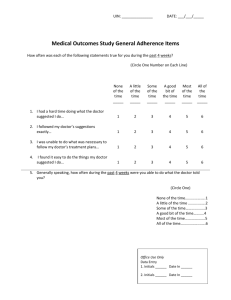
Банк тестових завдань до модульного контролю №1 з англійської
advertisement

Міністерство охорони здоров’я України ДВНЗ «Івано-Франківський національний медичний університет» Кафедра мовознавства База тестових завдань з навчальної дисципліни «Англійська мова за професійним спрямуванням» Модуль 1 Медичний факультет Спеціальність «Лікувальна справа», «Педіатрія» Виберіть український еквівалент англійського терміну: to possess A) позувати; B) установлювати; C) володіти; D) відкладати. antiserum A) антитіло; B) антисептика; C) антиген; D) антисироватка. benign A) дегенеративний; B) злоякісний; C) доброякісний; D) уразливий. nerve root A) корінь нерва; B) нервовий рік; C) нерв зуба; D) корінь волосся. neoplasm A) некроз; B) неонатолог; C) неоатологія; D) новоутворення. dry cough A) голосний кашель; B) рефлекторний кашель; C) сухий кашель; D) мокрий кашель. clot A) клон; B) тінь; C) оболонка; D) згусток. untreated infection A) спонтанна інфекція; B) неполікована інфекція; C) гнійна інфекція; D) хронічна інфекція. particle A) частка; B) паста; C) прохід; D) параліч. deposit A) депресія; B) відкладення; C) зниження; D) депіляція. fluid drainage A) трубчастий дренаж; B) рідинний дренаж; C) венозний дренаж; D) підводний дренаж. exacerbated disease A) смертельне захворювання; B) спадкове захворювання; C) загострене захворювання; D) гіпертонічне захворювання. impairment A) защемлення; B) порушення; C) заглиблення; D) покращення. imbalance A) баланс; B) дисбаланс; C) дисфункція; D) дифузія. gyri A) щілини; B) звивини; C) залози; D) гени. flavour A) квітка; B) рідина; C) допомога; D) смак. eye A) вухо; B) рік; C) вік; D) око. intricate A) інтригуючий; B) інтуїтивний; C) заплутаний; D) засмучений. innate immunity A) набутий імунітет; B) вроджений імунітет; C) пасивний імунітет; D) активний імунітет. inadvertenly A) ненавмисно; B) навмисно; C) непередбачливо; D) застережливо. DNA A) ДНА; B) РНК; C) ДНК; D) РНА. insect venom A) смачне вино; B) маленька вена; C) інтуїтивне відчуття; D) отрута комах. suffocation A) страждання; B) ядуха; C) вдихання; D) обертання. effusion A) виділення; B) дифузія; C) ефір; D) емульгатор. bronchiectasis A) бронхоектаз; B) бронхіт; C) бронхоскоп; D) екстаз від бронхіту. pupil A) студент; B) пупок; C) зіниця; D) зір. sensory nerve A) руховий нерв; B) спинний нерв; C) невралгія; D) чутливий нерв. to outstretch A) простягати; B) відволікати; C) страждати; D) аукати. neoplasm A) новостворена плазма; B) новий пласт; C) новоутворення; D) неон. headache A) біль у серці; B) біль у шиї; C) зубний біль; D) головний біль. aqueous humor A) внутрішньоочна рідина; B) скловидне тіло; C) рідкий гумор; D) спинномозкова рідина. cone A) кома; B) код; C) колбочка; D) канал. hearing loss A) випадання волосся; B) втрата зору; C) втрата слуху; D) втрата ваги. overt disease A) запущене захворювання; B) відкрите захворювання; C) інфекційне захворювання; D) променеве захворювання. macroscopic structure A) макроскопічна структура; B) мікроскопічна структура; C) гістологічна структура; D) анатомічна структура. antiserum A) антитіло; B) антисептика; C) антиген; D) антисироватка. benign A) дегенеративний; B) злоякісний; C) доброякісний; D) уразливий. immune system A) вроджена система; B) імунітет; C) система дихання; D) імунна система. to permeate A) пальпувати; B) проникати; C) позувати; D) оперувати. chickenpox A) грип; B) кір; C) вітряна віспа; D) свинка. myasthenia gravis A) легка міастенія; B) важка міастенія; C) вроджена анемія; D) перніціозна анемія. vulnerability A) вірусологія; B) варикоз; C) уразливість; D) недоступність. edemetous wheal A) набряковий пухир; B) ВІЛ інфекція; C) аерогенний алерген; D) антихолінергічний вплив. strangulation A) удушення; B) знесилення; C) стравохід; D) старання. debris A) діабет; B) мокротиння; C) слиз; D) залишки. respiratory tract A) репродуктивна система; B) система дихання; C) імунна система; D) шлунково-кишковий тракт. to inhibit A) інфікувати; B) ізолювати; C) гальмувати; D) відчувати. brain stem A) головний мозок; B) потилична доля; C) скронева доля; D) стовбур мозку. tingling A) поколювання; B) нечутливість; C) зсихання; D) стиснення. benign A) початковий; B) доброякісний; C) раковий; D) злоякісний. equilibrioception A) чутливість до температурних подразників; B) відчуття оніміння; C) відчуття нюху; D) відчуття рівноваги. antiserum A) антиген; B) антитіло; C) антисироватка; D) алерген. ointment A) проносне; B) екстракт; C) мазь; D) настоянка. protein A) білок; B) пептин; C) ензим; D) фермент. insect venom A) отруйне вино; B) отрута комах; C) комашина вена; D) інкубаційна комаха. epiglottis A) трахея; B) надгортанник; C) аденоїд; D) альвеола. cytokine A) цитокін; B) тимус; C) лімфоцит; D) клітина. active immunity A) вроджений імунітет; B) набутий імунітет; C) автономна імунізація; D) активний імунітет. pernicious anemia A) ревматичний поліартрит; B) перніціозна анемія; C) пемфігус; D) склеродерма. saliva A) слиз; B) сеча; C) слина; D) сльози. blurred vision A) поганий слух; B) неясний смак; C) розпливчатий зір; D) ясний зір. respiration A) дихання; B) потовиділення; C) травлення; D) нетравлення. to moisten A) масажувати; B) мурдувати; C) сушити; D) зволожити. cilia A) сіль; B) війки; C) волосинки; D) ворсинки. dizziness A) динаміка; B) запаморочення; C) озноб; D) гарячка. pneumonia A) грип; B) пептична виразка; C) запалення легень; D) вітряна віспа. pharyngitis A) горло; B) голосові зв’язки; C) фарингоскоп; D) фарингіт. to interpret A) тлумачити; B) інфікувати; C) інгібувати; D) оперувати. memory A) пам’ять; B) мембрана; C) амнезія; D) нерв. lung A) серце; B) селезінка; C) нирка; D) легеня. to expel A) приносити; B) розповсюджувати; C) виштовхувати; D) зрівнювати. to obstruct A) закупорювати; B) обурювати; C) охоплювати; D) озлоблювати. to debilitate A) сходити з розуму; B) виснажувати; C) бути психічно хворим; D) страждати психічним розладом. voluntarily A) свідомо; B) добровільно; C) несвідомо; D) войовниче. hearing A) ховання; B) зір; C) смак; D) слух. cranial nerves A) крайні нерви; B) коронарні нерви; C) нервовий крик; D) нерви черепа. nerve root A) корінь нерва; B) нервовий рік; C) нерв зуба; D) корінь волосся. neoplasm A) некроз; B) неонатолог; C) неоатологія; D) новоутворення. macrophage A) мікрофаг; B) макрофаг; C) цитокін; D) лімфоцит. hallmark A) імунітет; B) хвороба; C) ознака; D) хол. pathogenesis A) патогенез; B) патологія; C) папілома; D) прокол. fluid A) фурункул; B) вірус; C) інфекція; D) рідина. to injure A) інфікувати; B) робити ін’єкцію; C) іонізувати; D) пошкоджувати. strangulation A) дивакуватість; B) удушення; C) зусилля; D) непереносимість. nasal cavity A) черевна порожнина; B) грудна порожнина; C) носоглотка; D) носова порожнина. stridor A) струс; B) синюха; C) хрип; D) скрип. heart A) голова; B) нирка; C) кишка; D) серце. influenza A) грип; B) грибок; C) пліснява; D) цвіль. tonsillitis A) ларингіт; B) фарингіт; C) мигдалина; D) тонзиліт. smell A) смак; B) нюх; C) слух; D) зір. electrical message A) електричний заряд; B) електронне повідомлення; C) електромагнітне поле; D) електричне повідомлення. dry cough A) голосний кашель; B) рефлекторний кашель; C) сухий кашель; D) мокрий кашель. clot A) клон; B) тінь; C) оболонка; D) згусток. untreated infection A) спонтанна інфекція; B) неполікована інфекція; C) гнійна інфекція; D) хронічна інфекція. lymphatic vessel A) лікувальне весло; B) кровоносна судина; C) лімфатичний вузол; D) лімфатична судина. to target A) лікувати; B) обстежувати; C) робити мішенню; D) терти. abstinence A) утримання; B) бажання; C) перспектива; D) мононуклеоз. thymus gland A) гіпофіз; B) слинна залоза; C) зобна залоза; D) підшлункова залоза. measles A) віспа; B) поліомієліт; C) кір; D) свинка. vaginal secretions A) виділення з піхви; B) пухирцеві виділення; C) запалення піхви; D) корисні ферменти. needle A) потреба; B) голка; C) піпетка; D) шприц. basophile A) опасиста клітина; B) базофіл; C) нейтрофіл; D) мастоцит. tonsil A) аденоїд; B) надгортанник; C) трахея; D) мигдалина. to swallow A) ковтати; B) сварити; C) смоктати; D) відчувати. hemoptysis A) виділення; B) хемофілія; C) кровохаркання; D) холецистит. irritant A) райдужка; B) іриска; C) подразник; D) ірідопластика. chickenpox A) вітряна віспа; B) курячий грип; C) алергія на курячий бульйон; D) пліснява. laryngitis A) ларингоскоп; B) ларинголог; C) лор; D) ларингіт. taste A) дотик; B) тимус; C) смак; D) нюх. complex network A) комплексна робота; B) комплексне лікування; C) ускладнена хвороба; D) складна мережа. mast cell A) крихітна клітина; B) опасиста клітина; C) лейкоцит; D) еритроцит. itchy eyes A) болючі очі; B) очі, що сверблять; C) болючі вуха; D) шкіра, що свербить. mediastinum A) пристінкова плевра; B) нутрощева плевра; C) середостіння; D) діафрагма. air sacs A) повітроносні мішечки; B) мішечок у вусі; C) невизначена стать; D) повітроносні шляхи. to equalize A) ізолювати; B) викорінювати; C) економити; D) зрівнювати. asthma A) астма; B) алкоголь; C) аускультація; D) акне. to ingest A) інфікувати; B) поїдати; C) інгібувати; D) імунізувати. polio A) вітряна віспа; B) поліомієліт; C) кір; D) свинка. prick A) прищ; B) сперма; C) прокол; D) опух. donated blood A) докторська пожертва; B) дезинфікована кров; C) вдумливе рішення; D) донорська кров. airborne allergen A) аерогенний алерген; B) аерогенний антигістамін; C) алергія на повітря; D) протиалергічні ліки. flap A) надгортанний хрящ; B) бронх; C) клапоть шкіри; D) плевра. lungs A) очі; B) вуха; C) нирки; D) легені. finger clubbing A) “смішні пальчики”; B) “барабанні палички”; C) “барабанна перетинка”; D) “кручені пальчики”. sharp pain A) гострий біль; B) легкий дотик; C) хронічне захворювання; D) жорстка шкіра. fungus A) грип; B) грибок; C) віспа; D) інфлюенца. consciously A) свідомо; B) добровільно; C) несвідомо; D) нервово. sight A) смак; B) запах; C) зір; D) нюх. CNS A) СНІД; B) сон; C) ВІЛ; D) ЦНС. bedridden A) виснажений; B) прикутий хворобою до ліжка; C) прооперований на робочому столі; D) такий, що перебуває на лікарняному. willow A) калина; B) верба; C) бузок; D) овес. autonomic nervous system A) периферійна нервова система; B) автономна невралгія; C) автономна респіраторна система; D) вегетативна нервова система. intestinal contractions A) інтенсивна координація; B) скорочення кишечника; C) кишкові коліки; D) інтенсивне випорожнення. particle A) частка; B) паста; C) прохід; D) параліч. deposit A) депресія; B) відкладення; C) зниження; D) депіляція. fluid drainage A) трубчастий дренаж; B) рідинний дренаж; C) венозний дренаж; D) підводний дренаж. exacerbated disease A) смертельне захворювання; B) спадкове захворювання; C) загострене захворювання; D) гіпертонічне захворювання. impairment A) защемлення; B) порушення; C) заглиблення; D) покращення. lymph node A) лімфатична судина; B) кровоносна судина; C) лімфатичний вузол; D) лімфоцит. pemphigus A) офтальмопатія; B) пухирчатка; C) зоб; D) ревматичний поліартрит. mucous membrane A) молочна залоза; B) слизова оболонка; C) мононуклеоз; D) лімфатична мембрана. flushing A) почервоніння обличчя і шиї; B) посиніння кінцівок; C) блідість шкіри обличчя; D) дзвін у вухах. to sting A) дзвеніти; B) дзвонити; C) жалити; D) жаліти. parietal pleura A) надгортанний хрящ; B) мигдалевидна залоза; C) нутрощева плевра; D) пристінкова плевра. rib A) бронх; B) ребро; C) ріст; D) чоло. phlegm A) харкотиння; B) флегматик; C) шлунковий сік; D) внутрішньоочна рідина. bronchitis A) бронхіт; B) бронхоскоп; C) бронхи; D) бронхоектаз. to paralyze A) паразитувати; B) прививати; C) розбити паралічем; D) спричинити панкреонекроз. bundle A) банка; B) пучок; C) палка; D) рецептор. efferent nerve A) відцентровий нерв; B) симпатичний нерв; C) парасимпатичний нерв; D) нервове ураження. purge A) снодійний засіб; B) заспокійливе; C) проносне; D) настоянка. imbalance A) баланс; B) дисбаланс; C) дисфункція; D) дифузія. valve A) судина; B) хвиля; C) клапан; D) вена. heredity A) характер; B) спадковість; C) хірургія; D) герпес. family history A) історія хвороби; B) лікарський анамнез; C) професійний анамнез; D) сімейний анамнез. eardrops A) барабанна перетинка; B) вушні краплі; C) вушний пінцет; D) вушний біль. digestion A) обмін; B) травлення; C) дихання; D) дифузія. lungs A) нирки; B) кишки; C) легені; D) клітини. tumour A) тремор; B) пухлина; C) трубка; D) горбистість. throat A) язик; B) стравохід; C) горло; D) ясна. antibiotics A) антибіоз; B) антибіограма; C) антитіло; D) антибіотик. eye A) вухо; B) око; C) рік; D) ніс. acute disease A) хронічне захворювання; B) гостре захворювання; C) вроджене захворювання; D) інфекційне захворювання. hearing A) волосся; B) покрив; C) нюх; D) слух. recurrent attack A) гострий приступ; B) повторний приступ; C) приступ лихоманки; D) апоплектичний приступ. taste bugs A) смакові сосочки; B) втрата смаку; C) нюхові сосочки; D) відчуття смаку. axon A) агонія; B) ауксин; C) акція; D) аксон. protein A) білок; B) жир; C) вуглевод; D) еритроцит. mucous membrane A) слизова оболонка; B) прозора оболонка; C) напівпрозора оболонка; D) сітчаста оболонка. wrist A) ріст; B) залишок; C) зап’ястя; D) вага. panniculus adiposus A) зернистий шар; B) сітчастий шар; C) жировий шар; D) роговий шар. bundle A) баланс; B) буфер; C) випуклість; D) пучок. spleen A) кістковий мозок; B) печінка; C) селезінка; D) легеня. