Chapter 2
advertisement

Chapter 2
Inequalities and Proof
Section 2-1
Solving Inequalities in
One Variable
Properties of Order
Transitive Property - If a < b
and b < c, then a < c
Addition Property - If a < b,
then a + c < b + c
Multiplication Property
1. If a < b and c is positive,
then ac < bc
2. If a < b and c is negative,
then ac > bc
Equivalent Inequalities
Inequalities with the same
solution set
2x + 5 < 13 and 2x < 8 and x < 4
4x > 2(3 + 2x) and 2x > 3 + 2x
Transformations that Produce
Equivalent Inequalities
Simplifying either side of an
inequality.
Transformations that Produce
Equivalent Inequalities
Adding to (or subtracting
from) each side of an
inequality, the same
number or the same
expression.
Transformations that Produce
Equivalent Inequalities
Multiplying (or dividing)
each side of an inequality
by the same negative
number and reversing the
inequality.
Transformations that Produce
Equivalent Inequalities
Multiplying (or dividing)
each side of an inequality by
the same positive number
Examples
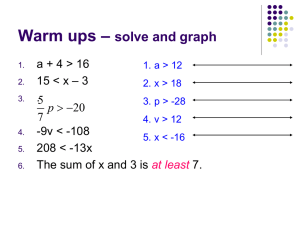
Solve each inequality and
graph its solution set
5x + 17 < 2
5(3-t) < 7 - t
Section 2-2
Solving Combined
Inequalities
ConjunctionA sentence formed by joining two
sentences with the word and. In a
conjunction both sentences are
true.
Example:
Graph the solution set of the
conjunction x > -2 and x < 3
DisjunctionA sentence formed by joining
two sentences with the word or.
It is true when at least one of the
sentences is true.
Example:
Graph the solution set for the
disjunction x < 2 or x = 2
Conjunctions in a Different form
Solve 3 < 2x + 5 ≤ 15.
First rewrite the conjunction with
and.
3 < 2x + 5 and 2x + 5 ≤ 15
Now solve each inequality and
graph the solution set for the
conjunction.
Conjunctions in a Different form
Solve -3 < -2(t -3) < 6.
First rewrite the conjunction with
and.
-3 < -2(t-3) and -2(t-3) < 6
Now solve each inequality and
graph the solution set for the
conjunction.
Disjunctions
Solve 2t + 7 13 or 5t – 4 < 6.
Now solve each inequality and
graph the solution set for the
disjunction.
2t + 7 13 or 5t – 4 < 6
Disjunctions
Solve y -1 or y 3
Now solve each inequality and
graph the solution set for the
disjunction.
y -1 or y 3
Section 2-3
Problem Solving Using
Inequalities
Solving Word Problems
Using Inequalities
Phrase
Translation
x is at least a
x is no less than a
x≥a
x is at most b
x is no greater than b
x≤b
x is between a and b
x is between a and b,
inclusive
a<x<b
a≤x≤b
Example:
Find all sets of 4 consecutive
integers whose sum is between 10
and 20.
Solution
Four consecutive integers –
n + (n + 1) + (n + 2) + (n + 3)
10 < 4n + 6 < 20
1 < n < 14/4
Which integers work?
Section 2-4
Absolute Value in Open
Sentences
Absolute Value
The distance between a number x
and zero on a number line
If | x | = 1, then x = 1 or -1
If | x | < 1, then -1 < x < 1
If | x | > 1, then x < -1 or x > 1
Example - Equality
Solve |3x - 2| = 8
To solve, set up two equations
3x – 2 = – 8
3x – 2 = 8
3x = – 6
3x = 10
x=–2
x = 10/3
The solution is {-2, 10/3}
Example - Inequality
Solve |3 – 2t| < 5
Set up a compound inequality
– 5 < 3 – 2t < 5
– 8 < – 2t < 2
4>t>–1
The solution set is { t: – 1 < t < 4}
Section 2-5
Solving Absolute Value
Sentences Graphically
Facts
The distance between x and
0 on a number line is | x |
The distance between the
graphs of real numbers a
and b is | a – b |, or | b – a |
Examples
Solve |5 - x| = 2
{3, 7}
Examples
Solve |b + 5| > 3
{b: b < -8 or b > -2}
Examples
Solve
|2n + 5| ≤ 3
{n: n ≤ -4 or n ≥ -1}
Section 2-6
Theorems and Proofs
Definitions
Theorem - A statement that can be
proved
Corollary – A theorem that can be
proved easily from another
Axioms – Statements that we
assume to be true (these are also
called postulates)
Cancellation Property of Addition
For all real numbers a, b, and c:
If a + c = b + c, then a = b
If c + a = c + b, then a = b
Cancellation Property of
Multiplication
For all real numbers a and b, and
nonzero real numbers c:
If ac = bc, then a = b
If ca = cb, then a = b
Zero – Product Property
For all real numbers a and b:
ab = 0 if and only if a = 0 or b = 0
Section 2-7
Theorems about Order and
Absolute Value