Biology Study Guide Answers
advertisement

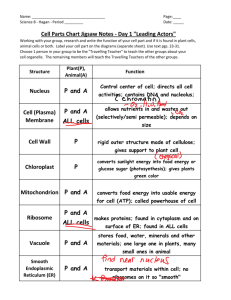
Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 • 1.) All living things are made of cells. • 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. • 3.) Cells come from pre-existing cells. 2 & 5.) Prokaryote Vs. Eukaryote Comparison Prokaryote Both *No Nucleus *No organelles *Have cell Eukaryote *Cells have a nucleus membranes *Cells have organelles *All are unicellular *Have DNA *Very small *Are alive *Can be unicellular, but most are multicellular *All are bacteria • Have ribosomes *All have cell walls Cells are 10x-100x larger than prokaryotic cells • Have cytoplasm *Some have cell walls • FRED H. GARC * Plants, algae, fungi, animals 3 & 6.) Plant Vs. Animal Comparison Plant Both *Have cell walls *Have chloroplasts • Have large central vacuoles • Are 10x larger than animal cells. *Have: cell membranes DNA, ribosomes, ER, GOLGI, nucleus, nucleolus, mitochondria, vesicles Animal *No cell wall • have: lysosomes, centrioles • Smaller than plant cells 4.) • Bacteria are the only example of a prokaryote 7 • The nucleus provides a barrier to keep the DNA safe. • The nuclear membrane prevents DNA from coming into contact with enzymes that could damage it. • The nuclear membrane (along with melanin pigment produced by other cells) prevents the DNA from being damaged by UV rays. 8 • Nucleolus is an RNA rich area of the nucleus where ribosomes are made. 9 • Golgi is most like a post office because: – It receives and ships proteins and carbohydrates. – It packages proteins/carbs into transport vesicles for delivery. 10 • GA Power is most like the mitochondria. • The mitochondria use sugar to produce usable energy. • GA Power uses coal or water or nuclear reactions to generate electricity. 11 • Janitor = lysosome • Both clean up/break down trash, unused/unneeded materials and prepare them for removal. 12 • Smooth ER makes lipids (and detoxify substances in the cell). 13 • The rough ER serves protein synthesis in two ways: – 1.) It provides a place for ribosomes to anchor and operate (however, they don’t HAVE to be attached to ER in order to work) – 2.) They put proteins (made on attached ribosomes) into transport vesicles and send them to the Golgi. 14 • Chloroplasts make sugar (food) in photosynthetic organisms. 15.) • Both the cell membrane and a bouncer work to control what (who) comes in/out of the cell (club). 16 • Vacuoles are for long term storage. • Vesicles are for short-term storage and transport. 17 • Ribosome Rough ER vesicle Golgi vesicle cell membrane (exocytosis) out. 18 • Since mitochondria produce usable cellular energy, a person with malfunctioning mitochondria would likely experience: – Difficulty moving – Lack of energy (more fatigue) – Difficulty regulating homeostasis – Increased immune problems 19 • Prokaryotes do a number of positive things: – Help us digest our food. – Keep parasitic fungi from growing on our skin – Help us make foods like yogurt, cheese and breads – Provide usable nitrogen for plants to grow Essays • Answers will vary… Cell Membrane & Cell Transport Questions 1 1 2 • Because the proteins in the membrane are scattered (like the pieces in a mosaic), but can move sideways due to the fluid-like nature of the membrane. • Like a mosaic, the membrane is made of smaller parts which combine to give the membrane its multiple functions. 3 • Passive – no cell energy needed – Moves with concentration gradient – Involves gases, carbohydrates and water – Examples: • Osmosis • Simple diffusion • Facilitated diffusion • Active – Needs cell energy – Moves against concentration gradient – Involves large molecules (food particles) and things dissolved in liquids. – Examples: • Sodium Potassium Pump • Endocytosis – Phagocytosis – Pinocytosis • Exocytosis 4 • Answers will vary, but here’s two: • When you are sitting in another room of the house, but you can smell the food being cooked in the kitchen. • Someone spraying perfume on the other side of the room and eventually you smell it. 5 • Facilitated diffusion uses proteins to help bring large molecules into the cell; • facilitated diffusion moves sugars and ions. • Simple diffusion does not use proteins. • Simple diffusion moves gases and liquids; 6 • It will shrivel up because the water in the cell will be pulled out due to the high solute concentration outside the cell. • Remember: “Where solutes are in large supply, water will always move close by.” 7 • Water will move into the cell due to osmosis. • There are more solutes inside the cell, so water moves in. • The plant cell will swell, but will not burst because it has a cell wall protecting it. 8 • Isotonic. • In an isotonic solution, water moves in and out of the cell freely (bringing nutrients in and getting rid of waste), but the cell does not swell or shrink. 9 • Hypotonic • Plants cannot get water whenever they need it; they must wait for rain. • So, plants want to let in as much water as possible so they can store it. • Also, plants rely on nutrients entering their cells through the roots. So, they need a large volume of water entering the roots. Chart • We will fill out in class.