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis A) Грейвса хвороба; B) зоб; C) пухирчатка; D) Шегрена синдром. contagious A) заразний; B) перспективний; C) патогенний; D) контрольований. tincture A) мазь; B) пігулка; C) настоянка; D) супозиторій. seasonal plant A) сезонний завод; B) пора року; C) зміна пір року; D) сезонна рослина. visceral pleura A) пристінкова плевра; B) дихальне горло; C) нутрощева плевра; D) гортанна частина глотки. chest A) черево; B) грудна клітка; C) чоло; D) сосок. hoarseness A) кіннота; B) хрипота; C) сліпота; D) хоробрість. sinusitis A) синус; B) сірка; C) синдром; D) синусит. unconscious A) непритомний; B) хворий; C) мертвий; D) універсальний. external stimulus A) внутрішній стимул; B) зовнішній подразник; C) екстравагантний; D) екстракт стимулу. to dilate A) звужуватися; B) зменшуватися; C) скорочуватися; D) розширюватися. cerebrum A) мозочок; B) головний мозок; C) гіпоталамус; D) півкуля. lacrimal A) слізний; B) носослізний; C) молочний; D) лактогенний. olfactory nerve A) очний нерв; B) нюховий нерв; C) секреторний нерв; D) чутливий нерв. duct A) рогівка; B) подвоєння; C) протока; D) порох. organism invasion A) продукування організму; B) виявлення організму; C) проникнення організму; D) знищення організму. eardrum A) барабанна перетинка; B) вушна раковина; C) слуховий прохід; D) мочка вуха. fever A) фурункул; B) інфекція; C) вірус; D) гарячка. wheal A) пухирець; B) ВІЛ; C) пухлина; D) розрив. elbow A) лімфа; B) коліно; C) лікоть; D) щиколотка. adrenal gland A) адреналін; B) надниркова залоза; C) нирка; D) підшлункова залоза. inspiration A) видих; B) дихання; C) вдих; D) удушення. acetylcholine A) ацетатхолін; B) ацетат хлору; C) оцтова кислота; D) ацетилхолін. dyspnea A) дифузія; B) дисбаланс; C) усмішка; D) задишка. rickets A) цинга; B) рахіт; C) авітаміноз; D) ксерофтальмія. fume A) випар; B) фон; C) рідина; D) тон. lower respiratory tract A) тонкий кишечник; B) нижні дихальні шляхи; C) нижня частина тулуба; D) верхні дихальні шляхи. apex A) дно; B) основа; C) верхівка; D) куточок. wheezing A) кропивниця; B) хрипіння; C) кашель; D) чхання. cerebellum A) головний мозок; B) кора головного мозку; C) мозочок; D) півкуля. to diminish tension A) підвищувати тиск; B) вимірювати тиск; C) понижувати тиск; D) стимулювати тиск. to receive stimuli A) притуплювати стимули; B) отримувати стимули; C) контролювати стимули; D) збільшувати стимули. stasis dermatitis A) атопічний дерматит; B) застійний дерматит; C) себорейний дерматит; D) навколоротовий дерматит. nerve fibers A) нервові волокна; B) нервові імпульси; C) нервові тканини; D) нервові клітини. sebaceous gland A) потова залоза; B) сальна залоза; C) щитовидна залоза; D) нитковидна залоза. HIV transmission A) зростання поширення СНІДу; B) лікування ВІЛ-інфікованих хворих; C) передавання ВІЛ інфекції; D) зниження кількості ВІЛ-інфікованих клітин. acquired immunity A) вроджений імунітет; B) пасивний імунітет; C) набутий імунітет; D) активний імунітет. lupus erythematosus A) важка міастенія; B) червоний вовчак; C) тиреоїдит; D) ревматичний поліартрит. lymph nodes A) лімфатичні вузли; B) лімфатичні судини; C) лімфа; D) кровоносні судини. hives A) лупа; B) хрипіння; C) дрож; D) кропивниця. over-the-counter sleep aids A) ліки від кашлю; B) ліки від головного болю, що продаються по рецепту; C) снодійне, що продається без рецепту; D) протиалергічний лікарський засіб. expiration A) дихання; B) видих; C) удушення; D) вдих. thoracic cavity A) черевна порожнина; B) носова порожнина; C) ротова порожнина; D) грудна порожнина. effusion A) виділення; B) засвоєння; C) лікування; D) запобігання. sulfur dioxide A) нашатирний спирт; B) різкий запах; C) двоокис сірки; D) азот діоксид. peppermint A) женьшень; B) бузок; C) болгарський перець; D) м’ята перцева. receptor A) чергова медсестра; B) приймальний покій; C) рецептор; D) рецидивіст. epinephrine A) адреналін; B) ацетилхолін; C) епізіоскопія; D) епіфіз. convoluted A) звивистий; B) конвертований; C) чутливий; D) контрольований. sternum A) мембрана; B) хребет; C) плевра; D) грудина. genetics A) генотип; B) генетик; C) генетика; D) генез. sedative A) сидячий; B) заспокійливий; C) спазмолітичний; D) сильнодіючий. smell A) усмішка; B) смак; C) запах; D) дотик. perforation A) втирання; B) перфоратор; C) перфорація; D) перфузія. dandelion A) часник; B) береза; C) кульбаба; D) материнка. congenital A) геніальний; B) вроджений; C) набутий; D) колючий. tears A) сльози; B) сеча; C) слина; D) грудне молоко. dander A) пилок; B) пил; C) отрута; D) лупа. suffocation A) смоктання; B) дихання; C) травлення; D) ядуха. breathing A) вдих; B) видих; C) дихання; D) бронхіола. tracheitis A) трахея; B) трахеїт; C) трахеотомія; D) капіляр. cough A) кашель; B) біль; C) свербіж; D) себорея. nitrogen A) сильний запах; B) нашатирний спирт; C) сірки діоксид; D) двоокис азоту. ammonia A) нашатирний спирт; B) амнезія; C) амброксол; D) ампутація. to recognize A) лікувати; B) запобігати; C) розпізнавати; D) інфікувати. pupil A) студент; B) пальпація; C) зіниця; D) рогівка. hemisphere A) кровотворна сфера; B) півкуля; C) геморагія; D) куля. pupil A) кришталик; B) повіка; C) зіниця; D) склера. to lubricate A) перетворювати; B) змащувати; C) відображати; D) захищати. optic nerve A) судиннозвужуючий нерв; B) секреторний нерв; C) міжреберний нерв; D) зоровий нерв. sour A) солодкий; B) кислий; C) солений; D) гіркий. fluoride A) флюороз; B) рідина; C) фтористий; D) фторування. eczema A) екзематозний; B) екзамен; C) набряк; D) екзема. perioral dermatitis A) алергічний дерматит; B) атопічний дерматит; C) сонячний дерматит; D) навколоротовий дерматит. antiserum A) антитіло; B) антисептика; C) антиген; D) антисироватка. benign A) дегенеративний; B) злоякісний; C) доброякісний; D) уразливий. nerve root A) корінь нерва; B) нервовий рік; C) нерв зуба; D) корінь волосся. neoplasm A) некроз; B) неонатолог; C) неоатологія; D) новоутворення. dry cough A) голосний кашель; B) рефлекторний кашель; C) сухий кашель; D) мокрий кашель. clot A) клон; B) тінь; C) оболонка; D) згусток. untreated infection A) спонтанна інфекція; B) неполікована інфекція; C) гнійна інфекція; D) хронічна інфекція. particle A) частка; B) паста; C) прохід; D) параліч. deposit A) депресія; B) відкладення; C) зниження; D) депіляція. fluid drainage A) трубчастий дренаж; B) рідинний дренаж; C) венозний дренаж; D) підводний дренаж. chamomile A) календула; B) жасмин; C) ромашка; D) ехінацея. impairment A) защемлення; B) порушення; C) заглиблення; D) покращення. imbalance A) баланс; B) дисбаланс; C) дисфункція; D) дифузія. miscellaneous A) відкритий; B) помилковий; C) змішаний; D) неправильний. to realease A) приєднувати; B) минати; C) спадати; D) вивільняти. contagious A) сусідній; B) безперервний; C) заразний; D) свідомий. to incorporate A) приєднувати; B) виявляти; C) передавати; D) роз’єднувати. stridor A) струс; B) хрип; C) синюха; D) скрип. to combat A) стримувати; B) загрожувати; C) лікувати; D) боротися. lobe A) глотка; B) лоб; C) доля; D) навантаження. antiserum A) антиген; B) антитіло; C) антисироватка; D) алерген. protein A) білок; B) пептин; C) ензим; D) фермент. cranial nerves A) крайні нерви; B) коронарні нерви; C) нервовий крик; D) нерви черепа. insect venom A) отруйне вино; B) отрута комах; C) комашина вена; D) інкубаційна комаха. immune system A) вроджена система; B) імунітет; C) система дихання; D) імунна система. epiglottis A) трахея; B) надгортанник; C) аденоїд; D) альвеола. ointment A) проносне; B) екстракт; C) мазь; D) настоянка. to expel A) приносити; B) розповсюджувати; C) виштовхувати; D) зрівнювати. to obstruct A) закупорювати; B) обурювати; C) охоплювати; D) озлоблювати. voluntarily A) свідомо; B) добровільно; C) несвідомо; D) войовниче. to debilitate A) сходити з розуму; B) виснажувати; C) бути психічно хворим; D) страждати психічним розладом. lung A) серце; B) селезінка; C) нирка; D) легеня. hearing A) ховання; B) зір; C) смак; D) слух. expiration A) видих; B) вдих; C) виштовхування; D) випрямлення. hives A) хрипіння; B) грибок; C) пліснява; D) кропивниця. vasodilator A) судинорозширюючий; B) судинозвужуючий; C) вазоактивний; D) судиноруховий. spinosum startum A) зернистий шар; B) блискуча дерма; C) остистий шар; D) роговий епідерміс. invader A) інший; B) інвалід; C) агресор; D) вакуум. cranial nerves A) нерви черепа; B) нерви обличчя; C) нерви язика; D) спинномозкові нерви. meninges A) мозок; B) менінгіт; C) мозкові оболонки; D) мозочок. to respond A) реагувати; B) зберігати; C) поважати; D) протистояти. cerebellum A) головний мозок; B) мозочок; C) кора головного мозку; D) довгастий мозок. lethality A) проказа; B) в’ялість; C) ураження; D) летальність. mediastinum A) пристінкова плевра; B) нутрощева плевра; C) середостіння; D) діафрагма. intestinal contractions A) інтенсивна координація; B) скорочення кишечника; C) кишкові коліки; D) інтенсивне випорожнення. to target A) лікувати; B) обстежувати; C) робити мішенню; D) терти. mast cell A) крихітна клітина; B) опасиста клітина; C) лейкоцит; D) еритроцит. willow A) калина; B) верба; C) бузок; D) овес. abstinence A) утримання; B) бажання; C) перспектива; D) мононуклеоз. itchy eyes A) болючі очі; B) очі, що сверблять; C) болючі вуха; D) шкіра, що свербить. autonomic nervous system A) периферійна нервова система; B) автономна невралгія; C) автономна респіраторна система; D) вегетативна нервова система. lymphatic vessel A) лікувальне весло; B) кровоносна судина; C) лімфатичний вузол; D) лімфатична судина. to equalize A) ізолювати; B) викорінювати; C) економити; D) зрівнювати. asthma A) астма; B) алкоголь; C) аускультація; D) акне. air sacs A) повітроносні мішечки; B) мішечок у вусі; C) невизначена стать; D) повітроносні шляхи. bedridden A) виснажений; B) прикутий хворобою до ліжка; C) прооперований на робочому столі; D) такий, що перебуває на лікарняному. fatigue A) забудькуватість; B) лихоманка; C) втома; D) втрата свідомості. to relieve A) загострювати; B) ускладнювати; C) полегшувати; D) видаляти. to depress A) натискати; B) стимулювати; C) пригнічувати; D) вживляти. olfactory response A) сповільнена реакція; B) нюхова реакція; C) температурна реакція; D) рухова реакція. fascia A) обличчя; B) фасція; C) функція; D) щілина. efferent nerve A) відцентровий нерв; B) симпатичний нерв; C) парасимпатичний нерв; D) нервове ураження. pemphigus A) офтальмопатія; B) пухирчатка; C) зоб; D) ревматичний поліартрит. bronchitis A) бронхіт; B) бронхоскоп; C) бронхи; D) бронхоектаз. flushing A) почервоніння обличчя і шиї; B) посиніння кінцівок; C) блідість шкіри обличчя; D) дзвін у вухах. phlegm A) харкотиння; B) флегматик; C) шлунковий