Sharks - Images
advertisement

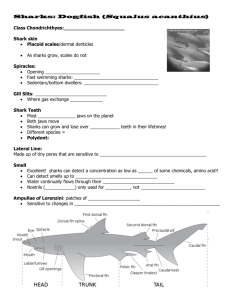
Types of Fishes Three types of fishes: Jawless fishes Cartilaginous fishes Bony fishes Jawless Fishes • Class Agnatha – Decendants of Ostracoderms (armored fishes) – Lack jaws, feed by suction with the aid of a round, muscular mouth and rows of teeth – Lack the paired fins and scales of most fishes • Hagfishes, or slime eels, feed on dead or dying fish • Lampreys, primarily freshwater, some move to the sea as adults. They attach to other fishes and suck their blood or feed on bottom invertebrates Cartilaginous Fishes • Class Chondrichthyes • Includes the sharks, rays, skates, and ratfishes • Cartilaginous fishes have a skeleton made of cartilage • Cartilaginous fishes have rough, sandpaper-like skin because of the presence of tiny scales, which have the same composition as teeth • Cartilaginous fishes have movable jaws and paired fins Sharks • Sharks are adapted for fast swimming and predatory feeding • The tail,caudal fin,is well developed and powerful. The upper lobe of the tail is usually longer than the lower lobe. Sharks Impact on Man • Approximately 50 to 75 people are attacked by sharks worldwide each year Approximately 8 to 10 die due mainly to loss of blood. • This is less than the number of people killed by bees, elephants, alligators,and lightening Man’s Impact on Sharks • During the last few decades, commercial and recreational shark fishing have increased • The increase in commercial fishing is a result in the increased demand for shark meat and fins • The increase in recreational shark fishing is due in part to the decline in numbers of other gamefish • The combined effect of the increase in fishing by both groups has led to a dramatic decline in large coastal shark species – The sandbar, blacktip, dusky, spinner, silky, bull, bignose, tiger, sand tiger, lemon, night, nurse, great hammerhead, and scalloped hammerhead Fisheries management • Plans have been developed and initiated in some areas of the U.S. to counteract the decline in shark species Shark Attacks • There are three sharks that have been identified repeatedly in shark attacks – The white shark – The tiger shark – The bull shark • Most sharks have very specific diets and do not often stray from these diets • Sometimes man may look like a prey item to a shark (a surfer may be mistaken for a seal or sea lion) Phylogeny of sharks • • • • • • Kingdom – Animalia Phylum – Chordata Class – Chondrichthyes Order – eight Families – twenty nine Species – over 350 Order • Squatiformes (angel-fish sharks) • Pristiophoriformes (saw carriers) • Squaliformes (dogfish sharks) includes the smallest shark – the spined pygmy • Carcharhiniformes(jagged rasp)includes the hammerheads • Lamiformes – includes the megamouth, basking, white, and thresher • Orectolobiformes – includes the whale sharks • Heterodontiformes (different teeth) includes bullhead sharks • Hexanchiformes – (six gilled sharks) the cow sharks Morphology • The skin – rough, covered with scales called dermal denticles or placoid scales • The fins – all sharks have one or two fins on the middorsal ridge called the first dorsal fin and the second dorsal fin. These fins are used as anti-roll stabilizers. – The pectoral fins are located behind the head and are used for steering. They also provide lift (sharks tend to sink because they lack a swim bladder) – The paired pelvic fins are modified into organs known as claspers – One anal fin is located between the pelvic and caudal fins in most sharks – The caudal fin is used for propulsion and helps to lift the body upward, providing some lift Ampullae of Lorenzini • Function as a sensory organ • The ampullae detect electrical currents (emitted by all living things) allowing the shark to detect prey • The ampullae are small sensory cells in jelly filled canals located on the snout of the shark The eyes • The eyes reflect light and are more efficient in low light conditions • Some sharks have a thickened eyelid called a nictitating membrane which protects the eye from injury when it is about to bite its prey Gill Slits • All sharks have five to seven pairs of gill slits that are external gill openings • Water enters the mouth of the shark, respiratory exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide take place on the gill filaments, and excess water exits through the gill slits The Mouth • Most sharks have jaws that can extend out when the shark is biting its prey • As the jaws recede back into the mouth, the prey is forced down the esophagus The Teeth • Sharks’ teeth have evolved for cutting, seizing, and crushing prey. • The shape of the teeth are adapted for the specific diet of the shark • All sharks have from five to fifteen rows of teeth • Teeth may be lost or damaged during the feeding process. Lost or damaged teeth are replaced after a few days from the row immediately behind the functional teeth The Lateral Line • A series of fluid filled canals that lie just beneath the skin on the sides of the shark’s body • The lateral line functions in conjunction with the inner ear and the ampullae of Lorenzini to detect