Energy
advertisement

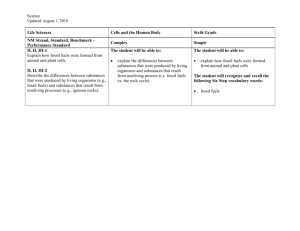
Air, Earth, Fire and Water An Introduction to Environmental Science Energy ~ Fossil Fuels Energy ~ Some Basic Ideas • Energy is the ability to do work • It is measured in J or kJ • Energy can be converted from one form to another • There are many different types of energy: Kinetic, Potential, Nuclear, Chemical, Electrical, Magnetic, Heat, Sound Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 2 Formation of Fossil Fuels • Work is the transfer of energy. • About 300 million years ago huge forests covered many areas. • These forests died and were replaced by others; until over the ages a thick layer of plant matter was built up this was called peat. • Over the years the seas came in and covered the peat with mud and sand. Thousands of years later the seas retreated and new forests grew. This happened many times and the compressed peat turned into coal. Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 3 Formation of coal www.minepermits.ky.gov/.../coal_formation.htm Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 4 Formation of Fossil Fuels • As this vegetation decays, the peat changes to coal, and methane gas is also formed. • Over the ages huge quantities of methane gas have been trapped under impervious rocks. • These methane sources have been found in many places including the North Sea and off the South coast of Ireland. Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 5 Types of Fossil Fuels • • • • Coal Oil Gas Peat Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 6 What is a Fuel • A fuel is a substance which can be used as an energy source. • We can burn fuels to create energy to power our homes, our cars and industry. • The amount of energy a fuel contains can be measured by burning a known mass • This gives us the fuels heat of combustion in kJ/kg. Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 7 Heat of combustion • Heat of combustion of a substance is the heat change which occurs when one mole of the substance is burned in an excess of oxygen. • A reaction in which heat is liberated is known as an exothermic reaction. • A reaction in which heat is taken in is known as an endothermic reaction. • Combustion reactions are exothermic. Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 8 Burning of fossil fuels Carbon: C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2(g) Methane: CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g)+ 2H2O (g) Oil: C6H6(l) + 7.5O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(g) Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 9 Some fuels are better than others! • The different fossil fuels give our different amounts of heat/kg and produce different amounts of CO2 • Thus some fossil fuels are better for the environment: Gas > oil > coal Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 10 Burning natural gas http://www.marymount.k12.ny.us/marynet/stwbwk05/05flashchem/lyreaction/ lyreaction.html Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 11 Heat of Combustion Calculate the heat of combustion of ethanol from the following experimental results, taken using a bomb calorimeter: Mass of ethanol = 20 g Mass of water in calorimeter = 10 kg Initial temperature of water = 18 ˚C Final temperature of water =32 ˚C Specific Heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg˚C Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 12 The calculation Heat gained by water ΔH = (Temperature rise, ۫C) x (Mass of water in calorimeter, kg) x (heat capacity of water, J/kg) = 10 x 4200 x 14 = 588000 J = 588 kJ Thus the combustion of 20g of ethanol liberates 588 kJ 1 mole of C2H5OH = 46g Therefore combustion of 46g liberates 46 x 588 kJ = 1352 kJ/mol 20 Heat of combustion = -1352 kJ (exothermic reaction) Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 13 Different Types of Fuels ~ Solid, Liquids, Gases • Predict what types of fuel you think would give the most energy? • Why? Kerosene Coal Ethanol Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels Oil Gas 14 Exothermic Reaction Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 15 Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/chemistry/chemicalreactions/2energychan gesrev2.shtml Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 16 How much fossil fuels is used worldwide? Source: Worldwatch Institute. World Fossil Fuel Consumption per Source, 1950-1998 (in million of tons of equivalent oil) Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 17 Irish energy use 1990-2005 Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 18 How much energy do we import? Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 19 Where do we use energy? Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 20 Energy in the Home • Ireland imports most of her energy needs at present. • We are still using fossil fuels to power most of our homes. • By completing an energy audit on your homes use can determine how much of these fuels you are using unnecessarily. Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 21 Energy Loss Common Areas of Energy Loss: • Radiation • Conduction • Convection • Condensation • Air Infiltration • Leaving Electrical Items on Standby • Energy Efficient Light Bulbs Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 22 Energy Loss Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 23 Energy Types Types of Energy: • Nuclear • Kinetic • Potential • Heat • Sound • Light • Electrical Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 24 Energy Efficient Home of the Future Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 25 Conclusion • Energy is something that we use in everything we do in every aspect of our lives. • Fossil fuels are being depleted rapidly and cause harmful gas emissions when they are burned to produce energy. • We should all watch our energy consumption in order to save energy for the future. Unit 1 ~ Energy ~ Fossil Fuels 26