Chapter 11 - Genetics
advertisement

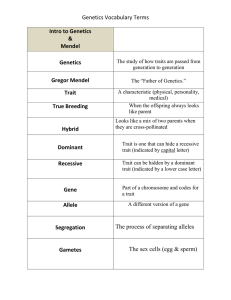
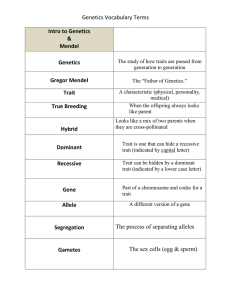
Name _______ Block _______ Date _______ Chapter 11 - Genetics The Essential Question Who is Gregor Mendel and what did he have to do with alleles, chromosomes, traits, or this topic called genetics? Chromosomes Homologous chromosomes Two nearly identical copies of each chromosome in an organism. One set is donated by the mother and the other set by the father. Sister chromatids After a chromosome has replicated during interphase they consist of two identical chromatids which are called sister chromatids. 2 Chromosomes Gene The basic unit of heredity. The sequence of DNA nucleotides on a chromosome encodes for the manufacturing of proteins and thus the traits of the organism. 3 Important terms and concepts • Gene: controls one characteristic • Alleles: alternative forms of a gene • Dominant: an allele that is phenotypically expressed regardless of the other allele • Recessive: an allele that is only phenotypically expressed when the dominant allele is not present • Locus: location of a gene on a chromosome 4 Important terms and concepts • Heterozygous: contains two different alleles for the trait being studied • Homozygous: contains identical alleles for the trait being studied • Genotype: the collection of alleles in an individual • Phenotype: the physical expression of the alleles (appearance & behaviour) 6 Gregor Mendel • He was a High School Biology teacher that gave up teaching to become a monk. • For his work in genetics, he earned the title of being know as: The Father of Genetics. Mendels first law • the Law of Segregation • Each organism has two hereditary factors for each trait, which are called ___________. And during meiosis, gamete (egg or sperm) formation, the two factors separate (segregate) into different gametes so that each gamete has only one type of each factor. 8 Mendel's second law • the Law of Independent Assortment • Genes located on different chromosomes assort independently of one another. 9 Punnett Squares • Monohybrid Cross • TT x tt