сік; D) внутрішньоочна рідина. parietal pleura A) надгортанний хрящ; B) мигдалевидна залоза; C) нутрощева плевра; D) пристінкова плевра. rib A) бронх; B) ребро; C) ріст; D) чоло. to paralyze A) паразитувати; B) прививати; C) розбити паралічем; D) спричинити панкреонекроз. to sting A) дзвеніти; B) дзвонити; C) жалити; D) жаліти. mucous membrane A) молочна залоза; B) слизова оболонка; C) мононуклеоз; D) лімфатична мембрана. lymph node A) лімфатична судина; B) кровоносна судина; C) лімфатичний вузол; D) лімфоцит. bundle A) банка; B) пучок; C) палка; D) рецептор. purge A) снодійний засіб; B) заспокійливе; C) проносне; D) настоянка. to nourish A) зволожувати; B) обстежувати; C) живити; D) подразнювати. dense network A) капілярна сітка; B) хроматична сітка; C) щільна сітка; D) широка сітка. skin A) сканер; B) шина; C) скальпель; D) шкіра. neurofibroma A) нейробластома; B) некрофіброз; C) невринома; D) нейрофіброма. hemorrhage A) геморой; B) гемотерапія; C) гемоглобін; D) кровотеча. cranial A) черевний; B) поперековий; C) черепний; D) порожнистий. stroke A) полоса; B) удар; C) стрес; D) сила. bony cage A) реберна клітка; B) грудна клітка; C) контрольна клітка; D) кісткова клітка. mumps A) кір; B) віспа; C) свинка; D) краснуха. contagious A) заразний; B) перспективний; C) патогенний; D) контрольований. hoarseness A) кіннота; B) хрипота; C) сліпота; D) хоробрість. tincture A) мазь; B) пігулка; C) настоянка; D) супозиторій. seasonal plant A) сезонний завод; B) пора року; C) зміна пір року; D) сезонна рослина. cerebrum A) мозочок; B) головний мозок; C) гіпоталамус; D) півкуля. unconscious A) непритомний; B) хворий; C) мертвий; D) універсальний. visceral pleura A) пристінкова плевра; B) дихальне горло; C) нутрощева плевра; D) гортанна частина глотки. spleen A) кістковий мозок; B) печінка; C) селезінка; D) легеня. chest A) черево; B) грудна клітка; C) чоло; D) сосок. sinusitis A) синус; B) сірка; C) синдром; D) синусит. external stimulus A) внутрішній стимул; B) зовнішній подразник; C) екстравагантний; D) екстракт стимулу. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis A) Грейвса хвороба; B) зоб; C) пухирчатка; D) Шегрена синдром. to dilate A) звужуватися; B) зменшуватися; C) скорочуватися; D) розширюватися. cerebral fluid A) клітинна рідина; B) черепна рідина; C) тканинна рідина; D) спинно-мозкова рідина. penetration A) погіршення; B) загострення; C) проникнення; D) сприйняття. acquired immunity A) пасивний імунітет; B) набутий імунітет; C) активний імунітет; D) природній імунітет. fold A) помилка; B) форма; C) сила; D) складка. oily skin A) суха шкіра; B) комбінована шкіра; C) жирна шкіра; D) чутлива шкіра. neurodermatitis A) некродерматоз; B) нейродерматит; C) нейродендрит; D) неврит. to avoid irritation A) уникати вологи; B) уникати подразнення; C) уникати лікування; D) уникати контакту. acetylcholine A) ацетатхолін; B) ацетат хлору; C) оцтова кислота; D) ацетилхолін. fever A) фурункул; B) інфекція; C) вірус; D) гарячка. wheezing A) кропивниця; B) хрипіння; C) кашель; D) чхання. elbow A) лімфа; B) коліно; C) лікоть; D) щиколотка. adrenal gland A) адреналін; B) надниркова залоза; C) нирка; D) підшлункова залоза. inspiration A) видих; B) дихання; C) вдих; D) удушення. dyspnea A) дифузія; B) дисбаланс; C) усмішка; D) задишка. rickets A) цинга; B) рахіт; C) авітаміноз; D) ксерофтальмія. fume A) випар; B) фон; C) рідина; D) тон. lower respiratory tract A) тонкий кишечник; B) нижні дихальні шляхи; C) нижня частина тулуба; D) верхні дихальні шляхи. apex A) дно; B) основа; C) верхівка; D) куточок. cerebellum A) головний мозок; B) кора головного мозку; C) мозочок; D) півкуля. wheal A) пухирець; B) ВІЛ; C) пухлина; D) розрив. lymph nodes A) лімфатичні вузли; B) лімфатичні судини; C) лімфа; D) кровоносні судини. hives A) лупа; B) хрипіння; C) дрож; D) кропивниця. over-the-counter sleep aids A) ліки від кашлю; B) ліки від головного болю, що продаються по рецепту; C) снодійне, що продається без рецепту; D) протиалергічний лікарський засіб. convoluted A) звивистий; B) конвертований; C) чутливий; D) контрольований. acquired immunity A) вроджений імунітет; B) пасивний імунітет; C) набутий імунітет; D) активний імунітет. expiration A) дихання; B) видих; C) удушення; D) вдих. effusion A) виділення; B) засвоєння; C) лікування; D) запобігання. sulfur dioxide A) нашатирний спирт; B) різкий запах; C) двоокис сірки; D) азот діоксид. thoracic cavity A) черевна порожнина; B) носова порожнина; C) ротова порожнина; D) грудна порожнина. peppermint A) женьшень; B) бузок; C) болгарський перець; D) м’ята перцева. receptor A) чергова медсестра; B) приймальний покій; C) рецептор; D) рецидивіст. lupus erythematosus A) важка міастенія; B) червоний вовчак; C) тиреоїдит; D) ревматичний поліартрит. epinephrine A) адреналін; B) ацетилхолін; C) епізіоскопія; D) епіфіз. congenital A) геніальний; B) вроджений; C) набутий; D) колючий. pupil A) студент; B) пальпація; C) зіниця; D) рогівка. tears A) сльози; B) сеча; C) слина; D) грудне молоко. suffocation A) смоктання; B) дихання; C) травлення; D) ядуха. hemisphere A) кровотворна сфера; B) півкуля; C) геморагія; D) куля. dandelion A) часник; B) береза; C) кульбаба; D) материнка. breathing A) вдих; B) видих; C) дихання; D) бронхіола. cough A) кашель; B) біль; C) свербіж; D) себорея. nitrogen A) сильний запах; B) нашатирний спирт; C) сірки діоксид; D) двоокис азоту. ammonia A) нашатирний спирт; B) амнезія; C) амброксол; D) ампутація. dander A) пилок; B) пил; C) отрута; D) лупа. to recognize A) лікувати; B) запобігати; C) розпізнавати; D) інфікувати. neoplasm A) некроз; B) неонатолог; C) неоатологія; D) новоутворення. chamomile A) календула; B) жасмин; C) ромашка; D) ехінацея. antiserum A) антитіло; B) антисептика; C) антиген; D) антисироватка. dry cough A) голосний кашель; B) рефлекторний кашель; C) сухий кашель; D) мокрий кашель. untreated infection A) спонтанна інфекція; B) неполікована інфекція; C) гнійна інфекція; D) хронічна інфекція. particle A) частка; B) паста; C) прохід; D) параліч. clot A) клон; B) тінь; C) оболонка; D) згусток. deposit A) депресія; B) відкладення; C) зниження; D) депіляція. fluid drainage A) трубчастий дренаж; B) рідинний дренаж; C) венозний дренаж; D) підводний дренаж. impairment A) защемлення; B) порушення; C) заглиблення; D) покращення. nerve root A) корінь нерва; B) нервовий рік; C) нерв зуба; D) корінь волосся. imbalance A) баланс; B) дисбаланс; C) дисфункція; D) дифузія. immune system A) вроджена система; B) імунітет; C) система дихання; D) імунна система. antiserum A) антиген; B) антитіло; C) антисироватка; D) алерген. lymphocyte A) лейкоцит; B) біле кров’яне тільце; C) лімфоцит; D) макрофаг. protein A) білок; B) пептин; C) ензим; D) фермент. insect venom A) отруйне вино; B) отрута комах; C) комашина вена; D) інкубаційна комаха. epiglottis A) трахея; B) надгортанник; C) аденоїд; D) альвеола. lung A) серце; B) селезінка; C) нирка; D) легеня. to expel A) приносити; B) розповсюджувати; C) виштовхувати; D) зрівнювати. to obstruct A) закупорювати; B) обурювати; C) охоплювати; D) озлоблювати. to debilitate A) сходити з розуму; B) виснажувати; C) бути психічно хворим; D) страждати психічним розладом. voluntarily A) свідомо; B) добровільно; C) несвідомо; D) войовниче. hearing A) ховання; B) зір; C) смак; D) слух. cranial nerves A) крайні нерви; B) коронарні нерви; C) нервовий крик; D) нерви черепа. lymphatic vessel A) лікувальне весло; B) кровоносна судина; C) лімфатичний вузол; D) лімфатична судина. to target A) лікувати; B) обстежувати; C) робити мішенню; D) терти. abstinence A) утримання; B) бажання; C) перспектива; D) мононуклеоз. mast cell A) крихітна клітина; B) опасиста клітина; C) лейкоцит; D) еритроцит. itchy eyes A) болючі очі; B) очі, що сверблять; C) болючі вуха; D) шкіра, що свербить. mediastinum A) пристінкова плевра; B) нутрощева плевра; C) середостіння; D) діафрагма. air sacs A) повітроносні мішечки; B) мішечок у вусі; C) невизначена стать; D) повітроносні шляхи. to equalize A) ізолювати; B) викорінювати; C) економити; D) зрівнювати. asthma A) астма; B) алкоголь; C) аускультація; D) акне. bedridden A) виснажений; B) прикутий хворобою до ліжка; C) прооперований на робочому столі; D) такий, що перебуває на лікарняному. discrimination A) приниження гідності лікаря; B) вміння розрізняти; C) бажання описувати; D) подразнювати. autonomic nervous system A) периферійна нервова система; B) автономна невралгія; C) автономна респіраторна система; D) вегетативна нервова система. intestinal contractions A) інтенсивна координація; B) скорочення кишечника; C) кишкові коліки; D) інтенсивне випорожнення. lymph node A) лімфатична судина; B) кровоносна судина; C) лімфатичний вузол; D) лімфоцит. pemphigus A) офтальмопатія; B) пухирчатка; C) зоб; D) ревматичний поліартрит. mucous membrane A) молочна залоза; B) слизова оболонка; C) мононуклеоз; D) лімфатична мембрана. flushing A) почервоніння обличчя і шиї; B) посиніння кінцівок; C) блідість шкіри обличчя; D) дзвін у вухах. to sting A) дзвеніти; B) дзвонити; C) жалити; D) жаліти. parietal pleura A) надгортанний хрящ; B) мигдалевидна залоза; C) нутрощева плевра; D) пристінкова плевра. rib A) бронх; B) ребро; C) ріст; D) чоло. phlegm A) харкотиння; B) флегматик; C) шлунковий сік; D) внутрішньоочна рідина. bronchitis A) бронхіт; B) бронхоскоп; C) бронхи; D) бронхоектаз. to paralyze A) паразитувати; B) прививати; C) розбити паралічем; D) спричинити панкреонекроз. bundle A) банка; B) пучок; C) палка; D) рецептор. efferent nerve A) відцентровий нерв; B) симпатичний нерв; C) парасимпатичний нерв; D) нервове ураження. saliva A) сальна залоза; B) залоза; C) слина; D) свиня. spleen A) кістковий мозок; B) печінка; C) селезінка; D) легеня. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis A) Грейвса хвороба; B) зоб; C) пухирчатка; D) Шегрена синдром. contagious A) заразний; B) перспективний; C) патогенний; D) контрольований. tingling A) тиск; B) стукіт; C) дрож; D) втома. seasonal plant A) сезонний завод; B) пора року; C) зміна пір року; D) сезонна рослина. visceral pleura A) пристінкова плевра; B) дихальне горло; C) нутрощева плевра; D) гортанна частина глотки. chest A) черево; B) грудна клітка; C) чоло; D) сосок. hoarseness A) кіннота; B) хрипота; C) сліпота; D) хоробрість. sinusitis A) синус; B) сірка; C) синдром; D) синусит. unconscious A) непритомний; B) хворий; C) мертвий; D) універсальний. external stimulus A) внутрішній стимул; B) зовнішній подразник; C) екстравагантний; D) екстракт стимулу. to dilate A) звужуватися; B) зменшуватися; C) скорочуватися; D) розширюватися. cerebrum A) мозочок; B) головний мозок; C) гіпоталамус; D) півкуля. elbow A) лімфа; B) коліно; C) лікоть; D) щиколотка. Sjogren’s syndrome A) Грейвса хвороба; B) Шегрена синдром; C) Хашімото хвороба; D) важкий синдром. fever A) фурункул; B) інфекція; C) вірус; D) гарячка. wheezing A) кропивниця; B) хрипіння; C) кашель; D) чхання. wheal A) пухирець; B) ВІЛ; C) набряк; D) розрив. inspiration A) видих; B) дихання; C) вдих; D) удушення. apex A) дно; B) основа; C) верхівка; D) куточок. dyspnea A) дифузія; B) дисбаланс; C) усмішка; D) задишка. fume A) випар; B) фон; C) рідина; D) тон. lower respiratory tract A) тонкий кишечник; B) нижні дихальні шляхи; C) нижня частина тулуба; D) верхні дихальні шляхи. acetylcholine A) ацетатхолін; B) ацетат хлору; C) оцтова кислота; D) ацетилхолін. adrenal gland A) адреналін; B) надниркова залоза; C) нирка; D) підшлункова залоза. cerebellum A) головний мозок; B) кора головного мозку; C) мозочок; D) півкуля. acquired immunity A) вроджений імунітет; B) пасивний імунітет; C) набутий імунітет; D) активний імунітет. lupus erythematosus A) важка міастенія; B) червоний вовчак; C) тиреоїдит; D) ревматичний поліартрит. lymph nodes A) лімфатичні вузли; B) лімфатичні судини; C) лімфа; D) кровоносні судини. hives A) лупа; B) хрипіння; C) дрож; D) кропивниця. over-the-counter sleep aids A) ліки від кашлю; B) ліки від головного болю, що продаються по рецепту; C) снодійне, що