Epistemology Review
advertisement

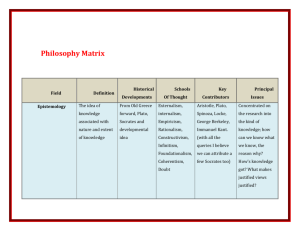
Epistemology One of the ‘pillars of philosophy” Explores the nature, scope, limits and origin of human knowledge Touches on all branches of philosophy Knowledge Justification Defining “knowledge”? Truth Science vs Epistemology Disciplines in constant disagreement Science: materialist (observation/evidence-based approach) Epistemologists may question the “evidence” of the senses (not reliable knowledge) Einstein and Heisenberg – order vs. chaos Kongfuzi say: At fifteen my heart was set on learning; At thirty I stood firm; At forty I had no more doubts; At fifty I knew the mandate of heaven; At sixty my ear was obedient; At seventy I could follow my heart's desire without transgressing the norm. Confucius The Analects Rationalism Reason the primary source of human knowledge The senses are ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Rationalists include: Plato, Descartes Empiricism All knowledge comes from experience which is ultimately acquired through the senses Mind is a _______ or _______ ________at birth. Experiences are gained through the senses giving birth to ideas Key players: ____________, ________________ Epistemology terms a priori – a posteriori- examples 5 is a prime number We had too much snow this winter All brothers are male siblings The coffee is too hot If Liam 1 has more pencils than Liam 2 and Loredana has more pencils than Liam 1 then Loredana has more pencils than Liam 2 Why does this matter? “I didn’t know I was that close” “I didn’t know that the ice was that thin” All facts, opinions and beliefs formed are exercises in epistemology. Eg. “I’m not going to be late”, “That’s not dirty yet” Common sense realism – “what you see is what you get” is ___________________________________ _________________________________________ Plato and knowledge Knowledge is defined as a “justified true belief” 3 conditions: -_________________________ -_________________________ -______________________________ Problem: What if statement is based on false assumption or knowledge? Eg. Cow in the field? Is this knowledge justified? Did the farmer “know” that the cow was in the field? Although he may be justified in making the claim his actual “evidence” was false The fact that his original statement was true does not mean that he “knew” the truth at the time Justified True Belief – Gettier style Statement is true Justification does not depend on false statement knowledge You are justified in believing your statement is true You believe your statement is true Types of knowledge Direct knowledge – ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ e.g. smelling someone’s perfume Indirect knowledge – ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ e.g. sitting on a chair, not seeing its legs, but still knowing it will support your weight. Not always reliable (i.e. thin ice) Types of knowledge Bertrand Russell – 20th century philosophyer Knowledge by acquaintance – ________________ ____________________________________________ But… how do we account for knowledge of true events that we do not experience (e.g. signing of Declaration of Independence)? Knowledge by description – ___________________ _____________________________________________ Types of knowledge Competence – “how to” knowledge. Knowledge as ability Propositional knowledge – information that can be conveyed in words. Propositions differ from statements as they can be judged as either _________ or __________ e.g. “Mike weighs 200 pounds” vs. “Shut the door!” Both are statements but only the 1st is a proposition as it can be said to have truth value Foundationalism vs. AntiFoundationalism Foundationalists believe that knowledge rests on the foundation of ___________ ____________ (Aristotle, Descartes, _______) Anti-foundationalists argue that knowledge is ________. (Plato) Experience A posteriori Knowledge A priori Innate Ideas