Algebra 2
advertisement

Algebra 2
Fall Semester Exam Review
Test Format
• Final Exam is all calculator
• 35 Questions
• All Multiple Choice
Key Concepts on Test
• Graphing Parent Functions and their
characteristics
• Domain/Range/Functions
• Interval Notation and Inequality Notation
• Transformations
– Order of transformations
– Graphing using transformations
• Graphing Absolute Value Functions
• Solving Absolute Value Equations and
Inequalities
Key Concepts on Test
• Horizontal and Vertical Parabolas
–
–
–
–
Graphing them given an equation
Finding Key Info (Vertex, Focus, Directrix)
Writing Equations given 2 pieces of info
Complete the Square to convert formats
Key Concepts on Test
• Linear/Quadratic Regressions (STAT)
• Data Analysis (Zoom 9)
• Quadratic Equations
–
–
–
–
–
–
Simplify positive and negative radicals
Simplify Complex Numbers
Factoring Methods
Square Roots Method
Complete the Square
Quadratic Formula
Calculator
• Can be used to solve 60% of your test
• Know the following:
–
–
–
–
How to graph
2nd trace (zeros and maximums)
Linear & quadratic regressions
Plug in numbers (watch out for negatives)
Testing Hints
•
•
•
•
If you can graph it in the calculator, then do so
Double graphing to compare
Be careful of negatives when solving equations
Questions with graphs! Look carefully at each
graph so you select the one you really want
• Plug in solutions to calculator to check
In Class Review: Today
•
•
•
•
•
Relations/Functions
Domain/Range
Transformations
Calculator Regression/Data Analysis
Quadratic Word Problems
Relations
Ordered Pairs
(2, 3)
(-3, 1)
(1, -2)
Graphs
Tables
X
2
-3
1
Y
3
1
-2
X
Mapping
Y
2
3
-3
1
1
-2
Example :
• Given the following ordered pairs, find
the domain and range. Is it a function
• {(4,5), (-2,3), (5,6)}
• Domain is {-2, 4, 5}
• Range is {3, 5, 6}
• YES, no duplicated x-values
8
Domain
6
(, )
4
Range
2
[2, )
-5
5
-2
Domain
(, )
Range
[0, )
y af (bx c) d
Rx
Ry
VS or VC
HS or HC
(+) Up
(-) Down
(+) Left
(-) Right
Example 1
f ( x) g ( x 5) 3
Right 5 , Up 3
Example 2
f ( x) g ( x 2) 1
Left 2 , Ry , Down 1
Example 3
f ( x) 2 | x 3 | 7
R 3 , VS 2, Rx , U 7
Data Analysis
Height
(meters)
15
30
45
60
75
90
105
Distance
Km
13.833
19.562
23.959
27.665
30.931
33.883
36.598
STAT Plotter “ON”
Zoom 9
What Parent Function??
Weeks
Experience
4
7
8
1
6
3
5
2
9
6
Speed
(wpm)
33 45 49 20 40 30 38 22 52 44 42
y-axis
45
40
35
30
25
y 4.064 x 16.300
20
15
10
r .986
5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
x-axis
7
Application Problems
y .0035 x 2 x 5
2
• Need to change the
viewing WINDOW
• x-min, x-max
• y-min, y-max
Put in Calculator
Window
Max Height (Vertex Pt)
290.7
Max Distance
(Zero)
573.9
Inverse Concept
• The main concept of an inverse is the x and
y coordinates have switched places
( x, y )
( y, x)
Inverses
• The inverse of any relation is obtained by
switching the coordinates in each ordered
pair of the relation.
• Example:
• { (1, 2), (3, -1), (5, 4)} is a relation
• { (2, 1), (-1, 3), (4, 5) is the inverse.
Graphing an Inverse
• Pick some Critical Points off
Original Graph (x, y)
• SWITCH the x and y values
• Re-plot the newly formed
ordered pairs.
