cell cycle tutorial
advertisement

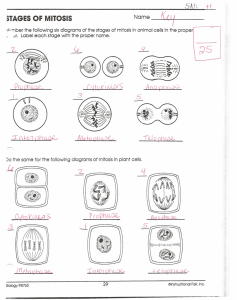
Module Five: Interactive Lesson: Storyboard Katherine M. Wright Grand Canyon University TEC-542 March 12, 2011 The Cell Cycle Picture of animal cell -- Picture of plant cell -- http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm OR How cells make new cells (Sullivan, J. 2010) Two major parts of the cell cycle: Interphase – resting and growing http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/micro/gallery/ mitosis/mitosis.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/ activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html Mitosis – dividing (University of Arizona, 2005) Interphase usually lasts 10-30 hours in mammals Three stages: GAP 1 (G1) – growing Cells increase in size, produce RNA and synthesize proteins, S Phase (S) – synthesizing Duplication of Chromosomes or DNA, forming chromatids connected with centromere http://education.kings.edu/dsmith/ Lesson%206.html http://education.kings.edu/dsmith/Lesson%206.html GAP 2 (G2) – checking Cell continues to grow and synthesize proteins at the end it double checks before starting mitosis (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Cell Cycle Animation http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm (Sullivan, J. 2010) Mitosis – cell division Mitosis (M phase) Shorter -- lasts 2-3 minutes in mammals Growth and protein production stops All cell’s energy is focused on the complex steps of cell division End result is two similar (identical DNA) daughter cells (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Go to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3kpR5RSJ7SA&feature=related http://movies-tigernathanielvladimir.blogspot.com/2011/03/cell-cycle-mitosis.html Prophase – first phase http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy /cells/mitosis/Mitotic_Prophase.png.html The nucleolus fades. http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell _bio/tutorials/cell_cycle/cells3.html Chromatin (replicated DNA and associated proteins) condenses into chromosomes. Each replicated chromosome has two identical chromatids. Microtubules of the cytoskeleton disassemble and centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell (during interphase are responsible for cell shape, motility and attachment to other cells) The microtubules are grow the mitotic spindle from the region of the centrosomes to the centrioles. (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Prometaphase http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy/ce lls/mitosis/Mitotic_Prometaphase.png.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell _bio/tutorials/cell_cycle/cells3.html Nuclear membrane dissolves Proteins attach to the centromeres creating the kinetochores. Microtubules (spindle fibers) attach at the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving. Other Microtubules (spindle fibers) elongate but instead of attaching to chromosomes, overlap each other at the cell center. (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Metaphase http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy /cells/mitosis/Mitotic_Metaphase.png.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell _bio/tutorials/cell_cycle/cells3.html Spindle fibers align the chromosomes along the middle of the cell nucleus. This line is referred to as the metaphase plate. This organization helps to ensure that when the chromosomes are separated, each new nucleus will receive one copy of each chromosome. A check is conducted insuring that the cell is ready to complete cell division (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Anaphase http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy /cells/mitosis/Mitotic_Anaphase.png.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell _bio/tutorials/cell_cycle/cells3.html Paired chromosomes separate at the kinetochores and move to opposite sides of the cell. ****Spindle fibers shorten ****Kinetochores separate ****Chromatids (daughter chromosomes) are pulled apart and begin moving to the cell poles. Motion results from a combination of kinetochore movement along the spindle microtubules and through the physical interaction of polar microtubules. (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Telophase http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell _bio/tutorials/cell_cycle/cells3.html http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy /cells/mitosis/Mitotic_Telophase.png.html Chromatids arrive at opposite poles of cell New membranes form around the daughter nuclei The chromosomes disperse and are no longer visible under the light microscope. The spindle fibers disperse, Cytokinesis (the division of the cell) may also begin during this stage. (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Cytokinesis http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy /cells/mitosis/Mitotic_Cytokinesis.png.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell _bio/tutorials/cell_cycle/cells3.html Spindle fibers not attached to chromosomes begin breaking down (until only that portion of overlap is left. In this region a contractile ring cleaves the cell into two daughter cells. Microtubules then reorganize into a new cytoskeleton for the return to interphase. In plant cells, the rigid wall requires that a cell plate be synthesized between the two daughter cells. (Sullivan, J. 2010; University of Arizona, 2005) Mitosis http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy/cells/mitosis/Mitosis_cells_sequence_large.jpg Mitosis Animation http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm (Sullivan, J. 2010) Let’s practice!! Label the stages game -http://www.purposegames.com/ game/cell-mitosis-quiz/info Control the stages game -http://nobelprize.org/educational/ medicine/2001/ For your viewing pleasure! The Cell Rap-- here are the lyrics, you add the tunes!! http://bizzarroworld.homestead .com/songs.html These gals sing their hearts out -www.youtube.com/watch?v=sa0u WNlqKyc&feature=related%20%20 Follow Bob on his most epic life journey-http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2xeEd n8EXyk&feature=related%20%20 Grading! From the Website: Cellsalive -- http://www.cellsalive.com Cells Alive Mitosis Crossword Puzzle -http://www.cellsalive.com/puzzles/mitosis/index.html Complete Online quiz: http://quizstar.4teachers.org/ CRA Biology classes -- The Cell Cycle Posttest your grade will also be based on the application of this information in the Onion Root Tip Lab, to be completed in the future. http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/ cell_cycle.html (You will need to identify the different stages of the cell cycle.) References Angier, Natalie (2002). Lesson 6: mitosis. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://education.kings.edu/dsmith/Lesson%206.html Davidson, Michael M. (2004) Molecular expressions. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: The University of Florida http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/micro/gallery/mitosis/mitosis.html Nobel Prize.Org. Games (2011) Control of the cell cycle. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/2001/ RierroTheCoolest (2008) Cell mitosis game. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://www.purposegames.com/game/cell-mitosis-quiz/info Srokes, Ms. (2007) The cell cycle featuring: mitosis. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3kpR5RSJ7SA&feature=related References Sullivan, Jim. (2010) Cells alive. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm The University of Arizona (2005). The Biology project. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle. html Valdimir, Nathanial (2011) The cell cycle mitosis. (Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://moviestigernathanielvladimir.blogspot.com/2011/03/cell-cycle-mitosis.html WP Clipart (n.d.). Medical section: mitosis. Retrieved February 26, 2011 from: http://www.wpclipart.com/medical/anatomy/cells/mitosis/