Supreme decision review
advertisement

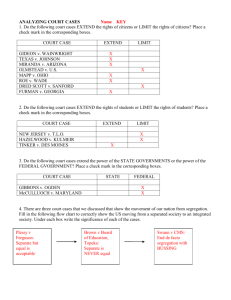
Title your paper “Famous Cases”. Fold your paper from the right edge to the red line. We will be answering five questions about Brewer v Hamilton Middle School and five questions about a real Supreme Court case that affects your lives. Paper Preparation Famous Cases Ben’s Case What right are we talking about? How is it limited? Precedent? Factors? What happened in the precedent case? Savana’s Case 1. What right are we talking about? What right did Ben claim was being violated? SUPREME DECISION REVIEW 2. How is the right limited? SUPREME DECISION REVIEW 3. Which case was used as precedent? When deciding this case, the justices looked at a previous case to see how they handled the situation in the past. SUPREME DECISION REVIEW 4. What factor(s) is/are used from the precedent case? In Tinker, the court determined that speech could be banned under certain circumstances. What are the circumstances? SUPREME DECISION REVIEW 5. What happened in the precedent case? Summarize the precedent case in one sentence. At the very least, include: WHO WHAT and WHY SUPREME DECISION REVIEW Savana’s Case Savana Redding’s school principal heard Savana had been giving pills to other students. He talked to Savana, and then ordered the school nurse and a female school employee to search Savana. They told Savana to take off her outer clothing and shake out her underwear. They didn’t find any pills. How the Supreme Court Decided The Fourth Amendment protects people from “unreasonable searches.” Nobody argued that what happened to Savana was not a search. But the Constitution puts a limit on the right to not be searched: it only protects people from unreasonable searches. How the Supreme Court Decided How does the Court know when a search is unreasonable? It looks for a similar case that was already decided, called a precedent case. A precedent case usually gives factors that must be considered in future cases. How the Supreme Court Decided To decide Savana’s case, the Court looked at a case called New Jersey v.T.L.O., where a school was allowed to search a high school student’s purse after she was caught smoking. In the T.L.O. case, the Supreme court had said that whether a search in school is unreasonable depends on two factors: How the Supreme Court Decided 1) whether the school had good reason to believe the search needed to be done 2) whether the search went too far Using these two factors, the Court decided that the school did have a good reason to believe they should search Savana, but that a strip search went too far. 1. What right are we talking about? What right did Savana claim was being violated? SAVANA’S CASE REVIEW 2. How is the right limited? SAVANA’S CASE REVIEW 3. Which case was used as precedent? When deciding this case, the justices looked at a previous case to see how they handled the situation in the past. SAVANA’S CASE REVIEW 4. What factor(s) is/are used from the precedent case? In New Jersey v. T.L.O., the court determined that searches could be carried out if two factors were taken into consideration. What are the factors? SAVANA’S CASE REVIEW 5. What happened in the precedent case? Summarize the precedent case in one sentence. At the very least, include: WHO WHAT and WHY SAVANA’S CASE REVIEW Turn to the back of your paper. We are going to discuss seven famous cases from the Supreme Court and summarize why they are important to your life. The case names will be on the upcoming slides, so don’t panic and yell “wait!” like you always do. Paper Preparation Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright Marbury v. Madison (1803) This case said the Supreme Court and other courts have the power to decide whether something is unconstitutional. Because of this case, courts can strike down government actions that violate the Constitution. Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. How does this case protect your rights? Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) This case said it was constitutional for places like schools, buses and restaurants to keep people of different races apart, as long as the services offered were “equal.” For example, it was okay to make black and white people ride on separate train cars. Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. If this were still law, what could the government require you to do? Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Meyer v. Nebraska (1923) This case said it’s unconstitutional for a state to ban the teaching of foreign languages. Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. How does this case change your options in school? Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright Brown v. Board of Education (1954) This case overruled Plessy v. Ferguson by saying it’s unconstitutional for the government to require students of different races to go to different schools. The Court said separate schools for students of different races are not equal. Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. How does this case affect your quality of education? Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) This case said that people accused of a crime must be given a lawyer even if they cannot afford one. It’s unconstitutional to deny them a lawyer just because they’re poor. Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. How does this case protect your rights? Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Tinker v. Des Moines (1969) This case said it’s unconstitutional to deny students the right to free speech at school, unless the students’ speech disrupts school activities. Gideon v. Wainwright Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. How does this case affect you at school? Marbury v. Madison Plessy v. Ferguson Meyer v. Nebraska Brown v. Board of Education Gideon v. Wainwright New Jersey v. T.L.O. (1985) This case said it’s unconstitutional for principals and teachers to search students and their belongings, unless: 1) there is a good reason (like safety and discipline) and 2) the search doesn’t go too far. Tinker v. Des Moines School District New Jersey v. T.L.O. How does this affect your rights in school?