udl-presentation-12-08
advertisement
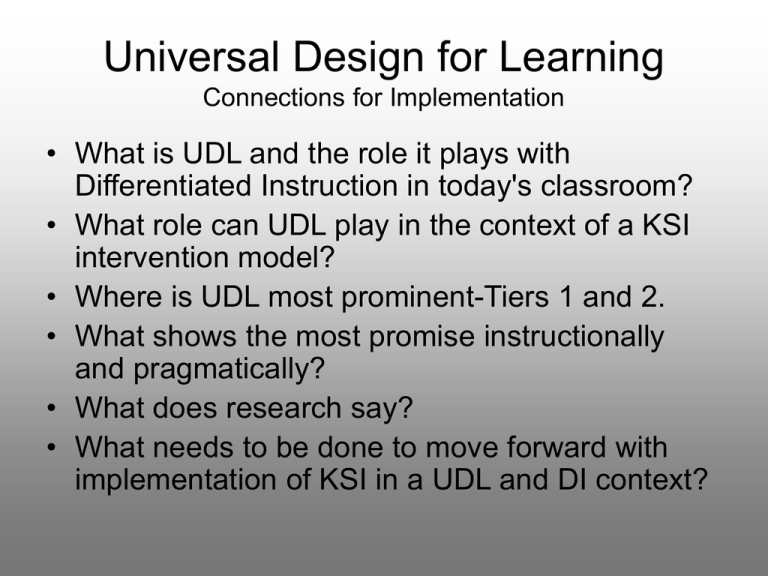
Universal Design for Learning Connections for Implementation • What is UDL and the role it plays with Differentiated Instruction in today's classroom? • What role can UDL play in the context of a KSI intervention model? • Where is UDL most prominent-Tiers 1 and 2. • What shows the most promise instructionally and pragmatically? • What does research say? • What needs to be done to move forward with implementation of KSI in a UDL and DI context? Universal Design for Learning Connections for Implementation What is UDL? • By definition, Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is the design of instructional materials and methods that makes learning goals achievable by individuals with wide differences in their abilities. Universal design is attained by means of flexible curricular materials and activities that provide alternatives for students. As much as possible, these "designed-in" alternatives, which include different assistive technologies and cognitive supports, do not have to be added by teachers. However, effective use of the materials requires that the teacher be familiar with the various teaching strategies necessary to reach students of widely varying abilities. Center for Applied Special Technology A universally-designed curriculum offers the following: • Multiple means of representation to give learners various ways of acquiring information and knowledge • Multiple means of action and expression to provide learners alternatives for demonstrating what they know, and • Multiple means of engagement to tap into learners' interests, challenge them appropriately, and motivate them to learn • www.cast.org The Teacher’s Role in a Differentiated Classroom “Teachers who differentiate instruction focus on their role as coach or mentor, give students as much responsibility for learning as they can handle and teach them to handle a little more.” Carol Ann Tomlinson Universal Design in Architecture Oslo Opera House Implications for curriculum design? Universal Design Principles Seven Principles from The Center for Universal Design at UNC • •One: Equitable Use • •Two: Flexibility in Use • •Three: Simple and Intuitive • •Four: Perceptible Information • •Five: Tolerance for Error • •Six: Low Physical Effort • •Seven: Size and Space for Approach and Use • Automatic Doors http://ncsudesign.org/content Implications for Meaningful 21st Century Instruction Traditional Curriculum Struggles to Meet Student Needs Instructional Challenges Regularly Faced by Students • • • • • • • • • • • • • Reading for content knowledge in textbooks Deficits in phonemic awareness, fluency, or comprehension Limited or no background knowledge Not reading at grade level Poor or limited vocabulary Few life experiences to connect with content Computing simple to complex math equations Visualization of the problem Comprehending the problem Operational knowledge Organizing & Analyzing the data Using correct operation Calculating for results • UDL Equivalent Flexible Display ….The summer evenings were long. It was not dark, yet. Presently Tom checked his whistle. A stranger was before him -- Tom Sawyer ….The summer evenings were long. It was not dark,… Tom Sawyer Example of Scaffolded Digital Curriculum http://www.windows.ucar.edu/ How Culture & Education are Blending Together Universal Design & Technology Play a Role in Education • • • • • • • • • TV & Music Life Experiences Personal Goals Values & Character Personal Lifestyle Jobs/Careers Games & Interests Family & Friends 250$ • • • • • • • • • Learning Style Abilities & Interests Team/Individual Work Technology Preference School Workstyle Engaging Curriculum Real World Experiences Multimedia Personalized Instruction The Instructional Application of UDL for Personalized Learning Content Technology Content Technology. Process Product= Personalized Product •Diagram •Map •illustration •graph •cartoon •video •model •music •commercial •rhythm •speech •Performance •Essay •Online quiz Personalized Learning Process •Use various content entry points •Traditional Teacher Driven •Using choice boards for work •Digital •Classroom Response assignments System •Break assignments into manageable •Digital Rights chunks management •Digital Smartboards & •Using flexible pacing to allow for content software •Portable differences in