продається без рецепту; D) проти алергічний лікарський засіб. expiration A) дихання; B) видих; C) удушення; D) вдих. effusion A) виділення; B) засвоєння; C) лікування; D) запобігання. sulfur dioxide A) нашатирний спирт; B) різкий запах; C) двоокис сірки; D) азот діоксид. upper respiratory tract A) нижні дихальні шляхи; B) верхня частина тулуба; C) товстий кишечник; D) верхні дихальні шляхи. receptor A) чергова медсестра; B) приймальний покій; C) рецептор; D) рецидивіст. epinephrine A) адреналін; B) ацетилхолін; C) епізіоскопія; D) епіфіз. convoluted A) звивистий; B) конвертований; C) чутливий; D) контрольований. passive immunity A) набутий імунітет; B) імуноглобулін у пасивному стані; C) пасивний імунітет; D) переможна імунізація. congenital A) геніальний; B) вроджений; C) набутий; D) колючий. tears A) сльози; B) сеча; C) слина; D) грудне молоко. dander A) пилок; B) пил; C) отрута; D) лупа. suffocation A) смоктання; B) дихання; C) травлення; D) ядуха. ammonia A) нашатирний спирт; B) амнезія; C) амброксол; D) ампутація. to recognize A) лікувати; B) запобігати; C) розпізнавати; D) інфікувати. hemisphere A) кровотворна сфера; B) півкуля; C) геморагія; D) куля. Виберіть англійський еквівалент українського терміну: проба A) sample; B) example; C) control; D) instance. успадкована хвороба: A) acquired disorder; B) infectious disease; C) inherited disease; D) insidious disturbance. орган дотику A) taste organ; B) touch organ; C) smell organ; D) visual organ. дотик A) touch; B) taste; C) smell; D) hearing. вроджена опірність A) inherited disease; B) inborn resistance; C) individual resistance; D) inborn disease. зіниця A) pupil; B) uvea; C) iris; D) retina. полегшити біль A) to release ache; B) to relieve pain; C) to relay pain; D) to rejoin pain. тканинне дихання A) internal respiration; B) external respiration; C) external perspiration; D) internal inspiration. СНІД A) SNID; B) AIDS; C) SAID; D) HIV. енцефаліт A) encephalomyelitis; B) encephalomalacia; C) encephalitis; D) encephalalgia. шкідливі речовини A) harmless substances; B) toxic substances; C) reticular substances; D) harmful substances. чутлива шкіра A) senseless skin; B) glossy skin; C) sensible skin; D) true skin. напівкруглий канал A) semilunar channel; B) semicircular canal; C) seminal channel; D) semidiaphanous canal. вугрі A) valve; B) acne; C) vessel; D) wound. частковий імунітет A) natural immunity; B) acquired immunity; C) partial immunity; D) inborn immunity. носослізний канал A) nasofrontal canal; B) nasolabial channel; C) nasomalar channel; D) nasolacrimal canal. кришталик A) pupil; B) eyelid; C) iris; D) lens. краснуха A) chickenpox; B) rubella; C) measles; D) mumps. зір A) listening; B) sight; C) smell; D) touch. очне яблуко A) eyelid; B) iris; C) eyeball; D) pupil. дотик A) touch; B) taste; C) smell; D) hearing. вроджена опірність A) inherited disease; B) inborn resistance; C) individual resistance; D) inborn disease. зіниця A) pupil; B) uvea; C) iris; D) retina. базальні ганглії A) basic ganglium; B) meninges; C) dura mater; D) basal ganglia. чутливий нерв A) motor nerve; B) sense neuritis; C) sensory nerve; D) sensitive neuralgia. колінний рефлекс A) elbow jerk reflex; B) knee jerk reflex; C) reflex of digestion; D) conductive reflex. млявий A) sluggish; B) vulnerable; C) malignant; D) rigid. зір A) sense; B) vision; C) smell; D) audition. відчуття оніміння A) blindness; B) equilibrioception; C) paresthesia; D) deafness. сприйняття: A) perception; B) sensitivity; C) infertility; D) flavour. райдужна оболонка: A) lens; B) membrane; C) iris; D) cornea. стремінце: A) hammer; B) anvil; C) ossicle; D) stirrup. шар: A) share; B) stratum; C) dermis; D) corium. терти: A) to rub; B) to scratch; C) to soothe; D) to aggravate. мигдалина: A) measles; B) hallmark; C) immunity; D) tonsil. явне захворювання: A) acute disorder; B) overt disease; C) chronic illness; D) evident treatment. непритомність: A) delirium; B) consciousness; C) pemphigus; D) tremor. заражений: A) vaccinated; B) inoculated; C) contaminated; D) pathologic. сонливість: A) sleeplessness; B) sedatives; C) wheezing; D) drowsiness. середостіння A) middle piece; B) average wall; C) sternum; D) mediastinum. синюха A) paleness; B) flushing; C) cyanosis; D) jaundice. грип A) chickenpox; B) pneumonia; C) influenza; D) Babinski’ reflex. рахіт A) beriberi; B) ossicle bone; C) thiamine; D) rickets. барабанна перетинка A) auditory meatus; B) auricle; C) eardrum; D) labyrinth. райдужна оболонка A) lens; B) choroid; C) cornea; D) iris. кульбаба A) dandelion; B) calendula; C) garlic; D) linden. коваделко A) hammer; B) incus; C) malleus; D) stirrup. вкритий лускою A) lucidum; B) squamous; C) corneum; D) spinosum. червоні вугрі A) acne; B) red skin; C) dermatitis; D) rosacea. полегшити біль A) to release ache; B) to relieve pain; C) to relay pain; D) to rejoin pain. рогівка: A) retina; B) cornea; C) iris; D) lens. вушна мушля: A) cochlea; B) saccule; C) pinna; D) malleus. дерма: A) corium; B) epidermis; C) heratinocyte; D) stratum. тріщина: A) crack; B) track; C) lack; D) sac. загострювати: A) to soothe; B) to interfere; C) to develop; D) to aggravate. гній: A) liquid; B) lymph; C) pus; D) fluid. набутий імунітет: A) innate immunity; B) passive immunity; C) active immunity; D) learned immunity. Грейвса хвороба: A) grave sickness; B) Hashimoto’s illness; C) Graves’ disease; D) Malaise of Grave. сім’я: A) semen; B) tears; C) mucous; D) saliva. жалити: A) to sting; B) to equalize; C) to expel; D) to debilitate. хрип A) hemoptysis; B) stridor; C) wheezing; D) dyspnea. грибок A) virus; B) fume; C) fungus; D) grippe. свідомо A) voluntarily; B) unconsciously; C) consciously; D) closely. тканинне дихання A) internal respiration; B) external respiration; C) external perspiration; D) internal inspiration. СНІД A) SNID; B) AIDS; C) SAID; D) HIV. енцефаліт A) encephalomyelitis; B) encephalomalacia; C) encephalitis; D) encephalalgia. шкідливі речовини A) harmless substances; B) toxic substances; C) reticular substances; D) harmful substances. чутлива шкіра A) senseless skin; B) glossy skin; C) sensible skin; D) true skin. напівкруглий канал A) semilunar channel; B) semicircular canal; C) seminal channel; D) semidiaphanous canal. лобна доля: A) temporal lobe; B) occipital lobe; C) parietal lobe; D) frontal lobe. тверда оболонка: A) cerebral cortex; B) dura mater; C) meninges; D) pia mater. нечутливість: A) feeling; B) tingling; C) numbness; D) fainting. спинномозкова пункція: A) electroencephalography; B) magnetic resonance imaging; C) spinal tap; D) cerebral angiography. головний біль: A) headache; B) pain in the heart; C) sick head; D) heartache. авгезія: A) gustation; B) paresthesia; C) anosmia; D) ageusia. гіркий: A) bitter; B) sour; C) salty; D) sweet. пристосовувати: A) to focus; B) to adjust; C) to produce; D) to transmit. склера: A) retina; B) iris; C) cornea; D) sclera. вухо: A) air; B) eye; C) ear; D) eyelid. зернистий A) corneum; B) lucidum; C) granulosum; D) spinosum. свербіж A) eczema; B) itching; C) rash; D) crack. дихання A) breathe; B) breather; C) breathing; D) breathlessness. вугрі A) valve; B) acne; C) vessel; D) wound. частковий імунітет A) natural immunity; B) acquired immunity; C) partial immunity; D) inborn immunity. носослізний канал A) nasofrontal canal; B) nasolabial channel; C) nasomalar channel; D) nasolacrimal canal. втрата слуху A) hair loss; B) hearing loss; C) taste loss; D) olfaction loss. скронева кістка A) hyoid bone; B) parietal bone; C) tail bone; D) temporal bone. гострий біль A) acute pain; B) slight pain; C) mild pain; D) chronic pain. таламус A) hypothalamus; B) thamuria; C) thalamocele; D) thalamus. слабкість A) weak; B) fainting; C) strength; D) confusion. дуга A) gait; B) bridge; C) arc; D) tap. м’язова нерухомість A) muscle rigidity; B) nonstriated muscle; C) musculomembranous; D) involuntary muscle. сліпота A) blindness; B) deafness; C) anosmia; D) ageusia. дотик A) gustation; B) audition; C) olfaction; D) touch. око A) year; B) ear; C) eye; D) air. цинга A) zinc; B) scurvy; C) rickets; D) beriberi. слізний нерв A) lacrimal nerve; B) tears neurology; C) nervous tear; D) aqueous nerve. стремінце A) hammer; B) malleus; C) anvil; D) stirrup. шар A) corneum; B) share; C) stratum; D) derma. лусочка A) lobe; B) scale; C) lotion; D) luck. лобна доля: A) temporal lobe; B) occipital lobe; C) parietal lobe; D) frontal lobe. тверда оболонка: A) cerebral cortex; B) dura mater; C) meninges; D) pia mater. нечутливість: A) feeling; B) tingling; C) numbness; D) fainting. спинномозкова пункція: A) electroencephalography; B) magnetic resonance imaging; C) spinal tap; D) cerebral angiography. головний біль: A) headache; B) pain in the heart; C) sick head; D) heartache. авгезія: A) gustation; B) paresthesia; C) anosmia; D) ageusia. гіркий: A) bitter; B) sour; C) salty; D) sweet. пристосовувати: A) to focus; B) to adjust; C) to produce; D) to transmit. склера: A) retina; B) iris; C) cornea; D) sclera. вухо: A) air; B) eye; C) ear; D) eyelid. зернистий A) corneum; B) lucidum; C) granulosum; D) spinosum. свербіж A) eczema; B) itching; C) rash; D) crack. дихання A) breathe; B) breather; C) breathing; D) breathlessness. надниркова залоза A) sweat gland; B) adrenal gland; C) sebaceous gland; D) pituitary gland. новоутворення A) newborn; B) neurofibroma; C) cancer; D) neoplasm. шар жирової тканини A) external layer; B) true skin; C) panniculus adiposus; D) papillary layer. лімфатичні судини A) lymph nodes; B) lymph layer; C) lymph fibers; D) lymph vessels. міжклітинна речовина A) intracellular substance; B) intramuscular material; C) intermuscular material; D) intercellular substance. тім’яна доля: A) occipital lobe; B) temporal lobe; C) frontal lobe; D) parietal lobe. спинномозкова рідина: A) cerebral liquid; B) cerebrospinal fluid; C) spinal water; D) cerebrospinal river. поколювання: A) numbness; B) tingling; C) fainting; D) confusion. уразливий: A) vulnerable; B) urgent; C) sluggish; D) disabling. відчуття: A) thermoception; B) equilirioception; C) perception; D) nociception. нюх: A) sight; B) hearing; C) smell; D) touch. аромат: A) flavour; B) area; C) iris; D) taste. зіниця: A) retina; B) pupil; C) lens; D) cornea. скловидне тіло: A) aqueous humor; B) optic chiasm; C) vitreous humour; D) lacrimal nerve. вушна мушля: A) ear thing; B) cochlea; C) eardrum; D) pinna. дерма A) corium; B) subcutaneous adipose; C) epidermis; D) skin. потові залози A) sebaceous glands; B) sweat glands; C) perspiration; D) sweet glands. успадкований A) inborn; B) unapparent; C) inherited; D) indolent. кровопостачання A) blood stream; B) blood supply; C) blood letting; D) blood flow. фізичне пошкодження A) psychic damage; B) physiological damage; C) physical damage; D) psychiatric damage. повіка A) eyebrow; B) eyelid; C) ear canal; D) inner ear. гіпоталамус A) thalamus; B) hypotympanum; C) hypothyroidism; D) hypothalamus. дезорієнтація у часі і просторі A) wheezing; B) confusion; C) fainting; D) time and space orientation. простягати A) to outstretch; B) to waste away; C) to shrivel; D) to jerk. тимчасове порушення мозкового кровообігу A) stroke; B) temporary blood supply of the brain; C) transient ischemic attack; D) cerebrovascular disorder. слух A) sight; B) deafness; C) hearing; D) touch. дотик A) olfaction; B) gustation; C) audition; D) tactition. зображення A) image; B) vision; C) imagination; D) lens. війчастий м’яз A) ophthalmic muscle; B) muscular lash; C) ciliary muscle; D) macula. потилична доля: A) frontal lobe; B) parietal lobe; C) temporal lobe; D) occipital lobe. спинний мозок: A) back brain; B) spinal cord; C) spinal cerebrum; D) cerebral spine. тупий: A) sharp; B) tube; C) blunt; D) tight. апоплектичний удар: A) stroke; B) Alzheimer’s disease; C) Parkinson’s disease; D) transient ischemic attack. відчуття: A) vessel; B) vertigo; C) sense; D) sight. нюх: A) gustation; B) olfaction; C) tactition; D) audition. кислий: