Metric Mania Metric Conversions and Length 2014
advertisement

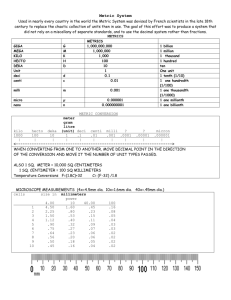
Warm up 1. What is the basic unit for length in the metric system? 2. What is the basic unit for volume in the metric system? 3. What is the basic unit for mass in the metric system? Lessons 1 & 2 Metric Conversions and Length T. Trimpe 2008 http://sciencespot.net/ I. Background A. The Metric System is a system of units for measurement B. Used by scientists around the world C. Easy to use because it is based on units of ten (10) Burma, Liberia, United States II. How it works… A. The basic units: 1. Length=meter 2. Volume=liter 3. Mass=gram B. Add prefixes for larger or smaller divisions 1. King Hector Doesn’t [usually] Milk! Drink Chocolate III. Ladder Method KILO 1000 Units HECTO 100 Units DEKA 10 Units DECI 0.1 Unit Meters Liters Grams CENTI 0.01 Unit MILLI 0.001 Unit A little trick… King Hector Doesn’t (usually) Drink Meters Liters Grams Chocolat e Milk 1 2 KILO 1000 Units 3 HECTO 100 Units DEKA 10 Units DECI 0.1 Unit Meters Liters Grams How do you use the “ladder” method? 1st – Determine your starting point. 2nd – Count the “jumps” to your ending point. 3rd – Move the decimal the same number of jumps in the same direction. CENTI 0.01 Unit MILLI 0.001 Unit 4 km = _________ m Starting Point Ending Point How many jumps does it take? 4. __. __. __. = 4000 m 1 2 3 Warm up 1. Read and complete the “Analyzing Elements of the Scientific Method” handout. 2. For the 6 questions at the bottom, underline, circle, or highlight the 1 word in each question that describes a step in the scientific method. Conversion Practice Try these conversions using the ladder method. 1000 mg = _______ g 1 L = _______ mL 160 cm = _______ mm 14 km = _______ m 109 g = _______ kg 250 m = _______ km Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm 6m 7g 698 mg Metric Abbreviations Write the correct abbreviation for each metric unit. 1) Kilogram ____ 4) Milliliter ____ 7) Kilometer ____ 2) Meter _____ 5) Millimeter _____ 8) Centimeter ___ 3) Gram _____ 6) Liter _____ 9) Milligram ____ Conversion Practice 1000 mg = _______ g 1 L = _______ mL 160 cm = _______ mm 14 km = _______ m 109 g = _______ kg 250 m = ______ km Conversion Practice Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm 6m 7g 698 mg Metric Conversion Challenge Try these conversions, using the ladder method. 10) 2000 mg = _______ g 15) 5 L = _______ mL 20) 16 cm = _______ mm 11) 104 km = _______ m 16) 198 g = _______ kg 21) 2500 m = _______ km 12) 480 cm = _____ m 17) 75 mL = _____ L 22) 65 g = _____ mg 13) 5.6 kg = _____ g 18) 50 cm = _____ m 23) 6.3 cm = _____ mm 14) 8 mm = _____ cm 19) 5.6 m = _____ cm 24) 120 mg = _____ g Warm up… 1.Convert 5,720 km to cm. 2.Convert 23 mg to dag. Scientific Method 1. Find the “Analyzing Elements of the Scientific Method” handout. 2. Look at the 6 words you circled, underlined or highlighted yesterday. 3. List those words in the boxes on the back of the sheet and DRAW A PICTURE to represent at least 3 of those steps in the scientific method. More conversions 1. Complete as many of the 25 practice problems as you can until Mrs. Lock stops the class. 2. Check your answers. Mark any that are incorrect with a colored pencil. 3. Turn in your sheet. 4. You may get an EXTRA COPY of the sheet if you want to practice at home. Warm up… 1.Convert 5,720 cm to hm. 2.Convert 23 kg to dag. Measuring Length in Metric Units Largest lines are centimeters 1 Smallest lines are millimeters 2 3 4 5 Measuring Length in Metric Units 1 2 3 4 How big is the oval? 5 How many mm are found in 1 cm? How long is the line segment in mm? How long is the line segment in cm? How long is the line segment in mm? How long is the line segment in cm? How long is the line segment in mm? How long is the line segment in cm? Practice Answer 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 0.05 0.02 3000 2.5 0.55 0.67 324 0.61 15 420 20 0.55 Now… Check your answers again. Which ones do you want to see me do on the board? 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 3 1.6 0.08 0.85 2000 10,000 0.00075 0.0001 0.075 0.01 10 2500 650