Healthy Homes - gozips.uakron.edu
advertisement

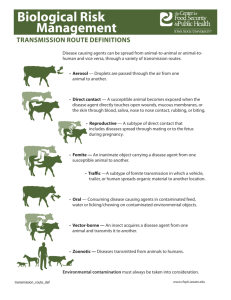
Healthy Home = Healthy Human There is A Link Between Housing & Health Overview Of A Healthy Home Discussion Describe housing problems and associated health risks . Identify populations that may be at higher risk for housing-related disease and injury. Identify housing systems that contribute to a comfortable living space. Identify codes used to enforce remediation of housingbased health threats. What Is A Healthy Home? A healthy home is: designed constructed maintained or rehabilitated in a manner that supports the health of residents WHY DO WE CARE ABOUT HEALTHY HOMES? Young children spend nearly 80%-90% of their time inside. Housing affects health both directly and indirectly: Physical, chemical,biological exposures Psychological, security, well-being Known or Suspected Harmful Health Effects Associated With Housing Conditions Respiratory infections Asthma Injuries and burns Reactions to extreme cold and extreme heat Irritations, allergy, rashes Poisonings, asphyxiation Neurotoxic exposures Cancer Death So, What Is An Unhealthy Home Often substandard construction Inadequate renovations Not adequately maintained Place residents at risk of illness or injury Sources of Exposure Typical sources of indoor exposures include: dust, insects, and pet allergens chemicals in wall coatings and furnishings penetrating outdoor toxics; pesticides environmental tobacco (smoke) Fungi (mold) Following Statistics From The American Housing Survey US Census Bureau Who Is Affected: Low Income Residents There are six million substandard housing units in the United States. Asthma rates are 40-50% higher among minority children living in U.S. cities. Children from low-income communities are eight times more likely to suffer from lead poisoning compared to moderate and upper income children. Cost of Unhealthy Homes Annual costs for environmentally attributable childhood diseases in the U.S: $54.9 billion $43.9 Billion from Lead Poisoning $ 9.2 Billion from Neurobehavioral Disorders $ 2.0 Billion from Asthma $ 0.3 Billion from Childhood Cancer Health & Safety: Categories for Residential Inspection Allergens/asthma Asbestos Combustion products Lead Mold and Moisture Insects and Rodents Weatherization Pesticides Radon Fire New Trend: Integrate Approach Integrated approach considers: People living in the home The structure Potential health hazards Result is more efficient and effective prevention system. Health Vs. Housing Epidemiologic Triangle of Disease/Injury Terms of The Epidemiological Triangle The HOST or PERSON is the who. The AGENT is the SOURCE or what, that can bring about changes in a person’s health. The ENVIRONMENT is where one lives. The TRANSPORT MECHANISM is any mechanism by which an agent is spread from the environment to the host. Transport Mechanisms A transport mechanism ties the HOST, AGENT and ENVIRONMENT together. A TRANSPORT MECHANISM is either a VECTOR or a FOMITE. a. A VECTOR is an insect or any living carrier which transports a pathogenic microorganism from the sick to the well b. A FOMITE is an inanimate object that transports the agent to the host. You Decide: Host Agent Vector Fomite You Decide: Host Agent Vector Fomite You Decide: Host Agent Vector Fomite You Decide: Host Agent Vector Fomite You Decide: Host Agent Vector Fomite You Decide: A 56 year old woman presents with a severe sinus infection and bronchial congestion. She has been seen 4 times for the same symptoms over the course of a 5 month period. Medical specialists suspect exposure as the source of her recurring illness. Upon returning home, she contacts her son to assist her in the investigation of potential exposures. She reports to her son that the first floor toilet holding tank has been leaking for sometime now, but she can’t image that would cause her any health issues. After all, it’s CLEAN water that is leaking from the holding tank! James, her son, enters the basement below which is sealed-off to save on heating. He finds the ceiling in the finished area in the following condition: List the Following: a. Environment b. Agent c. Host d. Transport