underwater sound and motion • The lateral line allows sharks to orient and home in on vibrations in the water (injured prey) Reproduction • All fertilization in sharks is internal • There are three modes of reproduction – Oviparity – the most primitive mode of reproduction found in the bullhead sharks, the nurse sharks, and the catsharks • Oviparous sharks lay eggs that contain an embryo that is in a leathery egg case – Ovoviviparity – the most common mode of reproduction in sharks, the sharks grow in the uterus without forming a placental connection with the mother. – Vivaparity – the most advanced mode of reproduction, the embryos of viviparous sharks are nourished by a placental connection to the mother Phylogeny of Bony Fishes • • • • • • Kingdom – Animalia Phylum – Chordata Orders –end in iformes Families – over 500 end in dae Class Osteichthyes Approximately 23,700 species, over half of all bony fishes live in the oceans Morphology • Fishes vary in shape but always have 3 major parts: the head, the body, and the tail • Usually have thin, flexible, overlapping scales that develop from bone • Fishes that are fast swimmers have a fusiform body shape • Counter shading is a type of coloration that allows the fish to blend in with the surface when viewed from below and to blend in with the bottom when viewed from above The head • The head has the eyes, nostrils, mouth, and gills. • The area in front of the eyes above the mouth is called the snout • Bony fishes have 2 jaws • The position of the mouth varies among species – – – – The mouth is terminal if it is at the tip of the head The mouth is inferior if it is underneath the head Superior if the lower jaw projects beyond the upper Subterminal when the upper jaw projects beyond the lower The gills • Fishes absorb oxygen from water, which is taken in through the mouth, flows over the gills and then passes out through the gill openings • A flap of bony plates and tissue known as the operculum (gill cover), protects the gills Fins of Bony Fishes • The fins consist of thin membranes that are supported by fin rays (bony spines) • The dorsal and anal fins are used as rudders, to steer and provide stability • The paired pelvic fins also help the fish turn, balance and brake • The caudal fin is almost always the same size The Mouth • The mouth of most bony fishes is located at the anterior end. • Bony fishes have jaws with more freedom of movement than those of sharks • The teeth are fused to the jawbones • Teeth can be replaced but new teeth do not move forth in rows like in sharks Swim Bladder • Most bony fish have a swim bladder, a gas filled sac just above the stomach and intestine • The swim bladder allows the fish to adjust its buoyancy to keep from sinking or rising • Many fish have special organs called the gas gland and the rete mirabile that take up gases for the swim bladder Summary of Bony Fishes • Bony fishes are the largest group of living vertebrates • have gills covered by an operculum • have highly maneuverable fins • have freely moveable jaws • usually have a swim bladder Biology of Fishes • The scientific study of fishes is called ichthyology Body Shape • The body shape of a fish is directly related to its lifestyle and may be useful for camouflage • Fast swimmers like sharks, tunas, mackerels and marlins have a streamlined body shape that helps them move through the water • Flatfishes such as flounders, soles, and halibuts are flat and adapted to live on the bottom. – They lie on one side, with both eyes on top. – They begin life with one eye on each side like other fishes but as they develop one eye migrates up to lie on the other side Coloration- chromatophores • Some bony fishes use color for camouflage • Chromatophores – colored pigments • The variation of colors and hues in marine fishes results from combinations of chromatophores with varying amounts of different pigment. • Many fishes can rapidly change color by contracting and expanding the pigment in the chromatophores. Coloration - iridophores • Fishes also have structural colors that result when a special surface reflects only certain colors of light • Most structural colors in fishes are the result of crystals that act like tiny mirrors – The crystals are contained in special chromatophores called iridophores – The iridescent, shiny quality of many fishes is produced by structural colors in combination with pigments Warning coloration • Color is used to indicate that the fish is dangerous, poisonous, or tastes bad Cryptic coloration • Some fish are adapted to blend with the environment • Flatfishes, some blennies, sculpins, and rockfishes can change color to match their surroundings Disruptive coloration • Color stripes, bars, and spots help break up the outline of a fish – Disruptive coloration is common among coral reef fishes Countershading • Open-water fishes and many shallowwater predators have silver or white bellies and dark backs, this is a form of disguise in open water • When viewed from below, the light belly blends with the bright light coming from the surface. • The dark back blends into the ocean’s color when seen from above