GRAPH the inverse
Inverse Concept
• The main concept of an inverse is the x and
y coordinates have switched places
( x, y )
( y, x)
NOTATION FOR THE INVERSE
FUNCTION
We use the notation
f
1
( x)
for the inverse function of f(x).
f
1
( x)
28
Find Inverse of f(x)= 3x + 2
• y = 3x + 2 (Replace f(x) with “y”)
• x = 3y + 2 (Swap variables)
• 3y = x - 4
1
4
y x
3
3
-1
Inverse is a function so replace y with f (x)
1
4
f ( x) x
3
3
1
Function Composition
Notation
( f g )( x) x
( g f )( x) x
Absolute Value Equations
There are ALWAYS 2 cases:
- Positive case
- Negative case
So for this Ex: |x-25|=17
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Case 1 (+ case)
(x –25) = 17
x=42
Check:
|42-25|=17
|17|=17
17=17
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Case 2 (- Case)
-(x - 25) =17
-x + 25 = 17
-x=-8
x=8
Check:
|8-25| =17
|-17|=17
17=17
BIG DIFFERENCE
Inequalities
If you multiply or divide by a
negative number then the order of
the inequality must be switched.
3x 9
3 x 9
3 3
x 3
Solve: |2x+4| > 12
•
•
•
•
|2x+4| > 12
(2x + 4) > 12
2x > 8
x>4
or
-(2x + 4) > 12
or
-2x - 4 > 12
or -2x > 16
or
x < -8
• Solution set: x > 4 or x < -8
-8
4
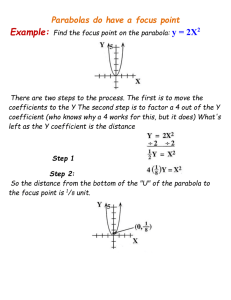
Parabola
• A parabola is a set of points in a plane that are all
the same distance from a fixed line called the
directrix and a fixed point not on the line called the
focus .
y a ( x h) k
2
Vertex Point: (h, k)
a Opens Up
a Opens Down
Vertical Parabola
x a( y k ) h
2
Vertex Point: (h, k)
a Opens Right
a Opens Left
Horizontal Parabola
Key Concept
Distance from Vertex to
1
Focus is
4a
Distance from Vertex to
1
Dirextrix is also
4a
1
p
4a
Vocabulary
• The perpendicular
WIDTH of parabola at
the focus point is the
LR.
1
LR
a
LR
Example 1:
1
2
y ( x 3) 6
12
Opening Direction?
Vertex Point?
Down
(3, 6)
1
Distance Calculation?
4a
Width Calculation? 1
a
1
1
4
12
1
1
12
12
3
Opening Direction? Down
Vertex Point? (3, 6)
Distance Calculation? 3
Width Calculation? 12
Focus Point? (3,3)
Directrix Line? y 9
Axis of Symmetry? x 3
Example 2:
1
2
x ( y 2) 4
8
Opening Direction?
Right
Vertex Point? ( 4, 2)
1
Distance Calculation?
4a
Width Calculation? 1
a
1
1
4
8
1
1
8
8
2
Opening Direction? Right
Vertex Point?( 4, 2)
Distance Calculation? 2
Width Calculation?
8
Focus Point? ( 2, 2)
Directrix Line? x 6
Axis of Symmetry? y 2
Opens Down
y a ( x h) k
2
y a( x 2) 9
2
Distance Calculation
1 3
4a 1
12a 1
1
a
12
1
2
y ( x 2) 9
12
Given :
Vertex ( 2,9)
Focus ( 2, 6)
Opens Left
Given :
x a( y k ) h
2
x a( y 3) 1
2
Distance Calculation
1 4
4a 1
16a 1
1
a
16
1
2
x ( y 3) 1
16
Vertex(1, 3)
Directrix : x 5
Converting to Vertex
•
•
•
•
•
y = x2 - 12x + 27
y = (x2 - 12x + ____) + 27
y = (x2 - 12x + _36_) +27 - 36
y = (x - 6)2 - 9
Vertex Point (6, - 9)
Converting to Vertex
x 3 y 12 y 18
2
x (3 y 12 y) 18
2
x 3( y 4 y) 18
2
4
x 3( y 4 y _____)
18
12
2
x 3( y 2) 6
2