A) bitter; B) sour; C) sweet; D) hot. ВІЛ: A) WHO; B) CNS; C) DNA; D) HIV. дряпати: A) to scratch; B) to rub; C) to itch; D) to crack. шкіра: A) epidermis; B) shin; C) skin; D) shivering. сальні залози A) fat tissue; B) sebaceous glands; C) sweat glands; D) lipocyte. вушна мушля A) ear shell; B) auricle; C) eardtum; D) utricle. запаморочення A) whirling; B) tingling; C) fainting; D) vertigo. часник A) chicory; B) garlic; C) parsley; D) onion. стремінце A) stapes; B) hammer; C) malleus; D) incus. роговий A) lucidum; B) granulosum; C) corneum; D) spinosum. навколоротовий дерматит A) perioral dermatitis; B) atopic dermatitis; C) stasis dermatitis; D) seborrheic dermatitis. середостіння A) hypopharynx; B) mediastinum; C) epiglottis; D) esophages. епідерма A) epidermic; B) epithelium; C) epidermitis; D) epidermis. кровопостачання A) bile supply; B) hemoptysis; C) blood vessel; D) blood supply. скронева доля: A) frontal lobe; B) parietal lobe; C) occipital lobe; D) temporal lobe. руховий нерв: A) active neuralgia; B) motor nerve; C) physical neuritis; D) sensory nerve. сіпатися: A) to sip; B) to kick; C) to jerk; D) to outstretch. тремтіння: A) tract; B) transfusion; C) tremor; D) trauma. зір: A) sight; B) audition; C) sense; D) smell. аносмія: A) paresthesia; B) ageusia; C) blindness; D) anosmia. вивчення запахів і їх дій: A) study concerning gustation; B) osphresiology; C) ophthalmology; D) a science dealing with tactition. слуховий прохід: A) pinna; B) auricle; C) auditory meatus; D) anvil. стремінце: A) malleus; B) anvil; C) incus; D) stapes. власне шкіра: A) derma; B) epidermis; C) skin; D) stratum. себорейний дерматит A) seborrheic skinitis; B) seborrhea derma; C) seborrheic dermatitis; D) neurodermatitis. вміння розрізняти A) description; B) desquamation; C) discrimination; D) disapprobation. носова порожнина A) cranial cavity; B) thoracic cavity; C) carious cavity; D) nasal cavity. злоякісна пухлина A) benign tumour; B) malignant tumour; C) cystic tumour; D) angry tumour. спинний мозок A) spinal cord; B) spinal fluid; C) brain of the back; D) spine. заразна хвороба A) atopic disease; B) systemic disease; C) contagious disease; D) disabling disease. ураження A) depression; B) lethargy; C) lesion; D) fatigue. кришталик А) optic organ; B) sclera; C) choroid; D) lens. орган чуття А) smell organ; B) touch organ; C) sense organ; D) taste organ. око А) year; B) eye; C) ear; D) air. колбочка А) coma; B) cone; C) code; D) cord. кора головного мозку A) adrenal cortex; B) cortex of hair shaft; C) cerebellopontine; D) cerebral cortex. поза A) gait; B) posture; C) polyuria; D) pore. кульбаба A) primrose; B) horsetail; C) dandelion; D) coltsfoot. злоякісний A) malignant; B) zymotic; C) lobular; D) benign. слух A) deafness; B) sight; C) audition; D) tactition. відчуття рівноваги A) nociception; B) equilibrioception; C) paresthesia; D) thermoception. кон’юнктива A) cornea; B) conjunctiva; C) choroid; D) retina. стареча далекозорість A) presbyopia; B) blindness; C) nearsightedness; D) far vision. дрібна кістка A) bone; B) bony thing; C) ossicle; D) great bone. м’яз, що натягує барабанну перетинку A) tensor tympany; B) tympanic membrane; C) semicircular tympany; D) muscle of Corti. блискучий A) corneum; B) lucidum; C) granulosum; D) spinosum. зволожувати A) to rub; B) to soothe; C) to moisturize; D) to dry. гума A) metal; B) soap; C) perfume; D) rubber. втрата зору А) hearing loss; B) smell loss; C) hair loss; D) sight loss. зменшувати напругу А) to diminish tension; B) to increase pressure; C) to raise tension; D) to take pressure. заспокійливі ліки А) essential drugs; B) prescribed drugs; C) sedative drugs; D) subpotent drugs. підтверджувати діагноз А) to confuse the diagnosis; B) to convert the diagnosis; C) to confirm the diagnosis; D) to carry the diagnosis. кісткова клітка А) thoracic cage; B) rib cage; C) bony cage; D) chest cage. реагувати А) to release; B) to respond; C) to refract; D) to record. кропивниця А) mumps; B) measles; C) rubella; D) hives. загрозливий А) treatment; B) threshold; C) threatening; D) threadlike. втрата працездатності А) disability; B) discharge; C) discrimination; D) disinfection. кровотеча A) blood shot; B) hemorrhage; C) blood group; D) hemodyscrasia. черепні нерви A) cervical nerves; B) centrifugal nerves; C) centripetal nerves; D) cranial nerves. складка A) false; B) fold; C) form; D) flux. змащування A) lumbarization; B) lubrication; C) luxation; D) luteinization. перфорація A) perforatorium; B) perfrication; C) perforation; D) perflation. мокротиння A) sputum; B) saliva; C) liquid; D) fluid. пилок амброзії A) ragweed pollen; B) pilocarpine; C) ambroid; D) ammonia. втома A) loss; B) reduction; C) fatigue; D) decrease. уражати A) to influence; B) to affect; C) to arrange; D) to regulate. мазь A) tincture; B) ointment; C) purge; D) pill. молоточок A) ossicle; B) hammer; C) anvil; D) incus. глухота A) blindness; B) deafness; C) ageusia; D) audition. заспокоювати A) to soothe; B) to aggravate; C) to moisturize; D) to interfere. хода A) gait; B) posture; C) atrophy; D) numbness. рогівка A) retina; B) sclera; C) cornea; D) pupil. відчуття болю A) nociception; B) pain olfaction; C) thermoception; D) equilibrioception. пляма A) macula; B) presbyopia; C) cataract; D) glaucoma. припиняти A) to narrow; B) to constrict; C) to dilate; D) to cease. остистий A) granulosum; B) lucidum; C) corneum; D) spinosum. доброякісний A) good-natured; B) benign; C) well-bread; D) malignant. ангіографія мозку A) electroencephalography; B) cerebral encephalogram; C) cerebral angiography; D) brain angiograph. мило A) soap; B) soup; C) rubber; D) metal. слух A) ear; B) vision; C) sound waves; D) hearing. органи чуття A) sense organs; B) external organs; C) sight organs; D) abdominal organs. дотиковий A) touch; B) perceptive; C) tactile; D) tasteful. проникність A) participation; B) permeability; C) pathogenesis; D) permission. сальна залоза A) sublingual gland; B) sebaceous gland; C) thyroid gland; D) thymus gland. спинномозкова рідина A) cerebral liquid; B) spinal water; C) cerebrospinal river; D) cerebrospinal fluid. кір A) mumps; B) measles; C) rubella; D) chickenpox. природній імунітет A) acquired immunity; B) passive immunity; C) natural immunity; D) active immunity. мозкові оболонки A) meningitis; B) pia mater; C) dura mater; D) meninges. атрофія A) attorney; B) numbness; C) paralysis; D) atrophy. підошва стопи A) sole of the foot; B) heel of the foot; C) feet; D) joint of the leg. новоутворення A) new thing; B) neoplasm; C) novel disease; D) neurofibroma. смак A) sense; B) smell; C) taste; D) touch. чутливість до температурних подразників A) thermometer; B) cold perception; C) thermoception; D) nociception. судинна оболонка ока A) choroid; B) cornea; C) sclera; D) retina. пігулка A) purge; B) pill; C) extract; D) caplet. молоточок A) anvil; B) incus; C) ossicle; D) malleus. мішечок A) saccule; B) cochlea; C) eardrum; D) pinna. лущитися A) to desquamate; B) to lose; C) to regain; D) to discharge. тріщина A) track; B) crack; C) patch; D) scale. авітаміноз A) ointment; B) beriberi; C) rickets; D) scurvy. проникнення A) permission; B) penetration; C) pathogenesis; D) participation. уражати A) to detect; B) to improve; C) to define; D) to impair. бронхіола A) bronchi; B) bronchus; C) bronchiole; D) bronchitis. вдих A) inspiration; B) expiration ; C) breath; D) air. прихований початок A) inside beginning; B) inscrutable onset; C) insidious onset; D) inquisitive beginning. спинно-мозкова рідина A) vital liquid; B) spinal fluid; C) cranial liquid; D) cellular fluid. волокно A) tissue; B) cell; C) bone; D) fiber. рецептор A) reactor; B) stimulus; C) receptor; D) structure. складки A) folds; B) fissures; C) gyri; D) glands. свинка A) rubella; B) mumps; C) tremor; D) measles. м’яка оболонка A) dura mater; B) arachnoid; C) meninges; D) pia mater. зсихатися A) to shrivel; B) to mature; C) to outstretch; D) to moisten. колінна чашечка A) elbow cup; B) knee glass; C) kneecap; D) ankle check. проносне A) caplet; B) purge; C) analgesics; D) scutvy. смак A) smell; B) gustation; C) ageusia; D) olfaction. здібність A) faculty; B) sense; C) perception; D) inability. сітківка A) pupil; B) lens; C) iris; D) retina. зорове перехрестя A) optic nerve; B) ophthalmic crossword; C) optic chiasm; D) ophthalmic muscle. коваделко A) malleus; B) anvil; C) hammer; D) stirrup. завитка A) cochlea; B) stapes; C) utricle; D) saccule. терти A) to rub; B) to scratch; C) to turn; D) to aggravate. вугрі A) cracks; B) scales; C) acne; D) eczema. нечутливість A) fainting; B) tingling; C) numbness; D) confusion. надниркова залоза A) renal membrane; B) kidney structure; C) adrenal gland; D) kidney cortex. потова залоза A) sebaceous gland; B) sweat gland; C) thymus gland; D) thyroid gland. вторгнення A) inborn; B) immunity; C) invention; D) invasion. вдих A) inspection; B) inspiration; C) insistence; D) intention. недоїдання A) malnutrition; B) malfunction; C) maltreatment; D) malformation. нагляд A) suspicion; B) success; C) surveillance; D) suggestion. ускладнення A) coordination; B) complaint; C) complication; D) complexion. серцева недостатність A) heart beating; B) heart failure; C) heart burn; D) heart throb. нервові волокна A) nerve tissues; B) nerve cells; C) nerve patients; D) nerve fibers. сітківка A) sclera; B) retina; C) iris; D) cornea. вушна раковина A) utricle; B) saccule; C) auricle; D) acoustic meatus. сальна залоза A) sebaceous gland; B) lacrimal gland; C) perspiratory gland; D) salivary gland. себорейний дерматит A) seborrheic dermatitis; B) solar dermatitis; C) stasis dermatitis; D) schistosome dermatitis. скловидне тіло A) aqueous humor; B) vitreous humor; C) vitelline body; D) carotid body. барабанна перетинка A) tutorial membrane; B) reticular membrane; C) papillary membrane; D) tympanic membrane. видих A) exploration; B) expiration; C) expression; D) expansion. віспа A) rubella; B) measles; C) chickenpox; D) mumps. рогівка A) retina; B) cornea; C) iris; D) lens. дотик A) touch; B) taste; C) smell; D) hearing. вроджена опірність A) inherited disease; B) inborn resistance; C) individual resistance; D) inborn disease. зіниця A) pupil; B) uvea; C) iris; D) retina. полегшити біль A) to release ache; B) to relieve pain; C) to increase pain; D) to rejoin pain. рахіт A) rickets; B) beriberi; C) scurvy; D) folate. СНІД A) SNID; B) AIDS; C) SAID; D) HIV. енцефаліт A) encephalomyelitis; B) encephalomalacia; C) encephalitis; D) encephalalgia. шкідливі речовини A) harmless substances; B) toxic substances; C) reticular substances; D) harmful substances. чутлива шкіра A) senseless skin; B) damaged skin; C) sensible skin; D) true skin. напівкруглий канал A) semilunar channel; B) semicircular canal; C) seminal channel; D) semidiaphanous canal. вугрі A) valve; B) acne; C) vessel; D) wound. частковий імунітет A) natural immunity; B) acquired immunity; C) partial immunity; D) inborn immunity. носослізний канал A) nasofrontal canal; B) nasolabial channel; C) nasomalar channel; D) nasolacrimal canal. потова залоза A) sweat gland; B) sebaceous gland; C) salivary gland; D) lacrimal gland. грудна клітка A) tympanic cavity; B) tension cavity; C) thyroid cavity; D) thoracic cavity. явна хвороба A) closed disease; B) open disease; C) overt disease; D) inherent disease. вивільняти A) to release; B) to remain; C) to recognize; D) to reproduce. ядро A) nuclei; B) nucleus; C) nucleoli; D) nucleolus. судинна оболонка A) vessel body; B) retina; C) choroid; D) ciliary body. орган смаку A) sense organ; B) taste organ; C) smell organ; D) sight organ. нюхова реакція A) perceptive reaction; B) allergic response; C) olfactory response; D) tactile reaction. легені A) airpipes; B) cells; C) lungs; D) kidneys. пухлина A) tremor; B) tumour; C) trouble; D) tumid. колінний рефлекс A) elbow jerk reflex; B) knee jerk reflex; C) reflex of digestion; D) conductive reflex. зір A) sense; B) vision; C) smell; D) audition. відчуття