students’ ability •Digital video/audio •Use different tools to perform the •Scaffoldedsame task Tiered Student Driven •Encourage independent study on •Audio/video •Digital/audio books topics of interest •On-going assessment of student •Ongoing •Online textbooks readiness Assessment •Online assessment •Graduated task- and product-rubrics •Use assessment as a teaching tool to extend versus merely measure instruction. •Provide a balance between teacherassigned and student-selected tasks Learning Instruction In a UDL/Differentiated Classroom Not Differentiated Fully Differentiated Reactive Fixed Closed – Proactive Fluid Open – Ongoing Assessment & Diagnosis – Use of Technology-----------– Independent Study/Work – Adjusting of Questions – Use of the Internet – Flexible Grouping – Tiered Activities – Anchor Activities – Learning Contracts – Curriculum Compacting – Differentiated Centers/Groups – Learning Centers/Learning Orbits – Graduated Tasks, Products, and Rubrics Use of Multiple Texts and Supplementary Materials MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS. Instructional and Management Practices UDL & Teaching Today Curriculum Materials • Digitally enhanced instruction-now – Smartboards & preloaded software – Intervention programs supported with interactive digital software focusing on core content (Read180, Thinking Reader) – Digital video, animation, graphics – Differentiated instruction (Content, Process, product) – Online/Classroom Response System (CRS) for immediate feedback and assessment of class • Digitally enhanced personal learning-now/coming soon – Interactive Digital books/reading devices – Interactive dialogue online c peers/teachers (blogs and wikis) • How to move forward – Planning for future that incorporates instructional approaches such as UDL, technology, and digital content – Teacher & student training – Technology support by dedicated technology coaches (not IT techs) Classroom Response System Multiple Means of Expressing Content knowledge Highly Visual Interactive Instant Feedback Interactive Templates PowerPoint Compatible Automatic Scoring Digital Smartboards Multiple Means of Representing Digital Content • GeometryMeasuring Angles Smartboard Screens • Spelling using Spin & Spell Read180 by Scholastic Thinking Reader by Scholastic • Product Features: • Research-based and validated • The only software program to include the unabridged text of award-winning core literature • Provides instruction on 7 reading comprehension strategies: summarizing, questioning, clarifying, predicting, visualizing, feeling, and reflecting • 5 levels of embedded reading comprehension support for differentiated instruction • Quizzes within the literature test recall, inference, and vocabulary skills Titles: A Wrinkle in Time, Bridge to Terabithia Bud, not Buddy, Dragonwings Esperanza Rising, The Giver, My Brother Sam is Dead, Roll of Thunder-Hear My Cry, Tuck Everlasting Research on Differentiated Instruction • Beecher & Sweeny, 2008. Closing the Achievement Gap With Curriculum Enrichment and Differentiation: One School’s Story. Journal of Advanced Academics, Vol. 19, 3. • • • • • Key Findings Low performing Elem. School Moved from Remedial Model to Enrichment & Differentiated Instruction Apporach Results-Lowered achievement gap b/t rich & poor students and ethnic groups Main Components Examined – – – • Analysis of school strengths & weeknesses of curriculum & instruction New strategic plan, school mission, specific learning objectives, action plans Teacher training, lesson modeling, coaching, planning time. School Improvement Planning Team monitors and reports results. Beecher & Sweeny, 2008. Beecher & Sweeny, 2008. Beecher & Sweeny, 2008. Universal Design for Learning Connections for Implementation UDL Multi-Means Recognition Expression Engagement School& Student Data Analysis DI Content Process Product Tier One School Planning Teacher Engagement & Training Instructional Planning Design/Align Student Interest Profiles KSI Linkages to UDL UDL Implications for KSI/RTI • Tier One – Content, Process, Product, Technology=Personalized Learning – CRS (Clickers)=Better data collection/engagement – Digital Smartboards & Content Software – Digital Video/Audio • Tier Two – Reading/Math Intervention with technology (Read 180, Voyager Math) – Computerized Tutoring Programs • Tier Three – More time intensive interventions