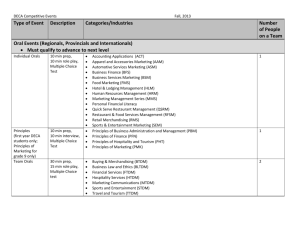
File - London Central DECA Team
advertisement

2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FMDM FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 1 1. What is one way that international banking impacts the financial services industry throughout the world? A. Controls interest rates C. Eliminates regulations B. Affects services and fees D. Increases value of investments 2. Which of the following is an example of an embargo: A. A country refusing to negotiate trade agreements B. A country placing a tax on certain imports C. A country limiting the amount of monthly imports D. A country banning exports to another country 3. Mr. Jones operates a small business serving several states. He needs to communicate with his customers but does not need an immediate response. The most economical method of delivering his messages would be through A. fax. C. e-mail. B. business letters. D. telephone. 4. What do business employees often need to do before they are able to write proposals? A. Evaluate technical skills C. Contact the customer B. Analyze personal biases D. Research the problem 5. A request made by an employee to a supervisor is an example of what type of communication? A. Grapevine C. Upward B. Downward D. Horizontal 6. When conducting staff meetings, what might managers do to make sure they cover all of the topics on the agenda? A. Limit discussion time C. Schedule an all-day session B. Present information in visual form D. Ask for written feedback 7. Businesses whose employees demonstrate a customer-service mindset often benefit from A. rapid employee turnover. C. reduced complaints. B. increased costs. D. decreased employee morale. 8. "I buy only the most expensive brands" is a statement that characterizes the __________ customer. A. domineering/superior C. suspicious B. disagreeable D. slow/methodical 9. What should salespeople avoid doing when handling customer complaints? A. Empathizing with the customer C. Discussing the problem B. Listening carefully D. Arguing politely 10. Which of the following is a characteristic of a tight money supply: A. Employment increases. C. Businesses expand. B. Consumers spend more. D. Credit is expensive. 11. The federal government oversees the charter, examination, and regulation of all national banks through the A. Supreme Court. C. Federal Reserve. B. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. D. Office of the Comptroller of the Currency. 12. What is the monetary policy of the Federal Reserve System sometimes intended to do? A. Guarantee a minimum wage C. Pay for national defense B. Monitor government spending D. Slow down the economy Copyright © 2008 by Marketing Education Resource Center®, Columbus, Ohio 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 2 13. The dollar value of all goods and services produced each year within a country's geographic boundaries is referred to as the A. gross domestic product. C. consumer price index. B. leading indicator. D. consumer catalog. 14. Which of the following is an example of a government making an economic decision that affects financial institutions: A. Monitoring exports C. Storing money B. Paying tariffs D. Raising taxes 15. Which of the following factors does not seriously affect fluctuating stock prices in the financial community: A. Stable economy C. Fear B. Time of year D. Positive or negative publicity 16. When the price of a product is high, consumer demand will usually be A. high. C. unchanged. B. low. D. about average. 17. Who decides how the economic questions will be answered in a communist command economy? A. Individuals C. Businesses B. Government D. Venture team 18. A government's fiscal policies that are intended to encourage economic growth are known as __________ policies. A. realistic C. appropriate B. complementary D. expansionary 19. Tom runs a company which produces pencils. In order to stay in business, Tom must A. employ a sales force. C. make a profit. B. order more machinery. D. have a distribution plan. 20. One advantage of labor specialization by job task is that workers' A. morale improves. C. dependency increases. B. transfers within the industry are easier. D. pride in the finished product increases. 21. Which of the following is an economic factor that often causes consumers to reduce spending: A. Family issues C. Low prices B. Personal needs D. Interest rates 22. People having job skills but being out of work because the jobs that require those skills do not currently exist is an example of __________ unemployment. A. structural C. organizational B. national D. industrial 23. What should a person always do when adapting to a new situation? A. Learn from another person's mistakes C. Resolve a difficult problem B. Control undesirable circumstances D. Make a choice 24. You have been asked to form a team of employees to identify the company's image among current customers. As a laissez-faire leader, you will work best with team members who are A. creative, somewhat independent, and empathetic. B. patient, accepting, and cooperative. C. dependent, quiet, and withdrawn. D. creative, self-confident, and self-disciplined. 25. Team building within an organization often includes A. recruiting. B. training. C. staffing. D. interviewing. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 26. Recognition is most effective if it A. is something everyone can use, such as money or a gift certificate. B. is something the giver would like to receive. C. informs others of the accomplishment. D. matches the person's cultural background. 27. A person with vision for the future wants to A. avoid making mistakes. B. create positive change. 3 C. make important decisions. D. set specific goals. 28. What is one factor that businesses take into consideration when determining the creditworthiness of customers? A. Retirement plan C. Payment record B. Marital status D. Education level 29. One reason customers who pay for products with a credit card usually want to know the interest charges is because those charges A. add to the cost of the purchase. C. are calculated on a yearly basis. B. increase the retail price. D. generate the profit for the business. 30. Which of the following speculative risks would most likely increase a business's income: A. Offering health benefits to employees C. Buying inexpensive liability insurance B. Investing in developing a new product D. Receiving a settlement for fire damage 31. Developing an efficient system to locate, gather, process, and use information for marketing decisions is one way that businesses can reduce A. taxes. C. sales. B. debts. D. risks. 32. Which of the following is a characteristic of a profit-and-loss statement: A. Lists assets and liabilities B. Is the same as a balance sheet C. Shows the owner's financial position D. Summarizes expenses and revenue from sales 33. Sales forecasters must consider changes in the competition, the market, and the economy, which are types of __________ changes. A. internal C. marketing B. operational D. external 34. As a business owner, you are trying to decide whether to expand. Cost/benefit analysis would tell you to expand A. as long as additional benefits exceed additional costs. B. only when additional benefits are twice as much as additional costs. C. as long as additional benefits match additional costs. D. when you can see a break-even point within five years time. 35. When interpreting financial statements, a business determines that a loss occurs if the statements indicate A. revenue is greater than expenses. C. sales exceed expenses. B. expenses are less than sales. D. sales are less than expenses. 36. What is the rate of return on common stock that currently sells for $30, pays an annual dividend of $2.50, and is expected to sell for $32 at the end of the year? A. 15% C. 8% B. 21% D. 13% 37. One way to optimize the rate of return on an investment is by investing in A. savings accounts. C. certificates of deposit. B. government securities. D. aggressive growth funds. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 4 38. With a retirement annuity, financial-service providers cannot distribute annuity payments by which of the following methods: A. Capital expenditure C. Annuitization B. Lump sum payment D. Systematic withdrawals 39. When the success of a project's financial plan requires achieving a specific profit margin, the manager can keep track of a margin increase or decrease by A. writing in a checkbook. C. using a software program. B. operating a cash register. D. reading an odometer. 40. Calculate the tax liability of a single client based on the following information: had adjusted gross income of $42,560, was entitled to the standard deduction of $7,000 and an exemption of $3,300, and earned $275 in interest. A. $32,535 C. $32,260 B. $31,985 D. $31,720 41. When making estimated tax payments, individuals usually base the amount they pay on A. the difference between profit and loss. C. predictions of long-term income. B. the funds available at the time. D. what they paid in taxes last year. 42. Why do tax preparers often complete various tax schedules for clients? A. To calculate exemptions C. To list allowances B. To itemize deductions D. To determine wage rates 43. When determining a client's financial situation, financial planners calculate the value of assets and liabilities to estimate A. total debt. C. cash flow. B. net worth. D. living expense. 44. Asset-management services often involve managing a client's A. investments. C. will. B. medical care. D. housing needs. 45. Financial institutions develop a system to maintain and report information about income and expenses in order to A. follow an investment strategy. C. eliminate the possibility of risk. B. adhere to a compliance plan. D. determine a way to diversify. 46. Which of the following is a factor that businesses consider when determining the overall cost of raising capital by obtaining a bank loan: A. Interest rates C. Trade credit B. Legal fees D. Cash flow 47. After developing a budget, businesses usually implement the budget by A. calculating costs. C. estimating revenues. B. paying expenses. D. generating sales. 48. When evaluating future cash flows from a particular asset, businesses do which of the following: A. Rank the cash flows from least to greatest. B. Assign a probability to each cash flow. C. Assess the importance of each cash flow to the business. D. Release the cash flows currently retained. 49. In order to forecast your company's financing needs, you've prepared a pro forma balance sheet for the coming year that includes assets of $1.25 million, liabilities of $450,000, and retained earnings of $525,000. How much outside financing will your company need in the coming year? A. $62,500 C. $275,000 B. $975,000 D. $375,000 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 5 50. Businesses need to have accurate information about the level of sales, anticipated profits, and the industry growth rate in order to determine the business's financial A. policies and procedures. C. accounts and investments. B. strengths and weaknesses. D. stocks and bonds. 