оніміння A) blindness; B) equilibrioception; C) paresthesia; D) deafness. коваделко A) hammer; B) incus; C) malleus; D) stirrup. рахіт A) beriberi; B) ossicle bone; C) thiamine; D) rickets. барабанна перетинка A) auditory meatus; B) auricle; C) eardrum; D) labyrinth. райдужна оболонка A) lens; B) choroid; C) cornea; D) iris. кульбаба A) dandelion; B) calendula; C) garlic; D) linden. базальні ганглії A) basic ganglium; B) meninges; C) dura mater; D) basal ganglia. вкритий лускою A) lucidum; B) squamous; C) corneum; D) spinosum. чутливий нерв A) motor nerve; B) sense neuritis; C) sensory nerve; D) sensitive neuralgia. червоні вугрі A) acne; B) red skin; C) dermatitis; D) rosacea. млявий A) sluggish; B) vulnerable; C) malignant; D) rigid. слабкість A) weak; B) fainting; C) strength; D) confusion. лусочка A) lobe; B) scale; C) lotion; D) luck. дуга A) gait; B) bridge; C) arc; D) tap. цинга A) zinc; B) scurvy; C) rickets; D) beriberi. сліпота A) blindness; B) deafness; C) anosmia; D) ageusia. шар A) corneum; B) share; C) stratum; D) derma. дотик A) gustation; B) audition; C) olfaction; D) touch. м’язова нерухомість A) muscle rigidity; B) nonstriated muscle; C) musculomembranous; D) involuntary muscle. око A) year; B) ear; C) eye; D) air. стремінце A) hammer; B) malleus; C) anvil; D) stirrup. таламус A) hypothalamus; B) thamuria; C) thalamocele; D) thalamus. слізний нерв A) lacrimal nerve; B) tears neurology; C) nervous tear; D) aqueous nerve. надниркова залоза A) sweat gland; B) adrenal gland; C) sebaceous gland; D) pituitary gland. простягати A) to outstretch; B) to waste away; C) to shrivel; D) to jerk. тимчасове порушення мозкового кровообігу A) stroke; B) temporary blood supply of the brain; C) transient ischemic attack; D) cerebrovascular disorder. часник A) chicory; B) garlic; C) parsley; D) onion. слух A) sight; B) deafness; C) hearing; D) touch. гіпоталамус A) thalamus; B) hypotympanum; C) hypothyroidism; D) hypothalamus. дотик A) olfaction; B) gustation; C) audition; D) tactition. дезорієнтація у часі і просторі A) wheezing; B) confusion; C) fainting; D) time and space orientation. війчастий м’яз A) ophthalmic muscle; B) muscular lash; C) ciliary muscle; D) macula. роговий A) lucidum; B) granulosum; C) corneum; D) spinosum. навколоротовий дерматит A) perioral dermatitis; B) atopic dermatitis; C) stasis dermatitis; D) seborrheic dermatitis. зображення A) image; B) vision; C) imagination; D) lens. стремінце A) stapes; B) hammer; C) malleus; D) incus. середостіння A) hypopharynx; B) mediastinum; C) epiglottis; D) esophages. поза A) gait; B) posture; C) polyuria; D) pore. кульбаба A) primrose; B) horsetail; C) dandelion; D) coltsfoot. гума A) metal; B) soap; C) perfume; слух A) deafness; B) sight; C) audition; D) tactition. блискучий A) corneum; B) lucidum; C) granulosum; D) spinosum. кон’юнктива A) cornea; B) conjunctiva; C) choroid; D) retina. злоякісний A) malignant; B) zymotic; C) lobular; D) benign. стареча далекозорість A) presbyopia; B) blindness; C) nearsightedness; D) far vision. дрібна кістка A) bone; B) bony thing; C) ossicle; D) great bone. м’яз, що натягує барабанну перетинку A) tensor tympany; B) tympanic membrane; C) semicircular tympany; D) muscle of Corti. кора головного мозку A) adrenal cortex; B) cortex of hair shaft; C) cerebellopontine; D) cerebral cortex. відчуття рівноваги A) nociception; B) equilibrioception; C) paresthesia; D) thermoception. зволожувати A) to rub; B) to soothe; C) to moisturize; D) to dry. D) rubber. хода A) gait; B) posture; C) atrophy; D) numbness. мазь A) tincture; B) ointment; C) purge; D) pill. доброякісний A) good-natured; B) benign; C) well-bread; D) malignant. глухота A) blindness; B) deafness; C) ageusia; D) audition. заспокоювати A) to soothe; B) to aggravate; C) to moisturize; D) to interfere. відчуття болю A) nociception; B) pain olfaction; C) thermoception; D) equilibrioception. пляма A) macula; B) presbyopia; C) cataract; D) glaucoma. молоточок A) ossicle; B) hammer; C) anvil; D) incus. припиняти A) to narrow; B) to constrict; C) to dilate; D) to cease. остистий A) granulosum; B) lucidum; C) corneum; D) spinosum. ангіографія мозку A) electroencephalography; B) cerebral encephalogram; C) cerebral angiography; D) brain angiograph. рогівка A) retina; B) sclera; C) cornea; D) pupil. мило A) soap; B) soup; C) rubber; D) metal. атрофія A) attorney; B) numbness; C) paralysis; D) atrophy. судинна оболонка ока A) choroid; B) cornea; C) sclera; D) retina. новоутворення A) new thing; B) neoplasm; C) novel disease; D) neurofibroma. тріщина A) track; B) crack; C) patch; D) scale. смак A) sense; B) smell; C) taste; D) touch. авітаміноз A) ointment; B) beriberi; C) rickets; D) scurvy. мозкові оболонки A) meningitis; B) pia mater; C) dura mater; D) meninges. чутливість до температурних подразників A) thermometer; B) cold perception; C) thermoception; D) nociception. пігулка A) purge; B) pill; C) extract; D) caplet. молоточок A) anvil; B) incus; C) ossicle; D) malleus. мішечок A) saccule; B) cochlea; C) eardrum; D) pinna. підошва стопи A) sole of the foot; B) heel of the foot; C) feet; D) joint of the leg. лущитися A) to desquamate; B) to lose; C) to regain; D) to discharge. завитка A) cochlea; B) stapes; C) utricle; D) saccule. колінна чашечка A) elbow cup; B) knee glass; C) kneecap; D) ankle check. проносне A) caplet; B) purge; C) analgesics; D) scutvy. смак A) smell; B) gustation; C) ageusia; D) olfaction. терти A) to rub; B) to scratch; C) to turn; D) to aggravate. здібність A) faculty; B) sense; C) perception; D) inability. сітківка A) pupil; B) lens; C) iris; D) retina. зорове перехрестя A) optic nerve; B) ophthalmic crossword; C) optic chiasm; D) ophthalmic muscle. м’яка оболонка: A) dura mater; B) arachnoid; C) meninges; D) pia mater. коваделко A) malleus; B) anvil; C) hammer; D) stirrup. вугрі A) cracks; B) scales; C) acne; D) eczema. зсихатися A) to shrivel; B) to mature; C) to outstretch; D) to moisten. нечутливість A) fainting; B) tingling; C) numbness; D) confusion. зіниця A) pupil; B) uvea; C) iris; D) retina. рахіт A) rickets; B) beriberi; C) scurvy; D) folate. носослізний канал A) nasofrontal canal; B) nasolabial channel; C) nasomalar channel; D) nasolacrimal canal. СНІД A) SNID; B) AIDS; C) SAID; D) HIV. дотик A) touch; B) taste; C) smell; D) hearing. вроджена опірність A) inherited disease; B) inborn resistance; C) individual resistance; D) inborn disease. енцефаліт A) encephalomyelitis; B) encephalomalacia; C) encephalitis; D) encephalalgia. шкідливі речовини A) harmless substances; B) toxic substances; C) reticular substances; D) harmful substances. полегшити біль A) to release ache; B) to relieve pain; C) to increase pain; D) to rejoin pain. вугрі A) valve; B) acne; C) vessel; D) wound. частковий імунітет A) natural immunity; B) acquired immunity; C) partial immunity; D) inborn immunity. чутлива шкіра A) senseless skin; B) damaged skin; C) sensible skin; D) true skin. напівкруглий канал A) semilunar channel; B) semicircular canal; C) seminal channel; D) semidiaphanous canal. базальні ганглії: A) basic ganglium; B) meninges; C) dura mater; D) basal ganglia. чутливий нерв: A) motor nerve; B) sense neuritis; C) sensory nerve; D) sensitive neuralgia. колінний рефлекс: A) elbow jerk reflex; B) knee jerk reflex; C) reflex of digestion; D) conductive reflex. млявий: A) sluggish; B) vulnerable; C) malignant; D) rigid. зір: A) sense; B) vision; C) smell; D) audition. відчуття оніміння: A) anosmia; B) equilibrioception; C) paresthesia; D) deafness. пластинка решітчастої кістки: A) plate of the bone; B) ossicle bone; C) tiny perforation in the bone; D) lamina cribosa. барабанна перетинка: A) auditory meatus; B) auricle; C) eardrum; D) labyrinth. райдужна оболонка: A) lens; B) choroid; C) cornea; D) iris. внутрішньоочна рідина: A) aqueous humor; B) eye liquid; C) vitreous humor; D) inner-eye river. коваделко A) hammer; B) incus; C) malleus; D) stirrup. вкритий лускою A) lucidum; B) squamous; C) corneum; D) spinosum. червоні вугрі A) acne; B) red skin; C) dermatitis; D) rosacea. таламус: A) hypothalamus; B) thamuria; C) thalamocele; D) thalamus. слабкість: A) weak; B) fainting; C) strength; D) confusion. дуга: A) gait; B) bridge; C) arc; D) tap. м’язова нерухомість: A) muscle rigidity; B) nonstriated muscle; C) musculomembranous; D) involuntary muscle. сліпота: A) blindness; B) deafness; C) anosmia; D) ageusia. дотик: A) gustation; B) audition; C) olfaction; D) touch. око: A) year; B) ear; C) eye; D) air. кришталик: A) iris; B) lens; C) pupil; D) retina. слізний нерв: A) lacrimal nerve; B) tears neurology; C) nervous tear; D) aqueous nerve. стремінце: A) hammer; B) malleus; C) anvil; D) stirrup. шар A) corneum; B) share; C) stratum; D) derma. лусочка A) lobe; B) scale; C) lotion; D) luck. надниркова залоза A) sweak gland; B) adrenal gland; C) sebaceous gland; D) pituitary gland. гіпоталамус: A) thalamus; B) hypotympanum; C) hypothyroidism; D) hypothalamus. дезорієнтація у часі і просторі: A) wheezing; B) confusion; C) fainting; D) time and space orientation. простягати: A) to outstretch; B) to waste away; C) to shrivel; D) to jerk. тимчасове порушення мозкового кровообігу: A) stroke; B) temporary blood supply of the brain; C) transient ischemic attack; D) cerebrovascular disorder. слух: A) sight; B) deafness; C) hearing; D) touch. дотик: A) olfaction; B) gustation; C) audition; D) tactition. зображення: A) image; B) vision; C) imagination; D) lens. війчастий м’яз: A) ophthalmic muscle; B) muscular lash; C) ciliary muscle; D) macula. барабанна перетинка: A) pinna; B) tympanic membrane; C) auricle; D) auditory meatus. стремінце: A) stapes; B) hammer; C) malleus; D) incus. роговий A) lucidum; B) granulosum; C) corneum; D) spinosum. навколоротовий дерматит A) perioral dermatitis; B) atopic dermatitis; C) stasis dermatitis; D) seborrheic dermatitis. середостіння A) hypopharynx; B) mediastinum; C) epiglottis; D) esophages. кора головного мозку: A) adrenal cortex; B) cortex of hair shaft; C) cerebellopontine; D) cerebral cortex. поза: A) gait; B) posture; C) polyuria; D) pore. електроенцефалографія: A) cerebral angiography; B) electronic image of encephalitis; C) electroencephalography; D) neurologic examination. злоякісний: A) malignant; B) zymotic; C) lobular; D) benign. слух: A) deafness; B) sight; C) audition; D) tactition. відчуття рівноваги: A) nociception; B) equilibrioception; C) paresthesia; D) thermoception. кон’юнктива: A) cornea; B) conjunctiva; C) choroid; D) retina. стареча далекозорість: A) presbyopia; B) blindness; C) nearsightedness; D) far vision. дрібна кістка: A) bone; B) bony thing; C) ossicle; D) great bone. м’яз, що натягує барабанну перетинку: A) tensor tympany; B) tympanic membrane; C) semicircular tympany; D) muscle of Corti. блискучий A) corneum; B) lucidum; C) granulosum; D) spinosum. зволожувати A) to rub; B) to soothe; C) to moisturize; D) to dry. гума A) metal; B) soap; C) perfume; D) rubber. припиняти: A) to narrow; B) to constrict; C) to dilate; D) to cease. хода: A) gait; B) posture; C) atrophy; D) numbness. ангіографія мозку: A) electroencephalography; B) cerebral encephalogram; C) cerebral angiography; D) brain angiograph. доброякісний: A) good-natured; B) benign; C) well-bread; D) malignant. глухота: A) blindness; B) deafness; C) ageusia; D) audition. відчуття болю: A) nociception; B) pain olfaction; C) thermoception; D) equilibrioception. рогівка: A) retina; B) sclera; C) cornea; D) pupil. пляма: A) macula; B) presbyopia; C) cataract; D) glaucoma. молоточок: A) ossicle; B) hammer; C) anvil; D) incus. стремінцевий м’яз: A) tensor tympany; B) stapedius muscle; C) Eustachian muscle; D) stapedius canal. остистий A) granulosum; B) lucidum; C) corneum; D) spinosum. заспокоювати A) to soothe; B) to aggravate; C) to moisturize; D) to interfere. мило A) soap; B) soup; C) rubber; D) metal. мозкові оболонки A) meningitis; B) pia mater; C) dura mater; D) meninges. атрофія