naturalization
(residency, citizenship test, oath of allegiance)
Specific guarantees of the Bill of Rights- freedom of speech, religion, assembly, press, and petition; right to bear arms;
compensation for private property; rights of the accused (warrants for search and seizure, protection from double jeopardy
and self-incrimination, speedy and public trial by jury, due process of law, right to an attorney, no excessive bail or cruel and
unusual punishment); other rights reserved to the people
Responsibilities as a citizen- military service, jury duty, paying taxes, obeying laws, holding public office
History
American Revolution (Revolutionary War) USE YOUR NOTES TO COMPLETE CERTAIN PORTION OF THIS SECTION
Causes of American Revolutionary War
o Stamp Acto Townshend Actso Tea Acto Intolerable Actso Boston Massacre Battles of War
o Battle of Saratoga- Major turning point in the war
o Battle of Trenton- Washington lead the army to attack Hessian (German soldiers) the day after Chirstmas and wins
o Battle of Yorktown- final battle of the war, French help the US win
Key figures during the American Revolution
o Benjamin Franklin- co-author of Declaration of Independence
o Thomas Jefferson- writer of the Declaration of Independence
o George Washington- commander in the army, lead at battle of Trenton
o John Hancock- first to sign declaration of Independence
Effect of the American Revolution
o national debt, local elections, state constitutions
Westward Expansion
Lewis and Clark- explorers who were to explore and map the newly acquired territory, find a route across the Western half of
the continent, and establish an American presence in this territory before Britain and other European powers tried to claim it
Great Plains- covered in prairie, steppe and grassland, that lies between the Mississippi River the Rocky Mountains
Indian Removal Act- signed by President Jackson, paid Native Americans to move west of the MS River to OK
Railroad Expansion/Transcontinental Railroad Manifest Destiny- God given right to move and settle in the west
Gold Rush- Gold found in CA, people begin to move west in large numbers to mine for gold
Trail Of Tears- Path Cherokee Indians took after being forced to move due to the Indian Removal Act (thousands of deaths)
Other Important Key Terms
Constitutional Convention- place where delegates met to discuss problems and concerns especially with great Britain.
Connecticut Compromise
Three-Fifths Compromise- slaves would be counted as 3/5 a person for population purposes
Spoils System
Monroe Doctrine- A document that states no European country may claim land in the western hemisphere or the US will
intervene.
Key People
Andrew Jackson- 7th president, Indian Removal Act, King Veto, Old Hickory
Thomas Jefferson- 3rd President, Louisiana Purchase, repealed acts from Adams presidency
James Monroe- Monroe Doctrine
Napoleon- French leader
Civil War (North vs. South)
Missouri Compromise- Missouri enters the Union as a slave state, Maine enters as free state; Slavery would be banned in the
Missouri Territory north of the 36 parallel
In the North: cities grew, factories were built, and transportation improved.
Many Northerners refused to obey the Fugitive Law, many Americans became abolitionists.
Key Terms
abolitionists – people who favored the ending of slavery
succeed- to remove oneself from the union
Fugitive Slave Law- Any slave that escaped and was caught in a free state must be returned to the owner
Sharecropping- owners of crops provided land, tools, and cabins to workers and a portion of the profit from the crop
Black CodesPoll tax – tax you must pay in order to vote
Literacy tests – required passing hard tests to vote
Plessy vs. Ferguson- court case that made it ok for all facilities (buildings, restaurants, trains etc.) to be “separate but equal”
Emancipation Proclamation- by Abraham Lincoln
o It declared all slaves in Confederate states were free.
o It did not free any slaves immediately.
o Confederate states ignored the proclamation, the fighting continued
Union- states apart of the United States
Confederacy- States that succeeded from the union and banned together to fight the Union.
The Gettysburg Addresso A speech given by Lincoln at a ceremony dedicating a cemetery on the battlefield.
Key People
Robert E. Lee- General in the confederate Army,
Ulysses S. Grant- Commander of Union Army
William Lloyd Garrison-editor of the “Liberator” an abolitionist newspaper
Harriet Tubman- conductor on the Underground Railroad; escaped slave, help free thousands of slaves
Frederick Douglass-former slave who became a leading abolitionists
Abraham Lincoln- 16th president, signed the Emancipation proclamation
Battles
Battle of Bull Run- 1st battle of the war, South wins
Battles of Gettysburg, PA – last major attempt of the South to invade the Union
Battle of Vicksburg, MS – Union gained control over the Mississippi River
Effects
The Civil War was the worst war in all of American history.
More than 600,000 soldiers died
War caused billions of dollars’ worth of damage.
The Civil War freed millions of African Americans.
Reconstruction
The period of time when the south was rebuilt after the Civil War
Suffrage- the right to vote
13th amendment- abolished slavery in all states
14th amendment- granted citizenship to African Americans
15th amendment- gave black men the right to vote