51. Which of the following represents a similarity between a trend analysis and an industry comparison: A. Providing clues about probable financial improvement or decline B. Showing possible financial outcomes C. Demonstrating the need for a balanced budget D. Giving reasons why a business succeeds or fails 52. When determining the optimal mix and type of assets to acquire, businesses consider their long-term financial needs as well as the need to A. issue stock dividends. C. access cash quickly. B. purchase property. D. calculate income taxes. 53. When evaluating alternative financing plans, a business should look for the plan that A. implements the company's mission statement. B. encourages the company to grow. C. promotes loyalty to the company. D. fulfills the company's specified requirements. 54. Deciding how to raise funds for a business usually involves considering whether it will be more effective to use __________ financing. A. public or private C. venture or angel B. bank or credit union D. debt or equity 55. What is the appropriate use of a large cash surplus? A. It should be issued to shareholders as a dividend. B. It should be set aside for unexpected events such as fires. C. It should remain in the cash budget for future operations. D. It should be used for profitable projects or invested, even for the short term. 56. Which of the following is a factor that businesses usually consider when deciding when to spend cash: A. Required loan schedule C. Projected interest rate B. Estimated capital budget D. Preferred cash balance 57. One reason why some businesses decide to factor accounts receivable is to obtain A. needed cash. C. equity financing. B. trade credit. D. leverage. 58. Which of the following is a source of short-term financing that is often easier for new businesses to obtain than traditional bank loans: A. Trade credit C. Private investors B. Venture capital D. Public offerings 59. When managing inventory by the "just-in-time" system, which of the following is necessary for success: A. Effective sales performance B. Effortless transportation logistics C. Seamless coordination between manufacturers and suppliers D. Clear communication between executives and employees 60. When computing the cost of inventory, businesses include the cost of purchasing the items as well as the cost of A. shipping and transporting. C. preparing visual displays. B. handling and storing. D. marking prices. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 61. When projecting future operations, it is important for businesses also to develop projected A. stock options. C. financial plans. B. tax schedules. D. inventory methods. 6 62. When selecting sources of capital, businesses consider their mix of debt and equity, also called their capital A. structure. C. risk. B. budget. D. model. 63. A business comparing standard costs with actual costs is an example of A. predicting returns. C. estimating payables. B. calculating expenses. D. analyzing variances. 64. When interpreting a quarterly report, investors should note that the financial statements provided are usually A. not audited. C. intended to clarify the annual report. B. written in a non-financial way. D. not meant for individual investors. 65. Which of the following is an expense source that businesses evaluate to control costs: A. Receivables C. Inventory B. Credit D. Interest 66. One important similarity between horizontal and vertical financial data analyses is the comparison of figures A. within the same time period. C. from different time periods. B. from different categories. D. within the same category. 67. The gain or loss associated with an investment is the A. dividend. C. capital. B. risk. D. return. 68. Accelerated depreciation methods, such as sum-of-the-year's-digits, produce higher initial tax savings and A. may make a given investment more attractive. B. may make a given investment less attractive. C. have no effect on the attractiveness of a given investment. D. should be the determining factor in choosing an investment. 69. "Debt and equity financing" can be restated as the difference between A. investing and financing. C. capital and borrowing. B. lending and owning. D. assets and liabilities. 70. A characteristic of a good pre-employment test is that it should be A. easy. C. reliable. B. biased. D. personal. 71. Information about an employee's current home address as well as information about pay level and benefits are maintained in the employee's A. insurance document. C. performance review. B. job application. D. personnel record. 72. Which of the following is a reason for presenting an overview of the company to new employees: A. It helps them feel a part of the company. B. It lets them know what is expected of them. C. It gives them a detailed explanation of their jobs. D. It provides them with specific product information. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 73. A manager who coaches his/her employees should remember that A. critical feedback is the most important element of coaching. B. most employees need a lot of guidance and time. C. employees have different learning styles. D. employee productivity rates improve quickly because of coaching. 7 74. Complaints regarding job evaluations could be categorized as complaints about A. coworkers. C. supervision/management. B. physical surroundings. D. pay. 75. Marketing is many interrelated activities whose main purpose is to A. meet consumers' noneconomic needs. C. direct the flow of goods and services. B. serve large businesses. D. follow the steps in the marketing concept. 76. Why is it important for businesses to maintain records about the quantities and types of products that customers are purchasing? A. To plan credit programs C. To forecast future sales B. To develop new displays D. To organize special events 77. Companies obtain internal information about the various business activities they need to operate effectively by monitoring A. government statistics. C. industry trends. B. trade publications. D. internal records. 78. The most important reason why workplace accidents which do not result in injuries should be reported to supervisors is because A. the next accident could result in an injury. C. the report prevents future liability. B. this is required by state law. D. this is an OSHA requirement. 79. Before analyzing potential products to purchase for a firm, the industrial buyer should first A. calculate the quantity needed. C. search for qualified sources. B. choose an order routine. D. determine the product needed. 80. A company that makes one specialty item at a time is using what type of production system? A. Assembly line C. Mass B. Batch D. Unit 81. A primary reason for a business to analyze and update its procedures is to A. boost its spending levels. C. decrease its inventory. B. reduce its outputs. D. increase its efficiency. 82. Why do managers continually evaluate the progress of a project? A. To stay on target C. To send a message B. To prepare charts D. To organize the group 83. What was a business's net profit for last year if it had income from sales of $936,500, operating expenses of $278,150, depreciation of $14,750, and cost of goods sold was $505,250? A. $138,350 C. $431,250 B. $153,100 D. $416,500 84. An operating expense incurred by a business when it fails to collect its receivables is called __________ expense. A. advertising C. bad debt B. interest D. administrative 85. Which of the following techniques for developing ideas is especially useful for project planning: A. Concept mapping C. Role-playing B. Brainstorming D. Redefining 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 8 86. After a job interview, you realize that you forgot to mention something important during the interview. What action should you take? A. Phone the interviewer to explain it. C. Fax an urgent message to the interviewer. B. Mention it in a follow-up letter. D. Go back to the business to tell the interviewer. 87. What is an important quality that all résumés should possess? A. Creativity B. Length C. Neatness D. Complexity 88. A three-day exhibition in a convention hall featuring the most up-to-date computer equipment, software, and related goods is an example of which of the following: A. Warehouse club C. Floor plan B. Central market D. Trade show 89. Which of the following is an example of a financial institution that provides deposit services: A. Investment firm C. Credit union B. Mortgage company D. Insurance agency 90. In order to decide which tasks are most important and the order in which the tasks are to be completed, planners can use the A. GDP Factor. B. ABC Principle. C. RH Factor. D. XYZ Principle. 91. Two primary factors in determining what financial goods or services to offer are consumer demand and A. product longevity. C. staff acceptance. B. product likeability. D. product profitability. 92. The minimum length of time a customer who purchased a government savings bond after February, 2003 must hold the bond before it is redeemable is __________ months. A. 6 B. 12 C. 18 D. 24 93. What is a financial plan intended to help individuals achieve? A. Financial goals C. Social status B. Significant wealth D. Financial careers 94. When obtaining financial product information from appropriate individuals, financial advisers usually A. provide clients with a number of portfolio options. B. retrieve a mutual fund's performance data from a reliable source. C. analyze the trends of a particular industry. D. expand the capabilities of the financial firm. 95. Which of the following is one way that businesses can benefit from substitute selling: A. More contentment C. Improved reputation B. Increased satisfaction D. Added convenience 96. What should salespeople try to establish if customers object to buying products they want? A. Purpose B. Motive C. Cost D. Need 97. What type of financial product might an investment company recommend to a business that is establishing a retirement program for its employees? A. Promissory notes C. Demand deposits B. Certified checks D. Mutual funds 98. Salespeople should make suggestions for additional purchases before the original item has been A. paid for. B. selected. C. identified. D. demonstrated. 99. As president of her large company, which should be Sandra's first priority? A. Supervising B. Planning C. Hiring D. Producing 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 9 100. A manager who takes credit for the work his/her employees perform without giving credit to the person(s) who actually did the work is acting in a(n) __________ manner. A. ethical B. truthful C. unethical D. successful 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 10 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 11 1. B Affects services and fees. As a result of the growth of international banking, many large banks now have foreign branches and operate throughout the world. This means that they have an impact on the international financial services industry. For example, a large international bank that does business in several countries affects the services that local banks offer and the fees they charge. If an international bank offers unique services for free, the local banks often must follow suit or risk losing business. Also, several international banks operating in the same city, such as New York, impact each other and increase competition. Most international banks are regulated. Governments usually control interest rates within their countries. International banking does not increase the value of investments. SOURCE: BA:123 SOURCE: Austin, D.V. (1998). The community bank survival guide: Overcoming the challenges of an increasingly competitive marketplace (pp. 136-139). Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 2. D A country banning exports to another country. An embargo is a total ban on specific goods leaving or entering a country. It usually involves one country, or several countries, banning trade with another country, often for political reasons. That means that the countries will not export goods to that country or import goods from that country. Many countries place a tax, or tariff, on imports. A quota limits the amount of a good that can be imported or exported, but this is not an embargo. Refusing to negotiate trade agreements is not an example of an embargo. SOURCE: BL:004 SOURCE: Farese, L.S., Kimbrell, G., & Woloszyk, C.A. (2002). Marketing essentials (3rd ed.) [pp. 101-102]. Woodland Hills, CA: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 3. C E-mail. There is no variable expense associated with most routine e-mail. There are expenses associated with business letters, such as the cost of paper and postage, and with the fax and telephone. SOURCE: CO:133 SOURCE: Hyden, J.S., Jordan, A.K., Steinauer, M.H., & Jones, M.J. (1999). Communicating for success (2nd ed.) [p. 303]. Cincinnati: South-Western Educational. 4. D Research the problem. Proposals are intended to answer questions or provide recommendations to solve problems. Business employees often need to research a particular situation or problem before they are able to write proposals. After employees do research and gather information, they write proposals that explain the problem and the solutions. The proposal is intended to persuade the business to follow the recommendations. Employees usually do not need to analyze personal biases, contact the customer, or evaluate technical skills before they are able to write proposals. SOURCE: CO:062 SOURCE: Hyden, J.S., Jordan, A.K., Steinauer, M.H., & Jones, M.J. (1999). Communicating for success (2nd ed.) [pp. 510-511]. Cincinnati: South-Western Educational. 5. C Upward. Upward communication is defined as communication that moves up the chain of command, e.g., employee to supervisor. Downward communication moves down the chain from management to employees. Horizontal communication is communication with someone on the same level within the business. Grapevine communication is unofficial messages passed among fellow employees. SOURCE: CO:014 SOURCE: Adler, R.B., & Elmhorst, J.M. (1999). Communicating at work: Principles and practices for business and the professions (6th ed.) [pp. 13-16]. Boston: McGraw-Hill College. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 12 6. A Limit discussion time. If there are a lot of important topics on the agenda, a manager might limit discussion time on each topic in order to cover all of the topics. This might involve opening the floor for 5 or 10 minutes of discussion or stopping the discussion if it goes on for a long time. If the topic cannot be resolved in that time period, a manager might table the topic and put it on the next agenda for continued discussion. The goal is to cover all of the topics while limiting the meeting to a reasonable length of time. Presenting information in visual form will not ensure that all of the topics on the agenda are covered. Staff meetings usually are an hour or so in length rather than all day. After covering all of the topics, a manager might give participants an opportunity to provide additional feedback in written form. SOURCE: CO:140 SOURCE: Locker, K.O. (2000). Business and administrative communication (5th ed.) [pp. 349350]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 7. C Reduced complaints. Handling complaints costs businesses money because of the time involved, the possible loss of business, and refunds to customers. Customers who receive excellent service are less likely to have complaints. Rapid employee turnover, increased costs, and decreased employee morale are not benefits to businesses. SOURCE: CR:004 SOURCE: HR LAP 32—Customer-Service Mindset 8. A Domineering/Superior. Domineering/Superior customers often appear overly self-confident and pushy by boasting about their purchases. Since these customers usually know what they want, they convince or sell themselves. Disagreeable customers are unpleasant and hard to help because they are argumentative, complaining, irritable, moody, insulting, impatient, and/or have a leave-mealone attitude. Suspicious customers question everything and want facts and proof before being convinced to buy. Slow/Methodical customers require a lot of time to make a purchase because of shyness or difficulty in making a choice or buying decision. SOURCE: CR:009 SOURCE: EI LAP 1—Making Mad Glad 9. D Arguing politely. Salespeople should never argue with the customer, not even in a polite manner. Allowing the person to express dissatisfaction will place the customer in a positive frame of mind. Therefore, you need to listen carefully, empathize with the customer's problem, and discuss the problem and possible solutions. SOURCE: CR:010 SOURCE: HR LAP 23—Handling Customer Complaints 10. D Credit is expensive. When the money supply is tight, there is less money in circulation which means there is less money available to loan. As a result, it is expensive to obtain credit because financial institutions usually charge high interest rates on the money that is available. Many consumers and businesses put off borrowing money when the money supply is tight. This also causes consumers to spend less, businesses to cut back on expanding, and employment to decrease. SOURCE: EC:047 SOURCE: O'Sullivan, A., & Sheffrin, S.M. (2003). Economics: Principles in action (pp. 430-431). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 13 11. D Office of the Comptroller of the Currency. This is a semiautonomous part of the U.S. Treasury Department, and the office is appointed by the president for five-year terms. The Supreme Court does not play an ongoing role in the financial services industry. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) provides insurance for deposits in both banks and savings and loans. The Federal Reserve can issue currency, in addition to other powers, which allows for a somewhat flexible money supply to best serve the needs of the country. SOURCE: EC:048 SOURCE: McConnell, C.R., & Brue, S.L. (2005). Economics: Principles, problems, and policies (16th ed.) [pp. 244-245]. Boston: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. 12. D Slow down the economy. The monetary policy of the Federal Reserve System has a significant effect on the economy. If the economy is growing rapidly and inflation is increasing, the Federal Reserve might try to slow down the economy by decreasing the money supply or increasing the interest rate it charges banks. The monetary policy of the Federal Reserve System is not intended to pay for national defense, monitor government spending, or guarantee a minimum wage. SOURCE: EC:050 SOURCE: McConnell, C.R., & Brue, S.L. (2005). Economics: Principles, problems, and policies (16th ed.) [p. 275]. Boston: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. 13. A Gross domestic product. Gross domestic product is the final total value of all the goods and services produced within a country's geographic boundaries in a year's time. The consumer price index measures monthly and yearly price changes for selected consumer goods in different product categories. A leading indicator is a value which gauges the stability of an economic system. Consumer catalog is a distractor. SOURCE: EC:017 SOURCE: EC LAP 1—Gross Domestic Product 14. D Raising taxes. Many of the economic decisions made by governments have a significant effect on financial institutions. Raising taxes is one of these economic decisions. When governments raise taxes, individuals pay more money, which reduces the amount of money they have to spend on other items. This affects financial institutions because individuals will not be able to save or invest as much, which means that the institutions will also have less money available to invest or loan. Businesses that import goods from other countries are responsible for paying tariffs. Storing money and monitoring exports are not economic decisions. SOURCE: EC:057 SOURCE: O'Sullivan, A., & Sheffrin, S.M. (2003). Economics: Principles in action (pp. 433-434). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 15. A Stable economy. With a stable economy, the fluctuation in stock prices would most likely remain steady. Fear, time of year, and positive or negative publicity affect the stock market. Fear and negative publicity cause investors to be cautious and sell off stock. Investors put more money into stocks at certain times of the year. Positive publicity can encourage investors to buy more stock. SOURCE: EC:058 SOURCE: Microsoft Corp. (n.d.). Stock prices. Encarta Encyclopedia [Online]. Retrieved September 25, 2007, from http://encarta.msn.com 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 14 16. B Low. There is an inverse relationship between consumer demand and the price of the product. In other words, the higher the price of a product, the lower the consumer demand for it will be. SOURCE: EC:005 SOURCE: EC LAP 11—It's the Law (Supply and Demand) 17. B Government. In communist command economies, the government is responsible for determining what will be produced, how the products will be produced, and how the products will be allocated. In market economies, individuals and businesses decide how these economic questions will be answered. A venture team is a group involved in product development. SOURCE: EC:007 SOURCE: EC LAP 17—Economic Systems 18. D Expansionary. A fiscal policy is the government policy that sets levels of government spending and taxation. The type of fiscal policy that a government uses depends on what the government wants the economy to do. For example, if the economy is slowing down and heading into a recession, a government would use an expansionary fiscal policy to encourage economic growth. To do this, the government might spend more and cut taxes to encourage businesses to expand. Complementary, appropriate, and realistic are not types of fiscal policies that are intended to encourage economic growth. SOURCE: EC:074 SOURCE: O'Sullivan, A., & Sheffrin, S.M. (2003). Economics: Principles in action (pp. 389-391). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 19. C Make a profit. A business will not survive unless it makes a profit—the monetary reward a business owner receives for taking the risk involved in investing in a business. The other alternatives are steps Tom may take if his business is successful. SOURCE: EC:010 SOURCE: EC LAP 2—Risk Rewarded 20. B Transfers within the industry are easier. This is because of the standardized nature of the tasks to be performed. Workers can easily take the skills learned on one job to another, similar job. Disadvantages of specialization include decreased morale and enthusiasm for the job, increased dependency of workers on each other, and decreased pride in work. SOURCE: EC:014 SOURCE: EC LAP 7—Specialization of Labor 21. D Interest rates. When interest rates increase, consumers often reduce spending, particularly on expensive items that they finance or buy on credit. The higher interest rates make these purchases even more costly. When consumption decreases, there is less demand for goods so production also decreases. The result often is a downturn in the economy. Therefore, the level of consumer spending is a good indicator of the health of the economy. Personal needs and family issues are not economic factors that cause consumers to reduce spending. Low prices often encourage consumers to increase spending because they think they are getting more for their money. SOURCE: EC:081 SOURCE: Arnold, R.A. (2004). Economics (6th ed.) [p. 185]. Cincinnati: Thomson/South-Western. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 15 22. A Structural. Structural unemployment results when people have job skills but the jobs that require those skills do not currently exist. For example, if new technology eliminates the need for certain types of jobs, the people who held those jobs may be terminated. These people have skills, but the structure of the jobs has changed and they are no longer needed. National unemployment affects workers throughout the country. If a business reorganizes, certain jobs may be eliminated or combined, which may result in unemployment. Industrial is not a type of unemployment. SOURCE: EC:082 SOURCE: McConnell, C.R., & Brue, S.L. (2005). Economics: Principles, problems, and policies (16th ed.) [pp. 136-137]. Boston: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. 23. D Make a choice. A person facing a new situation must always make a choice by choosing to adapt or choosing not to adapt. A person cannot always control undesirable circumstances. New situations do not always involve difficult problems. When adapting to a new situation, it is possible to learn from another person's mistakes; however, this does not always occur. SOURCE: EI:006 SOURCE: QS LAP 15—Stuff Happens 24. D Creative, self-confident, and self-disciplined. Laissez-faire leaders exercise very little or no control. Therefore, the people they supervise should be creative, self-confident, self-disciplined, assertive, able to set their own goals, and possess initiative. People who are patient, accepting, cooperative, dependent, quiet, and/or withdrawn will also need more direction than the laissez-faire leader will provide. SOURCE: EI:037 SOURCE: EI LAP 5—Can You Relate? 25. B Training. Team building within an organization often includes training because all members of the team may not have the same knowledge or skills. If the team is expected to address a certain problem or issue, it may be necessary to provide training so all members will understand. To be effective, the team must be able to work on the same level, which often means some basic training will be necessary. Team building within an organization usually does not include recruiting, staffing, or interviewing. SOURCE: EI:044 SOURCE: Lussier, R.N. (2003). Management fundamentals: Concepts, applications, skill development (2nd ed.) [pp. 222-223]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 26. D Matches the person's cultural background. Effective recognition relies on the giver's sensitivity to the cultures of others, who may or may not share the giver's enthusiasm for certain holidays, music, or entertainment. Recognition does not have to be something the giver would like to receive; the focus here is on the receiver's likes and dislikes. It also does not have to inform others of the accomplishment. It does not have to be something everyone can use, such as money or a gift certificate. In fact, personalized rewards and recognition are better. SOURCE: EI:014 SOURCE: QS LAP 13—Gimme Five! 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 16 27. B Create positive change. Vision is the future you desire to create and involves making positive changes to make it happen, which requires determination and hard work. A person who has a vision for the future does not avoid making mistakes and does not start out by setting specific goals. Visionary people often make important decisions, but this is not the reason why they want to make positive changes for themselves and for others. SOURCE: EI:063 SOURCE: QS LAP 11—Picture This! 28. C Payment record. Whether customers consistently pay their bills on time is an important factor in determining their creditworthiness. Businesses that are considering making credit available to customers want to find out if those customers have a history of paying promptly. Customers with good payment records are more likely to be granted credit because businesses expect that they will be repaid. Businesses do not consider a customer's marital status, retirement plan, or education level when determining creditworthiness. SOURCE: FI:020 SOURCE: Cole, R., & Mishler, L. (1998). Consumer and business credit management (11th ed.) [pp. 171-173]. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 29. A Add to the cost of the purchase. Using credit can add to the total cost of goods and services. For example, interest, or finance, charges are added to accounts that are not paid in full at the end of each payment period. When customers buy products with a credit card, they often pay over a period of time. Then, each month they pay interest on the unpaid balance. The interest charges add to the cost of the purchase. Interest charges do not increase the retail price because customers who pay in cash are not charged interest. Interest usually is calculated monthly rather than yearly. Interest generates profit for the credit-card company rather than the store. SOURCE: FI:002 SOURCE: FI LAP 2—Credit and Its Importance 30. B Investing in developing a new product. Investing in the development of a new product is a speculative risk because there is a chance of loss, no change, or gain. However, if the new product is the type that customers want and will buy, selling the new product has the potential of increasing a business's income. Businesses take risks when they invest in new products, but they do so because they hope to earn a profit. Offering health benefits to employees is a pure risk because the business can purchase medical insurance. Buying liability insurance is a way that businesses manage pure risks. Businesses usually obtain insurance coverage to protect them from loss due to pure risks such as fire. SOURCE: FI:080 SOURCE: Meyer, E.C., & Allen, K.R. (2000). Entrepreneurship and small business management: Teacher's manual (2nd ed.) [p. 387]. New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 31. D Risks. Risks are the possibility of financial loss. One way for businesses to reduce risks is to develop an efficient system to locate, gather, process, and use information for marketing decisions. Businesses need information systems for use in decision-making in order to effectively identify alternatives in planning. By gathering and using information, businesses often are able to recognize trends or potential problems and take steps to reduce risks. Businesses usually want to increase sales. Debts are financial liabilities. Taxes are part of the expenses of doing business. SOURCE: FI:084 SOURCE: BA LAP 2—Risk Management 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 17 32. D Summarizes expenses and revenue from sales. A profit-and-loss statement is a business's financial picture that lists all revenue and expenses for a certain time period. A profit-and-loss statement is not the same as a balance sheet. Characteristics of a balance sheet include listing assets and liabilities and showing the owner's financial position. SOURCE: FI:094 SOURCE: FI LAP 4—Watch Your Bottom Line (Income Statements) 33. D External. Businesses have no control over external changes, but forecasters must collect information about changes in the areas of competition, the market, and the economy. Marketing changes refers to the way in which a business may change its products or the way it markets those products. Operational changes refers to changes in the way a business is run, or operates. Internal changes refers to the changes that are going on within a business and are under the business's control. Internal changes include marketing, operational, and staff changes. SOURCE: FI:096 SOURCE: IM LAP 4—Forecasting Sales 34. A As long as additional benefits exceed additional costs. Cost/benefit analysis estimates the cost of an action and compares it with an estimate of the benefits of that action. As long as the benefits exceed the costs, the project should be pursued. Cost/benefit analysis does not require benefits to be twice as much as costs. Additional benefits should exceed, not match, additional costs. Cost/benefit analysis does not require you to estimate a break-even point in any particular time period. SOURCE: FI:357 SOURCE: Miller, R.L. (2005). Economics: Today and tomorrow (pp. 265-267). Columbus, OH: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 35. D Sales are less than expenses. If a business's expenses are greater than sales, a loss occurs. In the alternatives, a profit occurred because sales or revenue was greater than expenses. SOURCE: FI:102 SOURCE: Stull, W.A. (1999). Marketing and essential math skills: Teacher's edition (pp. 234-239). Cincinnati: South-Western Educational. 36. A 15%. The rate of return on common stock is calculated by dividing the sum of the gains (dividends and capital appreciation) by the beginning price. In this example, the gains add up to $4.50 ($2.50 in dividends plus $2 in capital gains). Gains of $4.50 divided by the purchase price of $30 equals 15% (4.50 ÷ 30 = .15 or 15%). SOURCE: FI:171 SOURCE: Shim, J.K., & Siegel, J.G. (2000). Financial management (2nd ed.) [p. 136]. Hauppauge, NY: Barron's. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 18 37. D Aggressive growth funds. Aggressive growth funds are a type of investment that involves purchasing stocks whose prices will increase substantially over a short period of time. These funds usually have a high rate of return; however, they are risky because the price of the stock could drop suddenly. Those who invest in aggressive growth funds watch the market closely in order to optimize the rate of return by selling the stocks when they are priced high. Government securities are a very safe investment; however, the rate of return is usually low. Certificates of deposit have a set value. Savings accounts are safe investments, but the interest rate may be low. SOURCE: FI:172 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (p. 331). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 38. A Capital expenditure. Capital expenditure is a term used for the money a business spends on upgrading its physical assets. Retirement annuities may be distributed, however, by lump sum payments, by annuitization (payments over a period of time), or by systematic withdrawals (paying varying amounts as requested). SOURCE: FI:175 SOURCE: Wachovia. (n.d.). Retirement income annuity. Retrieved September 25, 2007, from http://www.wachovia.com/personal/page/textonly/0,,326_503_675,00.html 39. C Using a software program. When the success of a project's financial plan requires achieving a specific profit margin, the manager can keep track of a margin increase or decrease by using a software program with tracking capabilities. Operating a cash register may be necessary during the project; however, it is not involved in tracking profit margin. Writing in a checkbook is not a good way to keep track of profit margin. Reading an odometer is something an automobile driver might do, since an odometer tracks miles driven. SOURCE: FI:178 SOURCE: AllPM.com. (2002, June 13). Modern cost management. Retrieved December 16, 2005, from http://www.allpm.com/print.php?sid=254 40. C $32,260. Taxable income is determined by subtracting the standard deduction and any exemptions from adjusted gross income. In this case, the exemption is $3,300 because the client is single and entitled to only one exemption. To calculate taxable income, subtract the standard deduction from adjusted gross income ($42,560 - $7,000 = $35,560), and the exemption from that amount ($35,560 - $3,300 = $32,260). The $275 in interest will have been added to salary and wages to determine the adjusted gross income. SOURCE: FI:180 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 390-399). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 19 41. D What they paid in taxes last year. Individuals who are self-employed usually make estimated tax payments because they do not have an employer who is withholding taxes on a regular basis. These individuals are expected to make payments that are as accurate as possible. Therefore, the amount they pay is usually based on what they paid in taxes last year. If individuals expect their income to increase significantly, they should increase the amount of estimated tax payments in order to avoid being charged penalties for underpayment. Individuals do not base estimated tax payments on the funds available at the time, predictions of long-term income, or the difference between profit and loss. SOURCE: FI:182 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 388-389). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 42. B To itemize deductions. By completing various tax schedules, tax preparers are able to itemize deductions and reduce the amount of the client's tax liability. For example, various schedules allow tax preparers to itemize medical and dental expenses, property taxes, expenses for home mortgages, etc. These deductions often are more than the standard deduction allowed so the client saves money by itemizing and claiming the higher deductions. Tax preparers do not complete various tax schedules for clients to calculate exemptions, to list allowances, or to determine wage rates. SOURCE: FI:183 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 393-394). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 43. B Net worth. When determining a client's financial situation, financial planners usually estimate the client's net worth or total value. To do this, planners calculate the value of assets such as cash, investments, and property. Then, they calculate the value of liabilities, or debts, and subtract the value of liabilities from the value of assets to determine net worth. The goal is to help clients increase their net worth. Liabilities are debts. Cash flow is the movement of funds. Living expense includes costs such as rent or a mortgage, food, clothing, etc. SOURCE: FI:185 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 479-481). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 44. A Investments. Asset-management services involve managing a client's assets, which are anything of value that the client owns. Assets often include investments such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, etc. Managing these assets might involve buying and selling investments to increase the client's net worth. Asset-management services do not involve managing a client's medical care, will, or housing needs. SOURCE: FI:187 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 479-481). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 20 45. B Adhere to a compliance plan. Financial institutions are required to comply with various governmental rules and regulations, such as reporting and paying different types of taxes. In order to comply with these rules and regulations, financial institutions develop a system to maintain and report information about income and expenses. This information might include payroll withholdings and required payments for unemployment compensation. Without an effective system in place, financial institutions may not be able to adhere to a compliance plan. Financial institutions do not develop a system to maintain and report information about income and expenses in order to follow an investment strategy or determine a way to diversify. It is not possible to eliminate all risk. SOURCE: FI:189 SOURCE: Everard, K.E., & Burrow, J.L. (2001). Business principles and management (11th ed.) [pp. 390-391]. Cincinnati: South-Western. 46. A Interest rates. Businesses often need to raise additional capital, or funds, to cover unexpected expenses or to make large investments. One way to raise capital is to obtain a bank loan. However, before obtaining a loan, businesses should consider the interest rates that they will be charged for the use of those funds. If the current interest rate is high and a business needs a five-year loan, the overall cost of the capital also will be high. Businesses may decide that the costs are too high and look for other ways to raise capital. Businesses usually do not pay legal fees when raising capital by obtaining a bank loan. Trade credit involves obtaining short-term credit from suppliers. Cash flow is the movement of funds into and out of a business. SOURCE: FI:191 SOURCE: Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2001). Entrepreneurship: A contemporary approach (5th ed.) [pp. 429-430]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 47. B Paying expenses. A budget is an estimate of what income and expenses will be for a specific time period or for a specific project. Once a businesses develops a budget, it usually implements the budget by paying expenses. For example, a business budgets $50,000 to complete a specific project. It needs to purchase $25,000 worth of materials for the project. Once the budget is in place, the business can pay for those materials, which is an expense. Businesses calculate costs and estimate revenues during the process of developing a budget. Not all budgets are intended to generate sales. SOURCE: FI:193 SOURCE: Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2001). Entrepreneurship: A contemporary approach (5th ed.) [pp. 259-261]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 48. B Assign a probability to each cash flow. To evaluate future cash flows from a particular asset, businesses assign a probability to each cash flow, so they can determine which is most likely to occur. Ranking the cash flows comes next, although the order is not necessarily from least to greatest. It can be from "most likely to occur" to "least likely to occur." Assessing the importance of each cash flow to the business and releasing cash flows currently retained are not functions of the evaluation activity. SOURCE: FI:196 SOURCE: Meeting, D.T., Luecke, R.W., & Garceau, L. (n.d.). Future cash flow statements. Retrieved January 4, 2006, from http://www.aicpa.org/pubs/jofa/oct2001/meeting.htm 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 21 49. C $275,000. The formula for a balance sheet is assets - liabilities = stockholders' equity. The formula can be rearranged to forecast required outside financing. That formula is outside financing = assets - liabilities - retained earnings. With assets of $1.25 million, liabilities of $450,000, and retained earnings of $525,000, outside financing required in the coming year is $275,000 ($1,250,000 $450,000 = $800,000 - $525,000 = $275,000). SOURCE: FI:198 SOURCE: Shim, J.K., & Siegel, J.G. (2000). Financial management (2nd ed.) [pp. 20, 61-64]. Hauppauge, NY: Barron's. 50. B Strengths and weaknesses. A business's financial strengths and weaknesses can be both internal and external. Therefore, having accurate information about the level of sales and anticipated profits will help the business determine its internal strengths and weaknesses. For example, a high level of sales is a strength, but low profit is a weakness. Also, having information about the industry growth rate will help the business determine its external strengths and weaknesses. If the industry has a steady growth rate, that is a strength for the business because it can anticipate that its sales will continue to increase as the industry grows. Having accurate information about the level of sales, anticipated profits, and the industry growth rate will not help to determine a business's financial policies and procedures, accounts and investments, or stocks and bonds. SOURCE: FI:199 SOURCE: Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2001). Entrepreneurship: A contemporary approach (5th ed.) [pp. 469-473]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 51. A Providing clues about probable financial improvement or decline. Trend analysis involves plotting a ratio over time to discover clues about probable financial improvement or decline. In a similar way, an industry comparison provides clues as to whether there's an increase or decrease on the earnings horizon. Neither trend analysis nor an industry comparison shows possible financial outcomes, demonstrates the need for a balanced budget, or gives reasons why a business succeeds or fails. SOURCE: FI:202 SOURCE: Brigham, E.F., Gapenski, L.C., & Ehrhardt, M.C. (1999). Financial management: Theory and practice (9th ed.) [pp. 85-86]. Fort Worth, TX: The Dryden Press. 52. C Access cash quickly. Businesses acquire a variety of assets over a period of time. These assets include equipment, property, investments in other companies, and cash. When determining the optimal mix and type of assets to acquire, businesses consider their long-term financial needs because certain investments increase in value over time and add to the net worth of the business. Businesses also consider the need to access cash quickly because some assets are easier to convert to cash than others. For example, savings accounts are assets that businesses can access quickly in order to obtain cash. Businesses want to develop the right mix of assets so they can access cash when necessary and also increase their net worth. Property is an asset. Not all businesses issue stock dividends, but if they do, dividends are expenses paid to others. Businesses do not determine the optimal mix and type of assets to acquire in order to calculate income taxes. SOURCE: FI:203 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 66-67). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 22 53. D Fulfills the company's specified requirements. An alternative financing plan must meet the criteria established by the company. If it does not meet the specified requirements, that particular plan does not suit the company's purpose. Alternative financing plans are not expected to encourage the company to grow, promote loyalty to the company, or implement the company's mission statement. SOURCE: FI:208 SOURCE: DCWatch. (2005, March 15). CFO releases evaluation of alternative financing plans for the baseball stadium. Retrieved September 25, 2007, from http://www.dcwatch.com/govern/sports050315.htm 54. D Debt or equity. There are two types of financing—debt and equity. Debt financing involves borrowing money and paying it back with interest. Equity financing involves raising funds by selling some of the ownership in the business. When deciding how to raise funds, a business considers which type of financing will be more effective. If the business needs additional funds for a short period of time, it is more effective to use debt financing and pay back the loan rather than give up some of the ownership. However, if the business needs a lot of capital, it may be more effective to use equity financing. Businesses weigh the advantages and disadvantages of both types of financing before deciding which one to use. Banks and credit unions are sources of debt financing. Venture and angel are forms of equity financing. Both debt and equity financing may be either public or private. SOURCE: FI:209 SOURCE: Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2001). Entrepreneurship: A contemporary approach (5th ed.) [pp. 428-434]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 55. D It should be used for profitable projects or invested, even for the short term. A large cash surplus is not productive for a company, and is best put to good use in profitable projects or external investment opportunities. Unexpected events, such as fires, are usually covered by insurance. A large cash surplus should not remain in the cash budget for future operations because it will be idle. The decision to issue dividends is made by a company's board of directors and is a planned event built in to a cash budget. SOURCE: FI:211 SOURCE: Cunningham, B.M., Nikolai, L.A., and Bazley, J.D. (2000). Accounting: Information for business decisions (pp. 99-100). Orlando, FL: Harcourt. 56. D Preferred cash balance. Businesses usually establish a preferred cash balance which is the amount of cash that the business always wants to have on hand. Cash in excess of that amount is available for the business to spend. If the business estimates that it will have expenses that will cost more than the available cash, it usually decides to begin financing activities in order to borrow money and maintain the preferred cash balance. When deciding when to spend cash, businesses usually do not consider the estimated capital budget, projected interest rate, or required loan schedule. SOURCE: FI:212 SOURCE: Cunningham, B.M., Nikolai, L.A., & Bazley, J.D. (2000). Accounting: Information for business decisions (pp. 99-101). Orlando, FL: Harcourt. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 23 57. A Needed cash. Factoring is a type of debt financing that involves selling accounts receivable for a discounted amount to another company. The factoring company buys a business's accounts receivable for less than they are worth and then collects the receivables. The business that sells its accounts receivable receives needed cash quickly rather than waiting for customers to pay their accounts. Some businesses factor accounts receivable if they are experiencing a cash-flow problem and need to obtain cash. Trade credit is another type of debt financing but it does not involve factoring accounts receivable. Equity financing involves selling part of the ownership of a business to acquire capital. Leverage is borrowing money to acquire an asset that will have more value than the cost of borrowing the money. SOURCE: FI:214 SOURCE: Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2001). Entrepreneurship: A contemporary approach (5th ed.) [p. 431]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 58. A Trade credit. Obtaining short-term financing is sometimes difficult for new businesses because they do not have an established credit history. Therefore, those businesses that buy goods from suppliers are often able to take advantage of trade credit which makes it possible for them to pay for the goods at a later date, such as in 90 days. This amounts to short-term financing because the business has the goods and also has time to generate the revenue to pay for the goods in the future. Suppliers often are willing to grant trade credit to new businesses because it is a way of attracting new customers. Venture capital, private investors, and public offerings are examples of equity financing that are long term. SOURCE: FI:216 SOURCE: Kuratko, D.F., & Hodgetts, R.M. (2001). Entrepreneurship: A contemporary approach (5th ed.) [p. 431]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 59. C Seamless coordination between manufacturers and suppliers. With "just-in-time" inventory management, supplies often arrive only a few hours before they are needed. This cuts down on storage costs, causing the company to rely heavily on a seamless coordination between manufacturers and suppliers. Although transportation logistics is important, it is not the main factor in "just-in-time" inventory management. Sales performance and executive-to-employee communication are also not central to the "just-in-time" inventory management system. SOURCE: FI:218 SOURCE: Brigham, E.F., Gapenski, L.C., & Ehrhardt, M.C. (1999). Financial management: Theory and practice (9th ed.) [p. 811]. Fort Worth, TX: The Dryden Press. 60. B Handling and storing. The cost of inventory includes more than the cost of purchasing the items. It also includes the cost of handling and storing the items, insuring the items, paying taxes on the items, etc. When businesses compute the cost of inventory, they include all of these costs to obtain an accurate dollar figure for the costs associated with maintaining an inventory. Shipping and transporting costs are included in the cost of purchasing inventory items. The cost of inventory does not include the cost of preparing visual displays or of marking prices. SOURCE: FI:219 SOURCE: Cunningham, B.M., Nikolai, L.A., & Bazley, J.D. (2000). Accounting: Information for business decisions (pp. 511-512). Orlando, FL: Harcourt. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 24 61. C Financial plans. Projecting future operations involves forecasting the condition of the business in the future. This might include projecting that sales will increase by a certain percentage, or that the size of the company will double, or that the workforce will increase, etc. When projecting these operations, businesses also need to develop projected financial plans in order to be prepared to fund the operations. If the size of the company will double, then there will be additional expenses to pay. The business must plan to pay those expenses. When projecting future operations, businesses do not develop projected tax schedules, stock options, or inventory methods. SOURCE: FI:221 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 671-675). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 62. A Structure. A business can select either debt or equity as a source of capital—or a mix of both. The agreed-upon selection or mix is called the firm's capital structure. A budget is an estimate of upcoming expenses listed by expense category. Risk is the possibility of (financial) loss. "Capital model" is not a term used to describe a company's mix of debt and equity. The Capital Asset Pricing Model is a tool used to analyze how risk and rates of return are related. SOURCE: FI:222 SOURCE: Brigham, E.F., Gapenski, L.C., & Ehrhardt, M.C. (1999). Financial management: Theory and practice (9th ed.) [pp. 178, 579]. Fort Worth, TX: The Dryden Press. 63. D Analyzing variances. Standard costs are those costs that should be incurred if activities take place under normal circumstances. Businesses use standard costs as a benchmark when comparing costs to determine if actual costs varied from the standard. This process is known as analyzing variances. For example, if actual costs are higher than standard costs, a variance exists. This might indicate a problem that the business should identify and correct in order to bring actual costs in line with standard costs. Comparing standard costs with actual costs is not an example of calculating expenses, estimating payables, or predicting returns. SOURCE: FI:227 SOURCE: Cunningham, B.M., Nikolai, L.A., & Bazley, J.D. (2000). Accounting: Information for business decisions (p. 344). Orlando, FL: Harcourt. 64. A Not audited. The financial statements in a quarterly report may be unaudited. Quarterly reports are not necessarily written in a non-financial way. It's helpful to have the annual report handy when reviewing a quarterly report—so you can put the quarterly information into perspective. Individual investors are considered part of the intended audience for a quarterly report. SOURCE: FI:230 SOURCE: Shim, J.K., and Siegel, J.G. (2000). Financial management (2nd ed.) [pp. 38-39]. Hauppauge, NY: Barron's Educational Series. 65. C Inventory. Inventory is often a major expense for a business because there is cost involved in buying and maintaining an inventory of goods. Businesses evaluate inventory on a regular basis to control costs while keeping an adequate supply of goods in stock. Businesses do not want to invest more in inventory than is necessary because that ties up cash that could be used for other purposes. Credit, receivables, and interest are often sources of revenue. SOURCE: FI:231 SOURCE: Cunningham, B.M., Nikolai, L.A., & Bazley, J.D. (2000). Accounting: Information for business decisions (pp. 511-513). Orlando, FL: Harcourt. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 25 66. D Within the same category. Both horizontal and vertical financial data analyses compare figures within the same category. Ratio analysis is used to compare figures from different categories. Horizontal financial analysis typically compares one or more years' worth of data. Vertical financial analysis can compare data within one fiscal year. SOURCE: FI:235 SOURCE: Shim, J. K., & Siegel, J. G. (2000). Financial management (2nd ed.) [p. 42]. Hauppauge, NY: Barron's. 67. D Return. Return is the gain or loss. Risk is the possibility of loss. Capital is a term used for financial assets. A dividend is the regular payment from a stock. SOURCE: FI:245 SOURCE: Investopedia.com. (n.d.). Return. Retrieved September 25, 2007, from http://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/return.asp 68. A May make a given investment more attractive. Tax savings that result from accelerated depreciation methods result in higher present values for the tax savings, therefore making a given investment more, not less, attractive. Accelerated depreciation methods can indeed affect the attractiveness of a given investment, but they are unlikely to be large enough to be the determining factor. SOURCE: FI:252 SOURCE: Shim, J.K., & Siegel, J.G. (2000). Financial management (2nd ed.) [p. 163]. Hauppauge, NY: Barron's. 69. B Lending and owning. Debt financing occurs when a corporation raises capital by borrowing money (from a bank, for example) or by issuing bonds. In either case, someone is lending money to the corporation. Equity financing occurs when a corporation raises capital by selling stock, or shares of ownership. Investing and financing, capital and borrowing, and assets and liabilities do not accurately describe this activity. SOURCE: FI:260 SOURCE: Tyson, E. (2003). Investing for dummies (3rd ed.) [pp. 14, 18]. New York: Wiley Publishing. 70. C Reliable. A test is considered reliable when it provides the same or similar results each time it is administered. Pre-employment tests should also be valid, relevant, and fair. The tests should not be personal but job-related. They should also not be biased since that would favor one applicant over another. Whether the test is easy would depend upon the kind of job for which the test is being given. SOURCE: HR:356 SOURCE: MN LAP 51—Selecting New Employees 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 26 71. D Personnel record. Businesses maintain various types of information in an employee's personnel record because information on each employee is vital to the business. Addresses must be kept current. Payroll records contain information about the number of hours worked; regular and overtime earnings; and deductions for federal, state and local taxes, Social Security, Medicare, and any other deductions. Job applications and performance reviews are documents that usually are kept in an employee's personnel record. If the business provides insurance to the employee, that type of information would be in the personnel record. Businesses often need to refer to the information in personnel records for a variety of reasons such as considering an employee for a promotion, or in the event that an employee was injured on the job. SOURCE: HR:359 SOURCE: Dessler, G. (2000). Human resource management (8th ed.) [pp. 54-58]. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. 72. A It helps them feel a part of the company. To accomplish this, you should describe the entire company by summarizing its origin, objectives, development, growth, product/service line, outstanding or significant company achievements, future of the business, priorities for business and community involvement, company problems, trends for the industry, and a review of the company's organizational chart. In discussions of job-specific assignments, you can let employees know what is expected of them, provide an explanation of their jobs, and give them specific product information. SOURCE: HR:361 SOURCE: MN LAP 44—Orienting New Employees 73. C Employees have different learning styles. A coach is a person who enables other people to reach their true potential by helping them to overcome the barriers that are keeping them from doing something they want to achieve. Managers often take on the role of a coach to help their subordinates to reach their career goals, to increase their productivity, and to solve problems. Because employees have different skills and personalities, they learn information in different ways. An effective coach realizes these differences and works to tailor a coaching relationship that works best for the employee. Often, coaching requires that the manager spend more time with one employee than with another employee. Increases in an employee's productivity rates do not always happen quickly when a manager uses coaching in the workplace. Positive feedback is as important as constructive criticism when a manager coaches his/her employees. SOURCE: HR:364 SOURCE: Campbell, M. (n.d.). Ten keys for successfully coaching employees. Retrieved September 25, 2007, from http://www.spconsultants.org/articles/mcampbell.htm 74. C Supervision/Management. Employees often complain about the management of an organization and the ways in which employees are supervised. Evaluation is the responsibility of management/supervisors. Complaints about employee compensation deal with pay. Complaints about work environments are categorized as physical surroundings complaints. Complaints about coworkers may be job related, not work related, or about the habits of other employees. SOURCE: HR:366 SOURCE: MN LAP 45—Handling Employee Complaints 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 27 75. C Direct the flow of goods and services. Marketing is a process that enables goods, services, and ideas to get from producers to consumers. It serves businesses of all sizes and helps to meet consumers' economic needs. The marketing concept is a philosophy based on the belief that business activities should be aimed toward satisfying consumers, not a process with specific steps. SOURCE: MK:001 SOURCE: BA LAP 11—Have It Your Way! 76. C To forecast future sales. Businesses maintain a variety of records about the quantities and types of products that customers are purchasing. These records are usually known as sales records. By analyzing past sales records, businesses can determine what customers are buying, when they are buying, and how much they are buying. This helps a business forecast future sales so it can be prepared to offer the products that customers want. Businesses do not maintain records about what customers are purchasing to develop new displays, plan credit programs, or organize special events. SOURCE: NF:002 SOURCE: Burrow, J.L. (2006). Marketing (2nd ed.) [pp. 120-121]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 77. D Internal records. Companies keep many types of internal records about their various business activities. These records might contain information about sales, agreements with vendors, financial status, etc. Management and employees use the records to make decisions about day-to-day and future actions. For example, records that indicate that sales are increasing and the company is profitable might encourage the business to decide to expand. Businesses monitor their activities on an internal basis. Therefore, they would not monitor trade publications, industry trends, or government statistics in order to keep track of what they are doing in the business. SOURCE: NF:014 SOURCE: Burrow, J.L. (2006). Marketing (2nd ed.) [pp. 120-121]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 78. A The next accident could result in an injury. The fact that one accident does not result in an injury does not ensure that the next accident will have the same results. An accident that does not cause an injury should be reported to a supervisor so that the circumstances causing the accident can be corrected if possible. This may save someone else from injury. Government regulations vary from state to state and for different industries. Reporting a noninjurious accident does not prevent future liability. SOURCE: OP:009 SOURCE: RM LAP 3—Handling Accidents 79. D Determine the product needed. The buyer should anticipate or recognize problems that need to be solved and determine what product would best meet the firm's need. The other alternatives are steps in the buying process that occur after the need has been determined and possible products have been examined. SOURCE: OP:015 SOURCE: PU LAP 1—Purchasing 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 28 80. D Unit. The system that produces one item at a time or small quantities of an item at one time is unit production. This system also is known as job shop or jobbing and is used by businesses such as custom-car manufacturers and made-to-order clothiers. Batch production is the system of making small batches of a product at one time, such as several gallons of a certain color of paint. Mass production is the system of making large quantities of a standard product, such as televisions and radios. Assembly line is the system of specialized machines or work stations placed in a certain order to make large quantities of a specific product. SOURCE: OP:017 SOURCE: BA LAP 1—Nature of Production 81. D Increase its efficiency. A procedure is a step-by-step process for performing a specific task. A company must conduct many tasks to keep the business running. To make sure that the business is operating efficiently, it may evaluate its procedures to see if the business should make improvements so it can reach its various goals. Outputs are goods and services that result from combining inputs. Most businesses want to increase outputs rather than reduce them. Not all businesses carry inventory. Although spending can improve a business's efficiency, spending more money is not the primary purpose for analyzing and updating its procedures. SOURCE: OP:022 SOURCE: Everard, K.E., & Burrow, J.L. (2001). Business principles and management (11th ed.) [pp. 288, 330]. Cincinnati: South-Western. 82. A To stay on target. Managers should evaluate the progress throughout the life of the project. This means reviewing the project goals to make sure the project is on target. If the project starts to get off track, the manager needs to react and get the project refocused so all the members are working for the same goal. Coordinating the project often involves developing charts that list each project activity, who is responsible for the activity, and when the activity should be completed. The first step in project management involves organizing the group. Sending a message is a communication function. SOURCE: OP:002 SOURCE: QS LAP 18—Make It Happen 83. B $153,100. Net profit is calculated by subtracting operating expenses and cost of goods sold from income. To determine net profit, first calculate gross profit by subtracting cost of goods sold from income ($936,500 - $505,250 = $431,250). Then, subtract operating expenses from the gross profit figure to calculate net profit ($431,250 - $278,150 = $153,100). Depreciation is not a factor in determining net profit. SOURCE: OP:024 SOURCE: MN LAP 57—Operating Expenses 84. C Bad debt. Interest expense is money a borrower must pay for the use of the borrowed money. Expenses incurred in the general operation of the business are called administrative expenses. Advertising expenses include radio and television commercials, newspaper and magazine advertisements, etc. SOURCE: OP:029 SOURCE: Longenecker, J.G., Moore, C.W., & Petty, J.W. (2003). Small business management: An entrepreneurial emphasis (12th ed.) [pp. 416-417]. Cincinnati: Thomson/SouthWestern. