GFR estimation: The key to assessment of kidney disease
advertisement

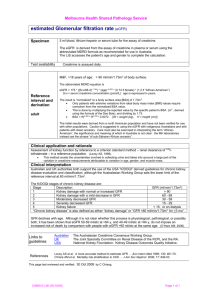
GFR estimation: the key to assessment of kidney disease Dr Graham Jones Department of Chemical Pathology St Vincent’s Hospital, Sydney RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Functions of the Kidney • Homeostatic / waste removal – water – hydrogen ions (pH) – sodium – potassium – calcium – phosphate – magnesium – nitrogen Kidney damage: abnormalities of these factors RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Homeostasis • For a person in steady state: input = output • Urine volume = water intake (food + drink) - fecal, sweat, respiratory losses • Sodium excretion = sodium intake – fecal and sweat losses RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Other Functions of the Kidney • Endocrine – 1-Hydroxylation of vitamin D – Erythropoietin production – Renin production • Metabolic – Glycogen storage (minor role) • Drug removal Kidney Damage: hypocalcaemia, anaemia Impaired drug removal Plus: acute phase changes RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR CKD Symptoms Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry: Renal Function and Nitrogen Metabolites RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR “Renal Failure” • Chronic – CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease • Acute – ARF: Acute Renal Failure – AKI: Acute Kidney Injury • Acute Classification – Pre-renal – Renal – Post-renal RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR The CKD problem • Clinically silent in the early stages • Cost of renal disease can be extreme to health care service • Effects of renal disease can be extreme on patient • Treatments now available to slow progression • Need an “early warning” system for CKD RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Diseases of the Kidney • • • • • Diabetes Hypertension Atherosclerosis Glomerular diseases Toxins – Gentamicin – NSAIDS – Compound analgesics • Inherited diseases • Tubular disorders All global renal diseases affect glomerular filtration rate (GFR) RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR K/DOQI (USA) RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR What is GFR? • Glomerular Filtration Rate is the volume of fluid passing through the glomerulus in a given period of time. • Influenced by renal perfusion pressure, renal vascular resistance, glomerular damage, postglomerular resistance. • “Normal Range” approx 90 - 150 mL/min – Approx 170 L per day • A larger healthy person has a higher GFR – Can be reported as 90 - 150 mL/min/1.73m2 • Values fall with increasing age RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Other reasons for estimating the GFR • Monitoring progression of CKD • GFR estimates are used for drug dosing decisions – Dosing of renally excreted drugs – Avoiding nephrotoxic drugs • Risk factor for cardiovascular disease mortality • Renal involvement in systemic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus or SLE RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR How do we measure GFR? • Ideal marker of GFR: – Constantly produced – Freely filtered at the glomerulus – Neither resorbed or secreted in the tubules – Not lost to the body in any other way • Inulin is the prototype GFR marker – Sugar of MW 5,000 – Requires constant inulin infusion – Not used in practice RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Measurement of GFR • Cr51-EDTA, I125-iothalamate, Tc99-DTPA, iohexol • Intravenous injection of substrate • Measure concentrations in blood and or urine at various time points • Calculate clearance as estimate of GFR • Time consuming • Expensive • Radioactive material • Significant Between-laboratory variation (5-20%) • “Gold standard” not very golden RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Estimate of GFR • • • • Measured GFR Serum creatinine Creatinine clearance Formulae based on serum creatinine – Cockcroft and Gault – MDRD All based on measurements • Other of serum creatinine – Eg Cystatin C RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Marker of GFR (creatinine) • Constant production • Freely filtered at the glomerulus • No tubular secretion or resorption – Some tubular secretion X • No extra-renal metabolism • No extra-renal loss – Some GIT loss X • Loss of creatinine through avenues other than glomerular filtration means Creatinine Clearance is slightly higher than the GFR RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Serum Creatinine Alone • Default / Historical position • Only marker universally available – Only marker for screening (case finding) • Concentration reflects rate of