GAW and CAS within WIGOS - Group on Earth Observations
advertisement

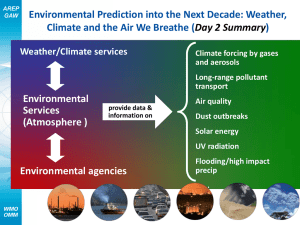
WMO GAW and CAS within WIGOS: Opportunities and Challenges Phil DeCola WMO/Sigma Space Corporation Oksana Tarasova WMO Global Atmospheric Watch (GAW) Sandro Fuzzi National Research Council, Italy WMO: Research Dept. What is the Global Atmosphere Watch Programme? WMO/GAW was established 1989 by merging GO3OS and BAPMoN. GAW focuses on global networks for GHGs, ozone, UV, aerosols, selected reactive gases, and total atmospheric deposition GAW is a partnership involving contributors from 100 countries. GAW is coordinated by the Research Division of WMO under the purview of WMO Commission for Atmospheric Science (CAS) Currently the observational component of GAW is based on activities at 30 Global stations, more than 400 Regional stations, and about 100 Contributing stations (http://gaw.empa.ch/gawsis/) 2 GAW organizational diagram Expert Groups Administration Management Central Facilities Observing Systems Users and applications 3 GAW Steering Bodies Scientific Steering Committee of the Open Programme Area Group on Environmental Pollution and Atmospheric Chemistry (EPAC SSC) Scientific Advisory Groups (SAGs) Ozone Greenhouse Gases UV Solar Radiation Reactive Gases Total Atmospheric Deposition Aerosols SAG GURME (urban pollution) SAG on NRT applications Expert Team: World Data Centres 4 Operational support functions GAW observational and data infrastructure is supported by Members operating central facilities: World Calibration Centres Central Calibration Laboratories World Data Centres Ozone and UV Solar Radiation Aerosols Greenhouse gases Precipitation chemistry The World Data Center for Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere GAW Station Information System (GAWSIS) This has created a sustainable system 5 GAW Station Information System GAWSIS Online - comprehensive information on all GAW stations • Database • Search / Update • Inventory / Audit (Supported by Switzerland) • GAWSIS became a part of OSCAR data base (with observational capabilities) • GAWSIS is being reviewed at the moment and works toward implementation of the WIGOS meta data standard ICG-WIGOS Fourth Session, 17-20 February 2015 6 CAS achievements within WIGOS (1) CAS deeply involved in Task Team – World Meta Data defining the WIGOS metadata standard Work of GAW ET-WDC very much aligned with WIGOS Discussion of WIGOS metadata standard at recent meeting of GAW Expert Team on Data Centers in Tokyo, January 2014 overall approval GAW Metadata profile of ISO19115 approved; compliant with WMO Core Metadata profile, and includes many aspects of WIGOS metadata requirements Notion of a “virtual GAW data center” with interoperable WDCs was approved strategy document planned Meanwhile, GAWSIS continues to serve as catalogue of GAW stations and to connect WDCs and related archives. SSC endorsed in June 2014 the Atmospheric Composition Vocabulary Task Team (already operational) which looks at the metadata related to atmospheric composition in a broader sense and feeds this information back to ET-WDC. 7 Evolution of the GAW observational network Using the Rolling Review of Requirements (RRR) Process according to WIGOS Manual: (i) a review of technology-free requirements for observations, within an area of application covered by WMO programmes and cosponsored programmes; (ii) a review of the observing capabilities of existing and planned observing systems, both surface- and space-based; (iii) a Critical Review of the extent to which the capabilities (ii) meet the requirements (i); and (iv) a Statement of Guidance based on (iii). Network development should be performed in a systematic way to address specific applications Application areas within GAW A Task Team on user requirements for atmospheric composition and related needs for satellite measurements was formed to assist the RRR process The broad “atmospheric chemistry” application area was substituted with more specific application areas: • “atmospheric composition forecasting”, • “atmospheric composition analysis and monitoring” • “urban services”. Task Team develops an approach to assess user requirements. The report of the first meeting is published (GAW Report No. 221). Second meeting of TT took place on 12-13 August 2015. CAS achievements within WIGOS Current application area “Atmospheric Chemistry” is split into 3 areas: Forecasting Atmospheric Composition: Applications global to regional with stringent timeliness (NRT) Monitoring Atmospheric Composition: Applications related to changes of atmospheric composition regionally and globally less stringent timeliness (no NRT) Providing Atmospheric Composition information to support services in urban and populated areas: Applications targeting limited areas (with horizontal resolution of a few km and stringent timeliness requirements (air quality forecasting) ICG-WIGOS Fourth Session, 17-20 February 2015 10 Challenges still to be addressed by CAS GAW implementation plan is currently under development The plan will be built around applications rather than around focal areas –> needs a lot of work to build understanding of cross-cutting applications The plan will take WMO priorities into consideration and build around them Major principles of network design and quality assurance (developed within WIGOS) are imbedded in GAW and will be further fostered Outreach strategy (how to explain NMHSs the role of atmospheric composition in understanding weather and climate) should be developed ICG-WIGOS Fourth Session, 17-20 February 2015 11 Needs for improving collaboration among TCs/RAs within WIGOS Need for recognition and support of GAW stations by NMHSs for observational network to be sustainable (long-term “cultural” and “political” improvement) WMO assumes that communicating with National Representatives is enough to correspond with the whole national Institutions involved (not always true!) Direct involvement of Institutions other than NMHSs needed for rationale and positive GAW contribution to WIGOS (procedures needed) ICG-WIGOS Fourth Session, 17-20 February 2015 12 GAW Implementation Plan (2015-2023) The plan concerns only implementation of the GAW Programme, WMO Strategic Plan is taken as an overall strategy Short (focuses on the major principles, SAG specific tasks are in the annex) Follows the concept “research enabling services” – the activities are around application areas rather than focused on GAW parameter specific areas More focus on modelling tools and value added products Provides clear framework for the programme implementation concerning network design, modelling tools, quality assurance principles, data management, collaboration with the other programmes IP builds upon the premise that atmospheric composition matters - to climate, weather forecasting, human health, terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, agricultural productivity, aeronautical operations, renewable energy production, and more. Example of the applications in GAW Support of climate negotiations: IG3IS Ecosystem services: analysis of total deposition, nitrogen cycle, deposition to the oceans/marine geoengineering Health: sand and dust storms, urban air quality (GURME), biomass burning Food security: atmospheric composition and agriculture Transport security: volcanic ash forecasting Thank you for your attention Sandro Fuzzi Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate National Research Council Bologna, Italy s.fuzzi@isac.cnr.it www.wmo.int