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 29 85. A Concept mapping. Concept mapping is a method of clarifying and organizing ideas by using a graphic format to show relationships. This technique involves drawing a map of your ideas so that you can see how one idea relates to another. Concept mapping can be used for developing ideas for many purposes, but it is especially useful for project planning. Redefining involves looking at a problem from a different angle if no solution seems apparent. Brainstorming is a technique used to produce a lot of ideas in a short period of time. Role-playing involves acting out a situation. SOURCE: PD:012 SOURCE: PD LAP 2—Creativity 86. B Mention it in a follow-up letter. Applicants should send follow-up letters to interviewers after interviews to thank them for the opportunity to interview, to reinforce key points mentioned during the interview, to express interest in the position, and to mention important topics that were omitted during the interview. Phoning or going back to the business requires interviewers to stop what they are doing, thus taking unnecessary time away from their jobs. The follow-up letter could be faxed if the interviewer is planning to make an immediate hiring decision; however, the omission should be addressed as part of a follow-up letter rather than being sent as a separate, urgent document. SOURCE: PD:029 SOURCE: Bailey, L.J. (2003). Working: Career success for the 21st century (3rd ed.) [p. 71]. Mason, OH: South-Western. 87. C Neatness. All résumés should be neatly prepared. Neat résumés make a good first impression on prospective employers who often form opinions of applicants based on their résumés. A neat résumé indicates that the person will be careful and thorough on the job. Also, employers are more likely to read neat résumés than those that are sloppy or contain errors. Résumés should not be creative but should contain exact information. Résumés should be brief rather than long. They should not be complex but easy to read and understand. SOURCE: PD:031 SOURCE: Daggett, W.R., & Miles, J.E. (1998). The dynamics of work: Introduction to occupations (2nd ed.) [p. 54]. Cincinnati: South-Western Educational. 88. D Trade show. Trade shows usually are held for only a few days in convention centers or exhibition halls in large cities. Trade shows feature the latest goods and related items in a specific product category, and are good sources of information that can contribute to professional development. They often are held on an annual basis. A three-day exhibition of computer equipment, software, and related goods is an example of a trade show. A central market is a city where many major suppliers of a product are located. A floor plan is a layout or design for a space. A warehouse club offers large quantities of consumer items, usually at discounted prices. SOURCE: PD:036 SOURCE: CD LAP 1—Trade Associations and Professional Organizations 89. C Credit union. A characteristic of many financial institutions is that they provide deposit services. This means that businesses and individuals can deposit funds into checking and savings accounts and access those funds at will. An example of a financial institution that provides deposit services is a credit union, which is a financial cooperative set up to provide savings and credit services to its members. However, some financial institutions do not provide deposit services. These include mortgage companies, investment firms, and insurance agencies. SOURCE: PD:085 SOURCE: Kapoor, J.R., Dlabay, L.R., Hughes, R.J., & Hoyt, W.B. (2005). Business and personal finance (pp. 128-131). New York: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill. 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 30 90. B ABC Principle. The ABC Principle is a time-management technique in which planners assign each task to an "A," "B," or "C" category according to the time needed to complete the task and its importance. Category "A" items are the most important and should be completed during workers' high-energy times. Category "B" items follow "A" items and can be used to provide relief from the concentration required by "A" items. "C" items are routine items that can be done during waiting time or free time. GDP, or gross domestic product, is a measure of the nation's economy. RH Factor is a medical term. XYZ Principle is a distractor. SOURCE: PD:019 SOURCE: OP LAP 1—About Time 91. D Product profitability. Consumer demand and product profitability go hand-in-hand in determining what goods or services to offer. First, financial institutions must know their markets and what consumers want and need to buy. But offering the most wanted product in the world would be useless if the product itself is not profitable for the organization. So, the product must also be priced in a way as to be attractive to consumers but also cover expenses and deliver a profit margin. Sometimes, financial institutions get distracted by the overall "likeability" of a product or whether the staff will accept it. The staff will accept any product that is sound and that customers respond to. Product longevity is another factor financial institutions fall prey to in determining products to offer. Simply having been around for a long time is not a good reason for continuing to offer the product. SOURCE: PM:125 SOURCE: Austin, D.V. (1998). The community bank survival guide: Overcoming the challenges of an increasingly competitive marketplace (pp. 88-90). Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. 92. B 12. In order for a bond purchased after February, 2003 to be eligible for redemption, the purchaser must have owned the bond for 12 months. Bonds purchased before that date may be redeemed after six months. The teller compares the issue date to the Table of Redeemable Values in order to determine the bond's value at redemption. SOURCE: SE:191 SOURCE: American Bankers Association (2005). Today's teller: Developing basic skills (pp. 134137). Washington: Author. 93. A Financial goals. A financial plan is a road map, of sorts, that guides individuals from Point A to Point B, or from where they are to where they want to be financially. Financial plans begin with establishing clear and measurable objectives, such as having sufficient income to pay for college or retirement. Once goals are established, a financial plan then outlines steps for achieving those goals and measuring progress along the way. Significant wealth could possibly be one of the goals an individual wishes to accomplish, but it is not, in and of itself, the purpose of a financial plan. Financial plans are not designed to help individuals achieve a financial career. Financial plans are not intended to increase social status. SOURCE: SE:193 SOURCE: CCH Inc. (n.d.). The financial planning toolkit: The financial planning process. Retrieved September 26, 2007, from http://www.finance.cch.com/text/c10s00d010.asp 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 31 94. B Retrieve a mutual fund's performance data from a reliable source. When obtaining financial product information from appropriate individuals, financial advisers usually retrieve performance data from a reliable source—whether the data is for a fund or for an individual stock. Analyzing the trend of a particular industry may or may not take place while gathering information on a particular stock or fund. Providing clients with a number of portfolio options usually takes place after the research has been completed. Expanding the capabilities of the financial firm may or may not be something within a financial adviser's control. SOURCE: SE:194 SOURCE: Futrell, C. M. (2006). Fundamentals of selling: Customers for life through service (9th ed.) [pp. 184-185]. New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. 95. C Improved reputation. The use of product substitution can benefit the business in several ways. When customers are provided the most satisfactory products, they have good feelings about that business and tell others about the service. It is important to serve customers well so that the business's reputation can be enhanced. Added convenience, increased satisfaction, and more contentment are ways that customers benefit from substitute selling. SOURCE: SE:114 SOURCE: SE LAP 111—Using Substitute Selling 96. D Need. A common objection occurs when there is a conflict between a "want" and a "need." Even though customers want an item very badly, the sale will not be made unless they are convinced that they have a real need for it. The salesperson's job is to try to establish that need by stressing the benefits of the product and the value it offers. Salespeople do not need to establish motive, cost, or purpose if customers object to buying items they want. SOURCE: SE:874 SOURCE: SE LAP 100—Converting Objections 97. D Mutual funds. A mutual fund is an assortment of diversified stocks and bonds that may be purchased by individuals or businesses. Investors often buy mutual funds because they do not want to spend the time identifying and selecting specific stocks. In most cases, the stocks that make up the mutual fund have been carefully evaluated in order to provide the best possible return on investment. An investment company might recommend that a business invest retirement money in mutual funds because the funds are safe and will increase in value over the years. A certified check is a bank check that guarantees that the customer's money is being held on account to cover the check. A demand deposit is money that can be withdrawn from a bank at any time. A promissory note is a legal form signed by a borrower promising to repay a loan. SOURCE: SE:215 SOURCE: Everard, K.E., & Burrow, J.L. (2001). Business principles and management (11th ed.) [pp. 464-465]. Cincinnati: South-Western. 98. A Paid for. Salespeople should make their suggestions for additional purchases before the original item is paid for and the transaction is complete. Otherwise, the customer may reject the suggestion because of the additional time involved in completing a new sales check. Salespeople should wait until the customer has selected and identified the original item to purchase before suggesting additional purchases. Salespeople should demonstrate the original item before suggesting additional purchases. SOURCE: SE:875 SOURCE: SE LAP 110—Using Suggestion Selling 2008 DECA Ontario Provincials Test 957 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS 32 99. B Planning. Top executives have the responsibility for planning a company's direction, which involves deciding what will be done and how it will be accomplished. In a large company, the president is not likely to be directly involved with supervising employees or the production of products. The president's only involvement with hiring would be hiring management personnel. SOURCE: SM:001 SOURCE: BA LAP 6—Manage This! 100. C Unethical. An ethical person always gives credit to the person who actually did the work. When a manager takes credit for the work of his/her people without identifying who really did the work, s/he is not only being unethical but also deceitful, dishonest, untruthful, and eventually not successful because the employees will begin performing poorly if not given recognition for their efforts. Managers should set and demonstrate ethical behavior for the employees they manage. SOURCE: SM:002 SOURCE: EI LAP 4—Work Right (Ethical Work Habits)