A) attorney; B) numbness; C) paralysis; D) atrophy. підошва стопи A) sole of the foot; B) heel of the foot; C) feet; D) joint of the leg. новоутворення A) new thing; B) neoplasm; C) novel disease; D) neurofibroma. смак A) sense; B) smell; C) taste; D) touch. чутливість до температурних подразників A) thermometer; B) cold perception; C) thermoception; D) nociception. судинна оболонка ока A) choroid; B) cornea; C) sclera; D) retina. зоровий нерв A) optic chiasm; B) optic nerve; C) ophthalmic neuralgia; D) nervous eye. молоточок A) anvil; B) incus; C) ossicle; D) malleus. мішечок A) saccule; B) cochlea; C) eardrum; D) pinna. лущитися A) to desquamate; B) to lose; C) to regain; D) to discharge. тріщина A) track; B) crack; C) patch; D) scale. шкіра A) shin; B) skin; C) skull; D) school. зсихатися A) to shrivel; B) to mature; C) to outstretch; D) to moisten. колінна чашечка A) elbow cup; B) knee glass; C) kneecap; D) ankle check. хвороба Паркінсона A) Parkinson illness; B) Parkinson’s disease; C) disorder of Parkinson; D) Parkinsons’ sickness. зорове перехрестя A) optic nerve; B) ophthalmic crossword; C) optic chiasm; D) ophthalmic muscle. коваделко A) malleus; B) anvil; C) hammer; D) stirrup. завитка A) cochlea; B) stapes; C) utricle; D) saccule. терти A) to rub; B) to scratch; C) to turn; D) to aggravate. Виберіть правильний варіант пояснення слова: immunity A) the body’s ability to live forever; B) the body’s ability to avoid or not be affected by infection or disease; C) the body’s disability to move; D) the person’s sudden wish or need to do something, without stopping to think about the results. infection A) an illness that is caused by bacteria or a virus and that affects one part of the body; B) the chemical processes in living things that change food, etc. into energy and materials for growth; C) the ability to know something by using your feelings rather than by considering the facts; D) the study and treatment of diseases and injuries. pathogenesis A) the scientific study about general regularities of development, course and termination of diseases; B) medical treatment of injuries or diseases; C) a slight disorder of the brain that causes difficulty in reading and spelling, for example, but does not affect intelligence; D) pain caused by difficulty in digesting food. asthma A) a medical condition of the oral cavity that causes gingivitis; B) a respiratory disorder characterized by difficulty in breathing; C) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth; D) a doctor qualified to treat respiratory disorders. hypertrophy A) underdevelopment of an organ; B) overdevelopment of an organ; C) organ excision; D) organ incision. hyposecretion A) diminished secretion; B) increased secretion; C) normal secretion; D) extremely high secretion. intracranial hemorrhage A) the death of brain tissue; B) an abnormality of the facial nerve that leads to paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face; C) abdominal bleeding; D) bleeding inside the skull. osphresiology A) a scientific study which deals with the reception of sound vibration by the ear; B) a scientific study of visual sensory system; C) a science which deals with the study of odours and the sense of smell; D) a scientific study of tactile perception. glaucoma A) hypertension, blood pressure higher than normal; B) an increased intraocular tension, “hardening” of the eyeball; C) a decreased intraocular tension, “lightening” of the eyeball; D) cloudiness of the lens of the eye. ophthalmometer A) an instrument for measuring the eye; B) an instrument for measuring the ear; C) a doctor qualified to treat ophthalmologic diseases; D) an instrument for measuring the blood pressure. cough A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) a crowing sound when breathing; C) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; D) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that result from partially obstructed airways. pharyngitis A) an inflammation of the bronchi caused by an infection; B) an infection of the lungs that involves alveoli and the tissues around them; C) an inflammation of the throat, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria; D) an inflammation of the voice box caused either by a virus or by bacteria. encephaloscopy A) study of the structure and functions of the brain; B) any disease of the brain; C) abnormal accumulation of fluid in the brain; D) examination of the brain. Parkinson’s disease A) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; B) inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord; D) a stroke or a transient ischemic attack causing disabling neurologic damage. hemiparesis A) faulty nerve conduction characterized by weakness and quick fatigue of muscles; B) slight paralysis affecting either right or left side of the body; C) paralysis affecting all four extremities; D) very severe paralysis of lower extremities. inborn resistance A) natural inherent power of the body not to be affected by infections, harmful microorganisms, diseases, etc.; B) the baby’s unwillingness to be born; C) gynaecological pathology in which a pregnant woman resists giving birth to her child; D) absence of any forces of the body to fight against infections, harmful microorganisms, diseases, etc. lymphocyte A) erythrocyte sedimentation rate; B) red blood cell; C) lymph node; D) white blood cell. pathogenesis A) the scientific study about general regularities of development, course and termination of diseases; B) medical treatment of injuries or diseases; C) a slight disorder of the brain that causes difficulty in reading and spelling, for example, but does not affect intelligence; D) pain caused by difficulty in digesting food. asthma A) a medical condition of the oral cavity that causes gingivitis; B) a respiratory disorder characterized by difficulty in breathing; C) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth; D) a doctor qualified to treat respiratory disorders. hypertrophy A) underdevelopment of an organ; B) overdevelopment of an organ; C) organ excision; D) organ incision. calcification A) of, containing, or concerned with lime or calcium; B) a hormone secreted by the thyroid that inhibits the release of calcium from the skeleton and prevents a build-up of calcium in the blood; C) the most common nutritional deficiency in the world; D) the process of calcifying or becoming calcified. A tissue hardened by deposition of lime salts. neurectomy A) the branch of chemistry that studies chemical processes in the nervous system; B) surgical removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve; C) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; D) a tumour of the myelinated sheaths of nerve fibers. encephalalgia A) inflammation of the brain; B) neoplasm of the spinal cord; C) examination of the brain; D) headache. antibody A) a drug that stops the blood from becoming thick and forming clots; B) a medicine that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; C) a protein that interacts with antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes; D) a remedy used to treat allergies, especially hay fever. vaccine A) a substance containing living organisms, killed bacteria or some toxins which is usually injected to prevent diseases; B) a substance containing alcohol and iodine which is sprayed onto the wound to prevent infection; C) a substance that people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat; D) a substance contained in the bronchi or lungs in any respiratory tract disorder. acquired immunodeficiency A) a diverse condition prevent from birth in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; B) a diverse condition that develops later in life in which the immune system functions inadequately; C) an immunity which may come about through natural processes that may follow exposure to the infectious agent; D) another name for learned immunity which is obtained or gained. autocystoplasty A) surgery on urinary bladder with the use of skin portions from the donor’s body; B) self-examination of the urinary bladder with the use of a mirror; C) plastic surgery on the face with the use of skin portions from the patient’s body; D) plastic surgery on urinary bladder with the use of skin portions from the patient’s body. HIV A) Very Important Person; B) Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome; C) Hot Intra-Venous Injection; D) Human Immunodeficiency Virus. food allergy A) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; B) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction; C) an allergic reaction to a particular meal or food product; D) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such as cold, heat, or minor injury. nasolabial A) pertaining to the mouth and nose; B) pertaining to the forehead and lips; C) pertaining to the nose and lips; D) inflammation of the nose mucous membrane. inspiration A) breathing in the air; B) expelling the air from the lungs; C) a double-folded membrane which envelops each lung; D) inability to breath in or expel the air. pharyngolaryngitis A) inflammation of the throat and trachea; B) inflammation of the throat and voice box; C) diagnostic procedure which visualized trachea and voice box; D) an instrument used for inspection of the throat mucous membrane. dyspnea A) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that result from partially obstructed airways; B) pain in the chest that arises from the pleura, lungs or chest wall; C) a sudden explosive movement of air that sends to clear material from the airways; D) shortness of breath, the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing. bronchoconstriction A) narrowing of the bronchus lumen; B) swelling of the mucosa of the bronchial tube; C) originating from the bronchi; D) surgical alteration of the configuration of a bronchus. peripheral nervous system A) the nervous system that consists of the brain and the spinal cord; B) the nervous system that consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves, which carry impulses between the brain and the head and neck; C) the nervous system that consists of 31 pair of spinal nerves, which carry messages between the spinal cord and the chest, abdomen, and extremities; D) the nervous system that consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. smell A) tactition – the sense of pressure perception; B) olfaction – one of “chemical” senses; C) gustation – one of “chemical” senses; D) audition – the sense of sound perception. gustation A) taste – one of “chemical” senses; B) smell – the other “chemical” sense; C) hearing – the sense of sound perception; D) touch – the sense of pressure perception. iris A) the black area in the middle of the iris; B) the circular, coloured area of the eye; C) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; D) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye. ossicles A) tympanic membrane; B) external auditory meatus; C) three tiny bones; D) small tubes that connect the middle ear with the bed of the nose. dermatotherapy A) treatment of skin diseases; B) any skin eruption due to emotional stimuli; C) an instrument used for inspection of the skin; D) inspection of the skin, usually with the aid of a lens. antibody A) post-mortem examination of the body; B) glycoprotein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign bodies; C) examination of tissue removed from the body to confirm the diagnosis; D) paralysis of one side of the body. HIV A) half intra-venous; B) Very Important Person; C) Human Infectious Viruses; D) Human Immunodeficiency Virus. rhinology A) knowledge concerning throat; B) a doctor qualified to treat ear diseases; C) knowledge concerning the nose; D) pertaining to the nose and mouth. neurodermatitis A) typically develops in areas where something, such as a tight garment, rubs or scratches the skin; B) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens; C) causes