6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle Trig Functions
advertisement

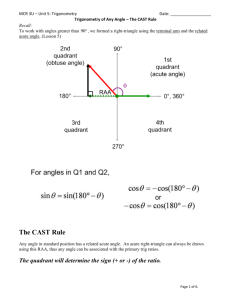
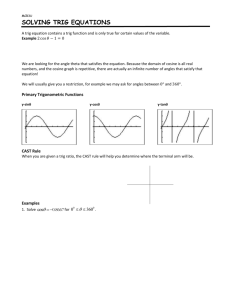
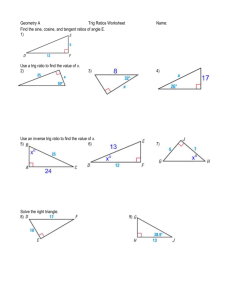
Pg. 323/361 Homework • Pg. 362 #39 – 47 odd, 51, 52 Memorize Trig. Info • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • #2 #8 #12 #16 #20 #24 #30 #36 #42 #48 #1 #4 #7 #8 #11 QIV #4 -250° #10 338°, 698°, -382°, -742° 11π/4, -5π/2 π/4, 9π/4, -15π/4, -23π/4 78°, 168° #26 90°, π/2 #32 -120°, -2π/3 #38 π/3 #44 59π/90 #50 8 #2 113 7/8 #5 7 113 11/15 2 26 11 ,8 113 , 7 , 8 , 113 , 113 8 7 8 7 #9 #12 QIII #6 QIII 470° #14 210°, 570°, -510°, -870° #18 29π/6, -19π/6 #22 67°, 157° 5π/12, 11π/12 #28 π/14, 4π/7 135°, 3π/4 #34 0°, 0, 2π -600°, -10π/3 #40 -1260°, -7π 7π/6 #46 11π/6 249π/180 #52 810/π 7 #3 8/7 113 113 #6 113 8 7 2 26 15 15 2 26 #10 #13 11 2 26 15/11 6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle Trig Functions • The six trig functions of any angle 0° < Ɵ < 90° are defined as follows: opp hyp adj cos hyp opp tan adj sin adj opp hyp sec adj hyp csc opp cot • Also, we know that from the basic three trig functions: 1 tan 1 sec cos 1 csc sin cot 6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle Triangle Trig • We use right triangles because they allow us to use the Pythagorean Theorem, which makes solving a much easier process! • Because 30°, 45° and 60° occur frequently, we will learn and memorize those triangles!! • If c = 2, determine the lengths of a and b and find the six trig values at 30° and 60°. 6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle More Trig Triangles • If a = 1, determine the length of c and find the six trig values. Cofunctions of Complementary Angles • If Ɵ is any acute trig angle, a trig function value of Ɵ is equal to the cofunction of the complement of Ɵ, as follows: sin cos cot tan 2 2 cos sin 2 sec csc 2 tan cot 2 csc sec 2 6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle Example: • Show that sin cos 2 are cofunctions. • Let Ɵ be an acute angle such that sin Ɵ = 5/6. Find all the trig functions of Ɵ. • One angle of a right triangle measures 38°, and the hypotenuse has length of 17. Find the measures of the remaining sides. 6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle Example: • They hypotenuse and one leg of a triangle measure 12 and 7 respectively. Find the measure of angle Ɵ formed by these two sides. Trig Functions of Any Angle • Let Ɵ be an angle in standard position, P(x, y) a point other than the origin on the terminal side of P, and r = x 2 y 2 The six trig values of Ɵ are defined as follows: y x sin cos tan r r r r sec csc cot x y y x x y 6.5 Trig Functions of an Acute Angle Example: • Find the values of the six trig functions at an angle Ɵ in standard form with point P(4, 7) on its terminal side. • **Note** If an angle does not appear acute in the first quadrant, you can work in any of the four quadrants to make the angle acute!! • Find the values of all six trig functions and the angle of measure of angle Ɵ, where P(-3, 2) is a point on the terminal side of Ɵ. • Find all the values of all six trig functions for the quadrantal angles of: 3 0, , , , 2 2 2