Functional Behavior Assessment Powerpoint Presentation

Functional Behavior
Assessments:
Rationale, Tools, and
Expectations
Overview of Presentation
The why and when of conducting a functional behavior assessment
Tools and process
Written summaries of FBA
Connection with Proactive Behavior
Intervention Planning
Minnesota Definition of a
Functional Behavior Assessment
"Functional behavioral assessment" or "FBA" means a process for gathering information to maximize the efficiency of behavioral supports.
(MN Rule 3525.0210 sup. 22)
Why Functional Behavioral
Assessments are Beneficial
Majority of student behavior is purposeful
Behavior (appropriate and inappropriate) relates to the context(s) in which it occurs
Past-to-present events influence behavior
FBAs provide a predictive function
Advantages of utilizing FBA’s
Improves understanding of the causes of behavior
Facilitates hypothesis-driven interventions
Emphasizes skill building rather than punishment
Increases chance of positive student outcomes
When is an FBA Required?
The emotional and behavioral disorders disability criterion currently requires that an FBA be conducted as part of the determination process
(Minnesota Rule 3525.1329).
When is an FBA Required?
An FBA is required before a student’s IEP team makes a determination that conditional procedures should be in a student’s comprehensive behavior intervention plan
(Minnesota Rule 3525.2710
Subp. 4F).
FBA Requirements Related to
Suspensions
Student removed for 1 school day or less (but not suspended)
Student suspended for less than 5 consecutive school days
Student suspended for 5 to 10 consecutive school days
Student removed for 10 cumulative school days in a school year or less
Student removed for 11 cumulative school days in a school year or more
Student placed on in-school suspension
Parent requests a manifestation determination following any removal for disciplinary reasons
Student suspended from the bus
IEP Team
Meeting
Required
No*
No*
Yes
No
Yes
No**
Yes
Depends***
Manifestation
Determination
Required
No*
No*
Yes
No
Yes
No**
Yes
Depends***
Functional Behavioral
Assessment Plan
Required
No*
No*
No*
No
Yes
No**
No*
Depends***
Pattern of Removal Requirement
When a pattern of removal has the effect of a change in placement for a student, a functional behavior assessment needs to be conducted
Other Instances for
Conducting an FBA
When a team is considering a more restrictive placement due to behavioral concerns
When emergency intervention used 2x in a month, team meeting to determine if additional evaluation needed and IEP amendment (MN Rule 3525.2900)
As outlined in the Behavior Intervention
Plan
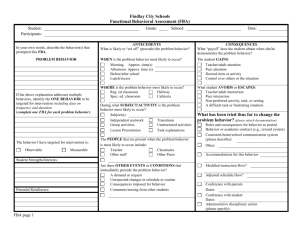
Current Data Collection Tool
Student:
Strengths
Hypothesis:
Ideas:
Age:
Slow Triggers
(setting, events)
Functional Behavioral Assessment
School: Date: Completed by :
Fast Triggers
(antecedents)
Problem
Behaviors
Perceived Function
Barriers to Ideas: Desired Behaviors :
Actual
Consequence
An FBA includes:
Description of problem behaviors:
Challenging behaviors defined in observable and measurable terms (i.e., one can see and count the behavior)
When the behavior is most likely to
occur: Identification of events, times, and situations that predict the occurrence of the behavior
When the behavior is least likely to
occur: Identification of events, times, and situations that predict the nonoccurrence of the behavior
An FBA includes (Cont.):
Identifies the Antecedents, Consequences,
and Reinforcers that maintain the behavior
Hypothesis statement: Possible functions of the behavior
Replacement behaviors: Possible positive alternative behaviors
Assessment tools: Includes a variety of data collection methods and sources that facilitate the development of hypotheses and summary statements regarding behavioral patterns
Data Collection Tools
Interviews
Parent and staff interviews
Conducted individually or through team process
Examples on website
Student interview
Frustration and stress survey
Examples on website
Team Interview Framework
Narrative Option
Visual Overview Option
Student:
Strengths
Age:
Slow Triggers
(setting, events)
When behavior most likely to occur:
Functional Behavioral Assessment
School: Date: Completed by :
Fast Triggers
(antecedents)
Problem
Behaviors
(observable and measureable)
Perceived Function
When Behavior least likely to occur: Replacement Behaviors:
Actual
Consequence
ABC’s of Behavior:
FBA Terminology
Antecedents
A
Behavior
B
Consequences
(Outcome/Function)
C
Reinforcement
Punishment
Setting
Events or
Slow
Triggers
Immediate or
Fast
Triggers
Environmental factors that influence behavior, not immediate
Occur immediately before a behavior
Problem
Behavior
Goal:
Decrease
Appropriate
Behavior
Access
Power/control
Avoid/Escape
Tasks
Goal:
Attention
Consequences
Acquire skill &
Increase
Acceptance
Affiliation
Individuals
Stress/anxiety
Gratification
Activities
Justice/revenge
Symptoms
Protection
Etc.
Etc.
Data Collection Tools (Cont.)
Direct Observations of Student
Purpose:
Opportunity to objectively support (or deny) a
relation between behavior and environmental events provides pre-intervention information useful for determining the significance of the problem
behavior and the effects of environmental, curricular, and replacement behavior manipulations.
Provide basis for hypotheses statements that will guide behavior support plan development.
File Review: Carefully review information for patterns and necessary information
Additional: Surveys and Checklists
FBA Process and Expectations
Team approach important
Lead needed to coordinate assessment and information gathered
Data collection requires communication and collaboration among team members who collects what information can vary
Written product contains required information
Written Expectations for FBA’s
Supplementary FBA’s
Notice of evaluation plan completed
Use supplementary evaluation report form in Campus
Integrated in a comprehensive evaluation
FBA’s Connection with Behavior
Intervention Plans
The data that is gathered through a Functional
Behavior Assessment forms the basis to develop
Behavior Intervention Plans
The objective of any behavioral intervention must be the following:
- pupils acquire appropriate behaviors and skills
- skill acquisition focus rather than merely behavior reduction or elimination
- designed to allow a student to benefit from an appropriate, individualized educational program