Gilbert.Renal_Clearance
advertisement
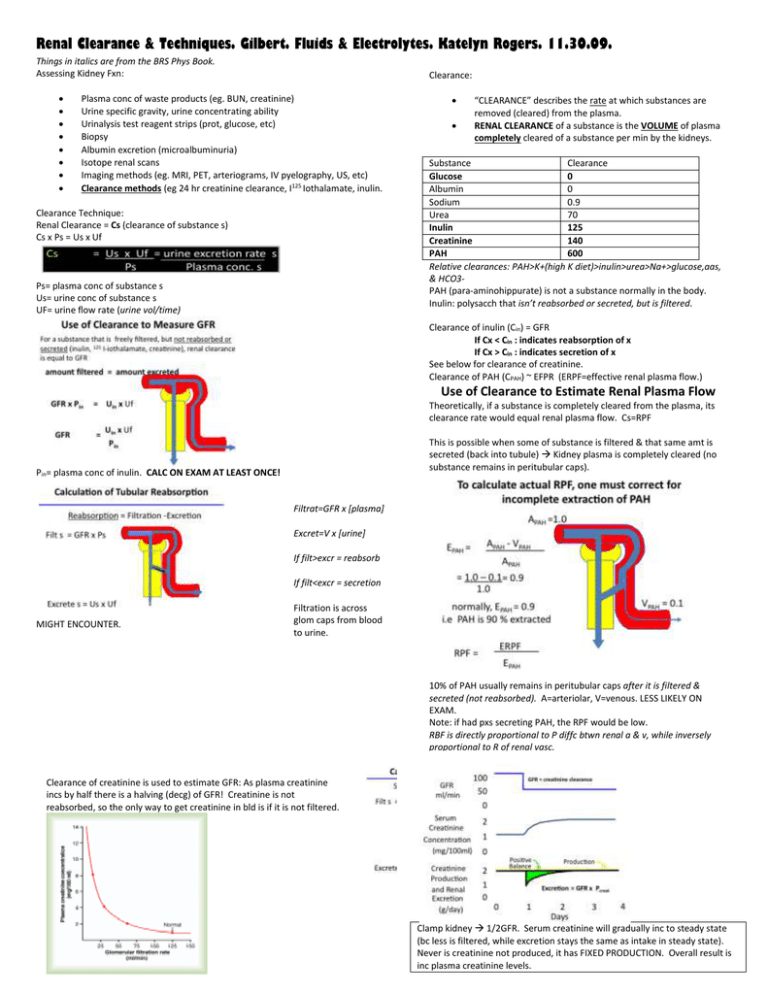
Renal Clearance & Techniques. Gilbert. Fluids & Electrolytes. Katelyn Rogers. 11.30.09. Things in italics are from the BRS Phys Book. Assessing Kidney Fxn: Clearance: Plasma conc of waste products (eg. BUN, creatinine) Urine specific gravity, urine concentrating ability Urinalysis test reagent strips (prot, glucose, etc) Biopsy Albumin excretion (microalbuminuria) Isotope renal scans Imaging methods (eg. MRI, PET, arteriograms, IV pyelography, US, etc) Clearance methods (eg 24 hr creatinine clearance, I125 Iothalamate, inulin. Clearance Technique: Renal Clearance = Cs (clearance of substance s) Cs x Ps = Us x Uf Ps= plasma conc of substance s Us= urine conc of substance s UF= urine flow rate (urine vol/time) “CLEARANCE” describes the rate at which substances are removed (cleared) from the plasma. RENAL CLEARANCE of a substance is the VOLUME of plasma completely cleared of a substance per min by the kidneys. Substance Clearance Glucose 0 Albumin 0 Sodium 0.9 Urea 70 Inulin 125 Creatinine 140 PAH 600 Relative clearances: PAH>K+(high K diet)>inulin>urea>Na+>glucose,aas, & HCO3PAH (para-aminohippurate) is not a substance normally in the body. Inulin: polysacch that isn’t reabsorbed or secreted, but is filtered. Clearance of inulin (Cin) = GFR If Cx < Cin : indicates reabsorption of x If Cx > Cin : indicates secretion of x See below for clearance of creatinine. Clearance of PAH (CPAH) ~ EFPR (ERPF=effective renal plasma flow.) Use of Clearance to Estimate Renal Plasma Flow Theoretically, if a substance is completely cleared from the plasma, its clearance rate would equal renal plasma flow. Cs=RPF This is possible when some of substance is filtered & that same amt is secreted (back into tubule) Kidney plasma is completely cleared (no substance remains in peritubular caps). Pin= plasma conc of inulin. CALC ON EXAM AT LEAST ONCE! Filtrat=GFR x [plasma] Excret=V x [urine] If filt>excr = reabsorb If filt<excr = secretion MIGHT ENCOUNTER. Filtration is across glom caps from blood to urine. 10% of PAH usually remains in peritubular caps after it is filtered & secreted (not reabsorbed). A=arteriolar, V=venous. LESS LIKELY ON EXAM. Note: if had pxs secreting PAH, the RPF would be low. RBF is directly proportional to P diffc btwn renal a & v, while inversely proportional to R of renal vasc. Clearance of creatinine is used to estimate GFR: As plasma creatinine incs by half there is a halving (decg) of GFR! Creatinine is not reabsorbed, so the only way to get creatinine in bld is if it is not filtered. Clamp kidney 1/2GFR. Serum creatinine will gradually inc to steady state (bc less is filtered, while excretion stays the same as intake in steady state). Never is creatinine not produced, it has FIXED PRODUCTION. Overall result is inc plasma creatinine levels. Questions: 1. 2. 3. T/F. Renal clearance of a substance is the rate at which the max volume of plasma is cleared. What does Cs=? Calculate the GFR from the following data: Calc GFR from following data: Pinulin=1.0mg/100ml Uinulin=125mg/100ml Uf=1.0ml/min 4. 5. T/F. Reabsorption = Excretion – Filtration T/F. If Cx < Cin : indicates reabsorption of x Answers: 1. F. RENAL CLEARANCE of a substance is the VOLUME of plasma completely cleared of a substance per min by the kidneys. 2. 3. GFR x Pin=Uin x Uf GFR x plasma conc of inulin = urine excretion rate of inulin GFR= [(125 mg/100ml)(1.0 ml/min)] / (1.0 mg/100ml) = 125 ml/min 4. 5. F. Reabsorption = Filtration – Excretion T. This makes sense, since inulin is not metabolized, so x is reabsorbed into peritubular caps decreasing the amt excreted in the urine (cleared).