Notes - Higher Music
advertisement

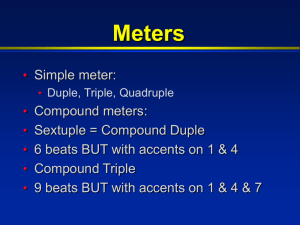
Notes Notes National 3 Step / Stepwise Step / Stepwise: Moving up or down between notes which are next to each other. Below is the stepwise movement of a major scale of C. Leap / Leaping Leap / Leaping: Moving between notes which are not next to each other. Crotchet and Minim A crotchet has a value of 1 beat: A minim has a value of 2 beats: Dotted minim A dotted minim as a value of 3 beats: Lines and Spaces Music is most commonly notated using the Staff The staff consists of five horizontal lines on which musical notes lie. The lines and the spaces between the lines represent different pitches. Lower pitches are lower on the staff and higher pitches are higher on the staff. Lines and Spaces Lines Spaces Note Names When moving consecutively from line to space the notes pattern is in alphabetical order. Chords Chords are notes played simultaneously. The most commonly used chords are constructed from stacked thirds. Chord Symbols There are various Chord Symbols that can be combined to indicate many different types of chords. Basic Chord Symbols: Letter Name (e.g., C) = Major chord m = minor chord + = Augmented chord o = diminished chord Seventh Chords: 7 = minor seventh M7 = Major seventh Discord A discord is a chord in which certain notes clash. Up to the end of the 19th century, discord was used sparingly in music in order to add tension, and it was almost immediately followed by a concord. In the 20th century composers made greater use of discords, merging them into further discords rather than resolving them into concords. Sequence A melodic phrase which is immediately repeated at a higher or lower pitch. Legato and Staccato Legato The notes are played or sung smoothly. Staccato The notes are short and detached. A note which is to be played staccato have a dot placed directly below or above the note. Octave The distance between a note and the nearest note with the same name, e.g. C to C'. Notes National 4 Quaver and Semiquaver A quaver has a value of ½ beat. A semiquaver has a value of 1/4 beat. Grouped semiquavers Below is a group of semiquavers which are joined together. Dotted rhythm A dotted rhythm is a long note followed by a shorter one or a short note followed by a longer one as in a Scots snap often used in a Strathspey Scotch snap A scotch snap is a very short accented note before a longer note. A feature of Strathspeys. Repeat sign Repeat Signs tell us to repeat a certain section of music during performance. A Repeat Sign looks like a double bar with two dots by it. Ornament An ornament decorates a melody by adding extra notes. Ornaments are often short and add melodic and rhythmic interest. The first example shows first how a mordent is written and then how it is played: the main note is played, followed by the note above, then the main note again. Ornament The second example shows a lower mordent again, illustrating first how a lower mordent is written in notation and then how it is played: the main note is played, followed by the note below, then the main note again. Ornaments Scale A pattern of notes moving by step in an ascending or descending order. or Scales are collections of notes arranged in patterns of half-steps, whole-steps, or other intervals. Composers and improvisers use scales as pitch resources in their music. They choose specific scales and choose notes from those scales to form melodies and harmonies in their music. Major /major scale An example of a scale is a Major Scale. A major scale has the following arrangement of half-steps (H) and whole-steps (W): Piece in major key W-W-H-W-W-W-H If we start this pattern on the note D we get a D Major scale: D, E, F-sharp, G, A, B, C-sharp, D. Minor / minor scale Music in a minor key, often described as having a sadder feel than major. Song in a minor key The Harmonic Minor scale has the following pattern of halfsteps, whole-steps and one augmented second (A2): W-H-W-W-H-A2-H Here is a Harmonic Minor scale starting on F: Pentatonic Any five-note scale. In practice, the most common one is that on which much folk music is based, particularly Scottish and Celtic. This song is based on the pentatonic scale: The Skye Boat Song Notes National 5 Dotted crotchet / Dotted quaver Dotted crotchet A note that last for 1½ beats Dotted quaver A note that last for ¾ beats Accidental A symbol that modifies the pitch of a note, turning it into a sharp, a flat, or a natural; also refers to the modified notes themselves. A sharp, double-sharp, flat, and natural (respectively) on the staff. Tone An interval of two semitones making a major 2nd, eg G to A on a keyboard, two frets on a guitar. Wholetone A scale containing no semitones but built entirely on whole tones. Debussy used the whole-tone scale in some of his pieces which were influenced by Impressionism. See Impressionist Semitone Half a tone, eg G to Ab on a keyboard. From one fret to another on a guitar. See Tone. Below is the chromatic scale in which every interval is a semitone. Chromatic A stepwise series of notes built up entirely of semitones. This is a chromatic scale beginning on C. Habanera: descending chromatic scale Grace notes A type of ornament played as a quick note before the main note of a melody. Sometimes there may be a group of grace notes at the start of a phrase and this is particularly evident in bagpipe playing. Pibroch Trill Trill - Rapid and repeated movement between two adjacent notes. Devil's Trill Sonata Contrary motion Two parts which move in opposite directions, eg as one part ascends the other part descends. Cadence Cadence Aural Workshop: Cadences