Mechanism Factors Effecting The Host It is know that personal factors impact health. Low socio-economic populations are disproportionately exposed to: Air pollution & related illness Lead (paint or pipes) Household pests & pesticides Injurious conditions Host: Varied Exposures Residents of the same household will experience varied exposures due to individual behaviors: Time and activity patterns Smoking Diet/exercise Personal hygiene & sanitation practices Host Susceptibility Some household members may experience greater susceptibility to health hazards: ie. Age (children & elderly) Pregnant or nursing women Pre-existing health conditions Poorly nourished individuals Medically under-served people Agents: Exposure Inside the Home We will discuss three major exposures: 1. Biologic 2. Chemical 3. Physical Biologic Agents: Infectious Disease Infections often spread due to: Overcrowding Inadequate water supplies Inadequate waste disposal Inadequate ventilation Examples: tuberculosis, rhinovirus, strep, E. coli, salmonella, influenza Biologic Agents: Allergens Respiratory illness & asthma are often precipitated by exposure to: Dust mites Pet dander Mouse droppings Mold & plants Biologic Agents: Mold Damp/wet houses provide an environment for mold growth Chemical Agents Many materials used in homes contain chemicals that have known/suspected health effects. Sources of chemical exposure include building materials, consumer products, and combustion processes. Chemical Agents Indoor combustion appliances release a wide range of compounds that affect health, including: nitrogen dioxide sulfur dioxide carbon monoxide fine particulate matter (PM). Appliances include: Water Heaters (Gas) Clothes Dryers (Gas) Ventless Heaters Gas stoves/ovens Furnaces/room heaters Fireplaces Chemical Agents Second Hand Smoke (ETS=Env. Tobacco Smoke) Contains 4000 substances 40 of them cause cancer, ie: Acetone Ammonia Benzene Carbon Monoxide Formaldehyde Lead Nicotine Tar Cyanide Chemical Agents Pesticides: Greater than 75% of households report use of pesticides. Many are know to affect human health: Respiratory systems Nervous system Immune & reproductive systems VOC’s Volatile organic compounds Emitted as gasses from solids or liquids Have adverse health effects Emitted by: Paints, lacquers, paint strippers Cleaning supplies, pesticides Building materials, adhesives Generally, any organic solvent will emit VOC VOCs Are A Group of Chemicals Benzene, formaldehyde, toluene, xylene Indoors, VOCs are often emitted by: new carpeting & furniture Fresh paint jobs New plastics & electronic devices Health Effects of VOCs Symptoms: Eye/nose irritation Headache Vomiting Dizziness Can lead to chronic problems: Cancer Asthma Liver damage Central nervous system damage Chemical Agents: Lead Lead-based paint is the most significant source of lead exposure in the U.S. today Exposures: Air, drinking water, food, contaminated soil, deteriorating paint, and dust Symptoms of Lead Poisoning High levels can cause convulsions, coma & death. Lower levels can cause adverse health effects: Central nervous system Kidneys Blood cells Blood lead levels as low as 10 micrograms per deciliter can impair mental and physical development in children. Peeling lead-based paint on exterior Chemical Agents: Radon What is Radon? Naturally occurring odorless cancer-causing, radio-active gas Derived from the breakdown of uranium (radio-active) in soil, rock and water Permeates air we breath Can be found in any type of building that bears on the earth. Chemical Agents: Radon (2006 Statistics) How Radon Gets In Chemical Agents: Asbestos Asbestos is a mineral that was frequently used in homes built between 1920 and 1972 Many building products contained asbestos: furnace ducts steam pipes floor tiles Shingles Insulation textured ceilings and siding Inhalation of asbestos fibers can lodge in the lungs and cause disease including lung cancer and asbestosis. Agents: Physical Electrical Shock Improperly installed wiring Improper childproofing. Burns: hazards include stoves, ranges, exposed steam pipes & portable heaters Slip/Fall Hazards Fire & Explosion Electrical Shock Hazard