production as well as rate of removal • Relationship to rate of removal is not linear – “rectangular hyperbola” • Requires doctor to take multiple (non-linear) factors into account RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) S.creatinine approx. = 1/GFR GFR RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Cockroft and Gault • Developed in 1976 from 249 people (96% male) – Subsequently validated in at least 58 studies • A measure of creatinine clearance • Estimate urine creatinine based on age, weight and sex of patient. • False elevation of serum creatinine assays (in 1976) gave lower results, serendipitously approximating the GFR • Newer (better) creatinine assays give falsely elevated GFR estimates (approx 15%) RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Cockcroft and Gault - questions • Should we correct for “new” creatinine measurements (decrease results by 15%) • Should we use ideal body weight (estimated from height) – If so, when RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Creatinine Clearance • Measurement of clearance of creatinine using: – Serum creatinine concentration – Timed urine collection (often 24 hours) – Urine creatinine concentration – Urine Volume – Clearance = Ucreat x Uvol / Screat x 24 hours • Timed urine samples notoriously difficult RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR GFR Assessment • • • • Measured GFR Serum creatinine Creatinine Clearance Cockcroft and Gault • or one of over 40 other formulae using serum creatinine RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR MDRD* Formula • • • • Levey et al Ann Intern Med 130:461-470, 1999 Approx 1070 in training set and 558 validation set New formula developed for GFR More accurate and precise than other formulae • *Modification of Diet in Renal Disease RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR MDRD – Notes: • Not good for people with normal renal function – Few normals in training set – Low creatinine measurement less good • Results reported as mL/min/1.73 m2 BSA – Good for grading renal failure – Effect on drug dosing? • “Abbreviated” MDRD only requires age, sex and race (African-American or not) RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR KHA, RCPA, AACB Proposal: • Report estimated GFR with MDRD with all creatinine requests for patients over 18 • Results >60 mL/min/1.73m2 reported as “>60 mL/min/1.73m2” – to be extended to 90 mL/min/1.73m2 • • • • Accuracy approximately +/- 30% Recommended in USA (www.nkdep.nih.gov) Recommended in UK (MDRD or C&G) Law in France (C&G) RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR www.nkdep.nih.gov www.kidney.org/ PROFESSIONALS/kdoqi www.kdigo.org www.kidney.org.au RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Limitations • Not a sensitive test for renal failure – Serum creatinine best for early detection and monitoring patients • Delayed response in severe acute renal failure (as with serum creatinine) • Wrong in dialysis patients • Drug dosing issues not well addressed • Interpretation in the elderly • Interpretation in different racial groups RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Actual Outcomes • Almost universal uptake of eGFR reporting • Near complete standardisation of units – umol/L and mL/min • Increase in referrals to nephrologists – Initial spike – Settled to approx. 30% increase – 85% of referrals were appropriate – Referrals were undertreated • Professor David Johnston (Queensland) • Awareness of reduced GFR increased RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR Meeting 2 • • • • • • • December 2006 Issues The “175” equation for IDMS-aligned assays Reporting up to 90 mL/min/1.73m2 Age-related decision points Drug Dosing Racial differences RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR The Future • Better detection and management of CKD • Better relationship with clinical colleagues – Started on urine albumin and protein – Starting on LFT and uric acid • Recognition of role of laboratory – Recognising and solving metrological issues – Effector organ for clinical guidelines • Better co-operation between laboratories for the benefit of doctors and patients RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR References • Assessing Kidney Function - Measured and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate – Stevens LA et al. NEJM 2006;354:2473-83. • Automated Reporting of Glomerular Filtration Rate - Just what the doctor ordered. – Levey AS et al. Clin Chem 2006;52:2188-93 • Australasian Creatinine Consensus Working Group. Chronic Kidney Disease and Automatic Reporting of eGFR. A position statement. – Med J Aust. 2005;183:138-141 RCPA / AACB 2007 - GFR