Lab12
advertisement

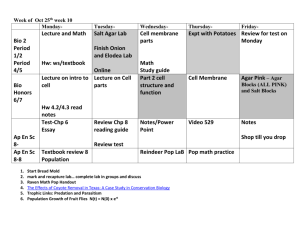
Lab 12 Goals and Objectives: Exercise 40: Hydrolytic and Degradative Reactions Read results: some will require additional reagents Exercise 41: Multiple Test Media No Kliger’s Iron Agar or Litmus milk, No inoculations for IMViC: discuss next lab, Inoculate SIM with straight stab for each unknown Inoculate three separate controls per pair using: Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus Each pair needs: 7 SIM stabs Exercise 71: Gram Negative Intestinal Pathogens Perform according to revised directions, supplement pg You still need to read the lab to know how the media works! Each pair needs: 3 MacConkey agar plates 7 Russell’s Double Sugar slants: streak and stab! Control broth cultures: Proteus vulgaris (Mac) Escherichia coli (Mac, RDS) Shigella flexnari (RDS) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (RDS) PA will inoculate additional controls for observation next lab Make new streaks for isolation on BHIA Each pair needs: 4 BHIA plates (new streaks for isolation) Starch Agar Plate Inoculation method: surface streak with loop Contains: the starches amylopectin and amylose in agar to solidify Additional reagents added: iodine, combines with starch to produce a blue-black precipitate Discriminates organisms that can produce amylase to hydrolyze amylopectin and amylose into maltose, glucose and dextrans Results: Halo around the streak = no starch present, positive for amylase production Blue-black precipitate up to/under streak = starch present, negative for amylase production + _ Skim Milk Plate Inoculation method: surface streak with loop Contains: fat free milk in agar to solidify (plate appears opaque white) Discriminates organisms that can produce proteases to hydrolyze the white milk protein casein into clear amino acids Results: Halo (clearing) around the streak = no casein present, positive for casein protease production Opaque white up to/under streak = casein present, negative for casein protease production + _ Spirit Blue Agar Plate Inoculation method: surface streak with loop Contains: tributyrin (triglycerides) in agar to solidify, Spirit Blue pH indicator: neutral pH = pale blue, acidic pH = dark or bright blue Discriminates organisms that can produce lipases to hydrolyze triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids (acid pH). (Some lipases will completely hydrolyze the tributyrin thus not producing acid wastes but instead completely clearing the visible lipids.) Results: Dark blue precipitate = partial hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production Halo around the streak (clearing of lipids) = complete hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production (agar could be pale blue due to complete clearing of all fatty acids or dark blue because a few fatty acids remain) Pale blue agar, no halo = tributyrin present, negative for lipase production Results: Dark blue precipitate = partial hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production Halo around the streak (clearing of lipids) = complete hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production (agar could be pale blue due to complete clearing of all fatty acids or dark blue because a few fatty acids remain) Pale blue agar, no halo = tributyrin present, negative for lipase production + _ + + acid neutral with halo _ Tryptone Broth Inoculation method: loop transfer Contains: high amounts of tryptophan Additional reagents added: Kovac’s reagent (amyl alcohol, hydrochloric acid, para-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde), reacts with indole to produce a red product Discriminates organisms that can produce tryptophanase to hydrolyze the amino acid tryptophan into indole, ammonia and pyruvic acid Results: Red with Kovac’s = cleavage of tryptophan into indole, positive for tryptophanase production Colorless = no indole present, negative for tryptophanase production + _ Urea Broth Inoculation method: loop transfer Contains: yeast extract, urea, buffer, Phenol red pH indicator: acidic/neutral pH = yellow/orange, alkaline pH = bright pink Discriminates organisms that can produce urease to hydrolyze urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia Results: Bright pink = cleavage of urea into ammonia, positive for urease production Yellow/orange = no ammonia present, negative for urease production + _ + _ Phenylalanine Slant Inoculation method: surface streak with loop Contains: high amounts of phenylalanine Additional reagents added: 10% ferric chloride, reacts with phenylpyruvic acid to form a green product Discriminates organisms that can produce phenylalanine deaminase to deaminate phenylalanine producing phenylpyruvic acid and ammonia Results: Green = cleavage of phenylalanine into phenylpyruvic acid, positive for phenylalanine deaminase production Yellow = no phenylpyruvic acid present, negative for phenylalanine deaminase production + _ Lab 12 Goals and Objectives: Exercise 40: Hydrolytic and Degradative Reactions Read results: some will require additional reagents Exercise 41: Multiple Test Media No Kliger’s Iron Agar or Litmus milk, No inoculations for IMViC: discuss next lab, Inoculate SIM with straight stab for each unknown Inoculate three separate controls per pair using: Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus Each pair needs: 7 SIM stabs Exercise 71: Gram Negative Intestinal Pathogens Perform according to revised directions, supplement pg You still need to read the lab to know how the media works! Each pair needs: 3 MacConkey agar plates 7 Russell’s Double Sugar slants: streak and stab! Control broth cultures: Proteus vulgaris (Mac) Escherichia coli (Mac, RDS) Shigella flexnari (RDS) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (RDS) PA will inoculate additional controls for observation next lab Make new streaks for isolation on BHIA Each pair needs: 4 BHIA plates (new streaks for isolation)