Presentation
advertisement

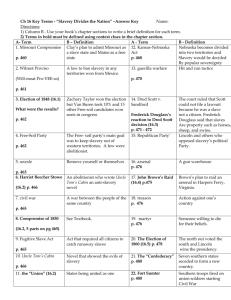
Chapter 14: A Divided Nation 1848-1860 Section 1: The Debate Over Slavery U.S. won Mexican-American War in 1848 Added 500,000+ acres to U.S. Missouri Compromise – no slavery above 36*30’ Popular sovereignty: political power belongs to the people; people make the choice about slavery. David Wilmot: Wilmot Proviso – document stated, “neither slavery nor involuntary servitude shall exist in any part of the (Mexican Cession)” Growing sectionalism: favoring interests of an area over the whole country. Free-Soil Party: (1848) anti-slavery northerners who supported Wilmot Proviso. The California Question Slave state or not? Would upset 15 free / 15 slave state balance Jefferson Davis (Senator – Mississippi) Compromise of 1850: Henry Clay (KY) 1. California enters union as a free state 2. Mexican Cession = fed. land, popular sovereignty rules on slavery issue 3. Texas gives up land west of Rio Grande Fugitive Slave Act 1. Made it a crime to help runaway slaves & let officials arrest slaves in free states. *Punishable by 6 months in jail & $1,000 fine. 4. The slave trade was outlawed in Washington D.C., but not slavery. 5. *New fugitive slave law* Section 2 : Trouble in Kansas Democrat – Franklin Pierce wins election of 1852. Stephen Douglas wants to build a RR that runs from Chicago to the Pacific Ocean. Opposed by southerners New Orleans Kansas-Nebraska Act (May 1854): plan to divide the rest of Louisiana Purchase into: 1. Kansas territory 2. Nebraska territory *Eliminates the Missouri Compromise 36*30’ line* Kansas Problems: 1. Abolitionists vs. pro-slavery settlers > Two Kansas legislatures = pro-slavery & anti-slavery > Sack of Lawrence: 1 man dies > Pottawatomie Massacre: John Brown & his men kill 5 pro-slavery men. 2. Brooks vs. Sumner: Preston Brooks uses his walking cane to beat Charles Sumner unconscious in the Senate chambers. Section 3: Political Divisions Republican Party (1854): Whigs, Democrats, Free-Soilers & abolitionists – party united against spread of slavery in West. Election of 1856: Democrats – James Buchanan Republicans – John C. Fremont Dred Scott Decision > 1857: Supreme Court addressed the 3 key issues. 1. Was Scott a citizen? 2. Time Scott spent living in north = freedom? 3. Constitutionality of prohibiting slavery in Louisiana Purchase? Lincoln-Douglas debates: Abraham Lincoln vs. Stephen Douglas for Illinois senate seat in 1858. * Central issue of debates was spread of slavery in the West * Freeport Doctrine: Local police would enforce voters’ decisions on slavery & Dred Scott case if it was different than Supreme Court’s ruling. Section 4 John Brown’s raid: he and his men took over Harpers Ferry arsenal in Virginia. Colonel Robert E. Lee captured John Brown in a firehouse; hanged on Dec. 2, 1859. Northerners split on John Brown’s actions Southern whites afraid of next “John Brown” “…safety of the south lies outside the Union.” Election of 1860 Abe Lincoln: Republican: WINNER Stephen Douglas: N. Democrat Breckinridge: S. Democrat Bell: Constitutional Union *Lincoln promised not to abolish slavery where it already existed* The South Secedes Within a week of Lincoln’s election, SC secedes from Union Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana & Texas also secede to form Confederate States of America. Jefferson Davis: elected President of Confederacy Lincoln inaugurated March 4, 1861. Announced he would keep all federal property in seceding states.