metric measurments and lab equipment
advertisement

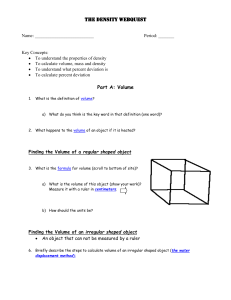
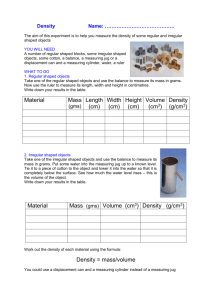
Decimals: The Nature of the Metric System Established in 1795, to include the meter, liter, and gram. With prefixes of centi, deci, deca, hecto, and kilo. The decimal metric system has gone unchanged as the basis for the modern International System of Units or SI for short, that we use in SCIENCE. Why Decimals? Which column would you rather add? Inch – Pound Units 1 yard, 2 feet, 3-1/4 inches 1 foot, 11 3-14 inches 2 feet, 5-1/2 inches 3 yards, 1 foot, 6-5/8 inches _______________________ ? Yards, ? Feet, ? inches 6 yards, 2 feet, 2 -9/16 inches Metric Units 1.607 meters 0.589 meters 0.749 meters 3.216 meters _______________ ? meters 6.161 meter Why Decimals? A room measures 15 ft 3-3/4 in by 21 ft 7-1/2 in ( 4.667 m by 6.591 m ) What is the floor area in square yards? What is the floor area in square meters? 36.79 sq yds 30.76 sq meters Why Decimals? In designing a calendar you wish to divide an area of 7-1/4 in by 11 inches ( 184 mm by 279 mm) into 35 rectangles; That is divide 7-1/4 in by 5 and divide 11 in by 7. What are the dimensions of each rectangle in inches? What are the dimensions of each rectangle in millimeters? 1-29/64 in by 1-37/64 in 36.8 mm by 39.9 mm Beakers - used for mixing volumes Ranging from 600 mL to 100 mL Graduated cylinders - used for measuring liquid volume 100 mL, 50 mL, 25 mL, 25 mL, 10 mL, 10 mL Read meniscus at eye level. 75 mL Examples of 25 mL Different cylinders each with the same volume measured out. 10 mL Different cylinders each with the same volume measured out. How do these cylinders differ? Flasks - used for liquid volume Erlenmeyer, Florence - How do they differ? How does the shape influence how it is used? Read meniscus at eye level. 6.4 mL 6.4 mL How do these cylinders differ? Each line is calibrated to .5 mL 20.5 mL 20.5 mL Why? Irregular shaped solids Volume of irregular shaped objects by the displacement method. Step 1: Calibrate cylinder and measure 15 mL Step 2: Lower object in water. Read new volume. 16 mL Finding volume of rock (irregular shaped object) Starting volume = 15 mL Ending volume = 16 mL Volume of object (rock) = 16 mL – 15 mL = 1 mL Volume of irregular shaped objects by the displacement method. Step 1: Calibrate cylinder &measure 15 mL Step 2: Lower object in water. Read new volume. 16 mL Finding volume of screw (irregular shaped object) Starting volume = 15 mL Ending volume = 16 mL Volume of object (screw) = 16 mL – 15 mL = 1 mL Volume of irregular shaped object using displacement method– metal weight Step 1: Calibrate cylinder and measure 7.0 mL Step 2: Lower object and read volume = 8.2 mL Finding volume of metal weight (irregular shaped object) Starting volume = 7.0 mL Ending volume = 8.2 mL Volume of object (screw) = 8.2 mL – 7.0 mL = 1.2 mL Using cylinder tips Takes practice Read meniscus at eye level (use of a background helps viewing) Calibrate cylinder Pour carefully and slowly Use dropper to add in last few drops Check calibrations and all measurements Volume of regular shaped object (rectangular prism) Measuring length = 8.5 cm Volume of regular shaped object (rectangular prism) Measuring width = 6.0 cm Volume of regular shaped object (rectangular prism) Measuring height = 2.0 cm Volume = L x W x H =8.5 cm x 6.0 cm x 2.0 cm = 102. cm3 Relationship between solid volume and liquid volume 1 cm3 = 1 mL Relationship between solid volume and liquid volume 1 cm3 = 1 mL