AP Government Review Unit 1: Constitutional Framework
advertisement

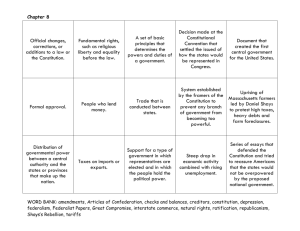
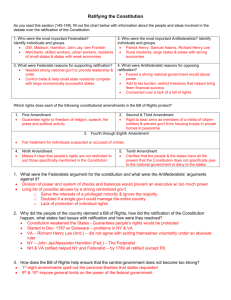
Chapters: “Constitution” and “Federalism Attitudes/Beliefs of Revolutionaries Weakness of Articles of Confederation Constitutional Convention (Compromises) Ratification (Federalist vs. Antifederalist) Constitutional Aspects (Structure, Key Provisions, Amendment Process, Full Faith and Credit) Federalist #10 Bill of Rights Federalism (Eras of Dual and Cooperative, Examples, Court Cases) Money and Control (Grants and Mandates) Unlike the Articles of Confederation, the Constitution does which of the following? A) Restricts the ability of Congress to tax B) Restricts the ability of Congress to establish an army or navy C) Establishes a unitary form of government D) Emphasizes state sovereignty over national sovereignty E) Emphasis both national sovereignty and federalism The debates between Federalists and AntiFederalists were primarily about which of the following issues? A) The right of people to rebel B) The existence of slavery C) The scope of power of the central government D) The need to establish a standard currency E) The representation of small and large states Which of the following statements about political parties and the United States Constitution is true? A) According to the constitution, only two major political parties may exist at any time B) The Constitution requires political parties to be restricted by both federal and state law C) The Constitution indicates that political party leaders at the national level be elected by political party leaders at the state level D) The Constitution specifies that political party leaders must be native-born United States Citizens E) The issue of political parties is not addressed in the Constitution Which of the following is a fundamental element of the United States Constitution? A) Recognition of the centrality of political parties in government B) Direct election of members of the executive branch C) An executive branch that is more powerful than the legislature D) Emphasis on a unitary system of government E) Division of governmental authority across political institutions The procedure for formally amending the United States Constitution best illustrates which of the following? A) The dominance of the national government over the state governments B) The dominance of the state governments over the national government C) The Founding Fathers’ desire to facilitate rapid constitutional revisions D) The Supreme Court’s power to review constitutional amendments E) The federal structure of the United States government In the Federalist #10, James Madison argued that factions in a republic are A) A more serious threat if the republic is large B) Natural but controllable by institutions C) Not likely to occur if people are honest D) Prevented by majority rule E) Prevented by free elections The Tenth Amendment to the Constitution has been interpreted by the Supreme Court to A) Prevent states from taxing agencies of the federal government B) Reserve powers to the states C) Restrict the application of judicial review D) Allow for the burning of the flag as an expression of protest E) Limit the use of the legislative veto In a federal system of government, political power is primarily A) Vested in local governments B) Vested in regional governments C) Vested in the central government D) Divided between central government and regional governments E) Divided between regional governments and local governments Of the following, which has been used the most to expand the power of the national government? A) The commerce clause of the Constitution B) The habeas corpus clause of the Constitution C) The bill of attainder clause of the Constitution D) The First Amendment E) The Fifth Amendment In McCulloch v. Maryland, The Supreme Court established which of the following principles? A) States cannot interfere with or tax the legitimate activities of the federal government B) The judicial branch cannot intervene in political disputes between the President and Congress C) The federal Bill of Rights places no limitations on the states D) The federal government has the power to regulate commerce E) It is within the judiciary’s authority to interpret the Constitution British “Obstructionism” Abrupt Taxation Crystallizes emerging philosophies Enlightenment Influences (John Locke) Natural Rights cannot be infringed on Life, Liberty, Property Government by consent rather than decree Declaration of Independence Restatement of Locke’s principles Listed 27 specific abuses by Britain Structure and Power Key Weaknesses Unicameral Legislature Each state had one vote 9 of 13 for passage of law Powerless Executive and No Judicial Unanimous Consent for Amendment No power to tax, had to request from states No power to regulate commerce, no national economy No court system to deal with conflict between states No money to fund military Shay’s Rebellion Reveals weaknesses of Articles Issues Dealt With Representation ▪ Virginia Plan ▪ New Jersey Plan ▪ Compromise Slavery ▪ 3/5 Compromise Voting (left to states) Key Concepts (Madison) Separation of Power Checks and Balances Limits on Majority Power Federalism Technically Illegal Federalists vs. Antifederalists Federalists (Strong National Gov/Pro-Constitution Antifederalists (State’s Rights/Anti-Constitution The Federalist Papers Federalist 10: Danger of factions, virtue of republic Federalist 51: Separation of Powers to control factions Bill of Rights Antifederalists pushed for one, added after ratification Ratification Special Conventions Formal Proposal 2/3 vote of both Houses of Congress Ratification ¾ vote of State Legislatures National Convention called by Congress State Conventions ratify in ¾ of the at the request of 2/3 of state legislatures states. Informal Judicial Interpretation Political Practices (Parties for example) Federalism A political system in which power is shared between local/regional governments (states) and a national government Continues due to Commitment to local government Congress being elected by local constituency Clear Advantage Increase participation and activity Based on 10th Amendment Federal and State Relationships No state can make treaties No state can coin money Elastic Clause muddies the waters Decided by Supreme Court State to State relationships “Full Faith and Credit Clause” “Privileges and immunities” Extradition Dual Federalism (Layer Cake) Early interpretation which held the States had powers in some areas and the federal in others but they did not overlap Cooperative Federalism (Marble Cake) More recent interpretation (1930s on) that hold the Federal and State governments both have power and responsibilities in certain areas. Leads to federal solutions implemented through the state’s apparatus. 1919 McCulloch v. Maryland Implied Powers Federal Supremacy 1924 Gibbons v . Ogden Court defines commerce broadly, increasing Federal power Nullification and the Civil War Loss of distinction between Interstate and Intrastate commerce Devolution 1995 United States v. Lopez ▪ Restricts commerce clause Medicaid and Medicare debate Grants-In-Aid Categorical Grants ▪ Grants for specific purposes. Often require matching funds. Have many conditions of aid. Block Grants ▪ Grants for general purposes. Have little to no conditions of aid. Stronger lobby for Categorical Grants Two Types of Federal Control over States Conditions of Aid ▪ What states must do to get grant money Mandates ▪ Regulations and Requirements State must meet (Environmental and Civil Rights mostly) ▪ Often vague, left up to Federal Gov to define ▪ Unfunded Mandates: Requirements given to states without providing funding to meet. • • • • • • • • • Amendment Process Antifederalists Bicameral Bill of Rights Checks and Balances Constitution Declaration of Independence Factions Federalism Federalist Papers Federalists Great Compromise Judicial Review Natural Rights New Jersey Plan Ratification Republic Separation of Powers Shay’s Rebellion Virginia Plan Unalienable Unicameral Block Grants Categorical Grants Conditions of Aid Cooperative Federalism Devolution Dual Federalism Extradition Federalism Federal System Full Faith and Credit Gibbons v. Ogden Grants in aid Initiative Mandates Mc.Culloch v. Maryland Nullification Privileges and Immunities Referendum Unfunded Unitary System