a red rash with a yellowish and somewhat “oily” scale; D) often occurs with allergies and frequently runs in families in which other family members have asthma or hay fever. dermatotherapy A) pertaining to the mucous membrane and the skin; B) ossification of the dermis; C) any disease of the skin; D) treatment of skin diseases. myringoplasty A) plastic surgery of the Eustachian tube; B) plastic surgery of the pinna; C) plastic surgery of the eardrum; D) inflammation of the eardrum. labyrinth A) the external part of the ear and the ear canal; B) the part of the ear containing eardrum and a chain of three ossicles; C) also called the inner ear, a complex structure consisting of the cochlea, the semicircular canals, utricle and sacule; D) also called the pinna or auricle, which consisting of cartilage covered by skin is rigid yet flexible. iridoplegia A) bleeding from the iris; B) paralysis of the iris sphincter; C) any pathology of the iris; D) blood in the retina. conjunctiva A) a thin membrane of the eye; B) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; C) a membraneous lining inside the sclera; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. anaesthesiologist A) a doctor trained to administer anaesthisia; B) instrument for measuring tactile sensitivity; C) excessive sensitiveness; D) a doctor trained to treat vision impairment. neurasthenia A) weakness of the voice from fatigue; B) fragility and weakness of blood vessels; C) faulty nerve conduction characterized by weakness and quick fatigue; D) psychoneurosis characterized by abnormal fatigability. cerebrotomy A) inflammation of the brain; B) incision of part of the brain; C) inflammation of the spinal cord; D) headache. pectoralgia A) pertaining to the breast or chest; B) pain in the chest; C) difficult breathing; D) the expectoration of blood or blood stained sputum. cough A) a sudden quick movement of air which tends to clear material or substances from the nose; B) a crowing sound heard during treating mainly during inhalation; C) a reflex in which the lungs and airways are protected; D) a condition in which the level of oxygen in the blood becomes dangerously low or the level of carbon dioxide becomes dangerously high. expiration A) the spelling of the air from the lungs; B) the inhaling of the air into the lungs; C) coughing up of pus from the lungs; D) suffocation or strangulation. AIDS A) Affected Individual Disorder Severely; B) Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection; C) All Injured Doctors’ Sufferings; D) Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. trachea A) throat; B) voice box; C) windpipe; D) cilia. cytokines A) large white blood cells that ingest microbes and antigens; B) proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes; C) 18 proteins which act in a cascade, with one protein activating the next protein; D) “the messengers” secreted by cells of the immune system in response to stimulation which amplify some aspects of the immune system and inhibit others. bronchitis A) inflammation of the bronchi; B) an instrument used for inspecting bronchi; C) inflammation of the lungs; D) a doctor qualified to treat the diseases of the bronchi. hyposecretion A) diminished secretion; B) increased secretion; C) normal secretion; D) extremely high secretion. intracranial hemorrhage A) the death of brain tissue; B) an abnormality of the facial nerve that leads to paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face; C) abdominal bleeding; D) bleeding inside the skull. osphresiology A) a scientific study which deals with the reception of sound vibration by the ear; B) a scientific study of visual sensory system; C) a science which deals with the study of odours and the sense of smell; D) a scientific study of tactile perception. brain A) the enlarged and highly developed mass of nervous issue that forms the upper end of the CNS; B) the portion of the CNS enclosed in the vertebral column; C) a part of the CNS that lies beneath the cerebrum just above the brain stem and coordinates the body movements; D) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions the brain against minor injury. Babinski’s reflex A) an immediate involuntary response of the patient Babin to the eaten poisonous meal; B) a test in which a doctor asks a person to touch his nose with a forefinger, next to touch the doctor’s finger, and then to repeat these actions rapidly; C) a test in which the patient is asked to touch his nose, first with his eyes open, then with his eyes closed; D) a reflex which is tested by firmly stroking the outer border of the sole of the foot with a blunt object and in which the toes curl downward. blindness A) the inability to hear; B) the inability to see; C) the ability to see very distinctly; D) the inability to taste. audiometry A) study of the sense organs; B) method of hearing loss measuring; C) instrument for measuring smell sensitivity; D) impairment of vision and audition. labyrinth A) the external part of the ear; B) the middle ear; C) the inner ear; D) external auditory meatus. corium layer A) also called the dermis is a living tissue composed of blood and lymph vessels and nerve fibers, which lies directly below the external layer of the skin; B) a skin layer composed of connective tissue which specializes in the formation of fat; C) a total name for all the three layers of the skin; D) the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. lymphocytes A) large white blood cells that ingest microbes and antigens; B) relatively small cells of the lymphatic system which fall into B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and natural killer cells; C) proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes; D) 18 proteins which act in a cascade, with one protein activating the next protein. autotrepanetion A) treatment by administration of the patient’s own blood; B) erosion of skull bones in patients suffering from brain tumours; C) self-destruction of tissues or cells; D) vaccine prepared from the parent’s own tissue or secretion. rhinolalia A) change in speech as a result of the pathology in nose structures; B) inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose and voice box; C) allergic rhinitis; D) any disease of the nose. larynx A) throat; B) windpipe; C) trachea; D) voice box. cyanouria A) subjective visual perception of the blue colour; B) bluish colouration of the skin and mucous membranes; C) discharging of urea coloured blue; D) discharging of urea coloured red. amnesia A) a disorder characterized by the tendency to have recurring seizures; B) the total or partial inability to recall recent or remote experiences; C) the death of brain tissue resulting from the lack of blood flow; D) bleeding inside the skull. neuralgia A) formation of the nervous tissue; B) trauma of the nervous system; C) acute pain along a peripheral sensory nerve; D) inflammation of a peripheral nerve. glaucoma A) hypertension, blood pressure higher than normal; B) an increased intraocular tension, “hardening” of the eyeball; C) a decreased intraocular tension, “lightening” of the eyeball; D) cloudiness of the lens of the eye. ophthalmometer A) an instrument for measuring the eye; B) an instrument for measuring the ear; C) a doctor qualified to treat ophthalmologic diseases; D) an instrument for measuring the blood pressure. cough A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) a crowing sound when breathing; C) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; D) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that result from partially obstructed airways. pharyngitis A) an inflammation of the bronchi caused by an infection; B) an infection of the lungs that involves alveoli and the tissues around them; C) an inflammation of the throat, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria; D) an inflammation of the voice box caused either by a virus or by bacteria. encephaloscopy A) study of the structure and functions of the brain; B) any disease of the brain; C) abnormal accumulation of fluid in the brain; D) examination of the brain. Parkinson’s disease A) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; B) inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord; D) a stroke or a transient ischemic attack causing disabling neurologic damage. hemiparesis A) faulty nerve conduction characterized by weakness and quick fatigue of muscles; B) slight paralysis affecting either right or left side of the body; C) paralysis affecting all four extremities; D) very severe paralysis of lower extremities. diagnosis A) the act of discovering or identifying the exact cause of an illness or a problem; B) a change in your body or mind that shows that you are not healthy; C) the state of being physically or mentally ill; D) an illness affecting humans, animals or plants, often caused by infection. vitamins A) macronutrients needed by the body in large quantaties; B) components of many enzymes affecting important chemical reactions throughout the body; C) fragility and weakness of blood vessels; D) essential micronutrient, required by the body in small amounts for maintenance of metabolism. neurology A) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; B) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; C) trauma of the nervous system; D) a physician specializing in the field of neurology and trained to diagnose, treat, and manage patients with neurological disorders. myelitis A) inflammation of the brain; B) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain; C) inflammation of the spinal cord; D) any disease affecting the gray substance of the spinal cord. nociception A) the perception of pain; B) the perception of balance or acceleration; C) the sense of cold and the absence of heat; D) the sense of pressure perception. iridectomy A) pertaining to eyes and face; B) excision of the iris thickened part; C) paralysis of the iris sphincter; D) bleeding from the iris. oval window A) tympanic membrane; B) external auditory meatus; C) the entrance to the inner ear; D) a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose. dermatalgia A) inflammation of the skin; B) ossification of the dermis; C) any disease of the skin; D) localized pain confined to the skin. major histocompatibility complex molecules A) secrete antibodies; B) kill certain microbes and cancer cells as soon as they are formed; C) initiate an immune response and send signal to mobilize neutrophiles to join them at a trouble spot; D) help the body to distinguish self from nonself. AIDS A) acknowledged infection developing suddenly; B) acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; C) alcohol, insulin, drug screening; D) human immunodeficiency virus infection. rhinallergosis A) pertaining to the nose and month; B) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose; C) allergic rhinitis; D) change in speech as a result of pathology in nose structures. encephalitis A) resembling brain, brain-like; B) inflammation of the spinal cord; C) abnormal accumulation of fluid in the brain; D) inflammation of the brain. amnesia A) bleeding inside the skull; B) a malfunction of the peripheral nerves; C) a disorder characterized by the tendency to have recurring seizures; D) the total or partial inability to recall recent or remote experiences. touch A) the sense of pressure perception, generally in the skin; B) one of the “chemical” senses; C) the sense of sound perception; D) the ability to detect electromagnetic waves within the visible range by the eye and the brain to interpret the images. cornea A) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; B) a membraneous lining inside the sclera that contains many blood vessels; C) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; D) an area at the back of the eye on which the light is focused. otosclerosis A) inflammation of the eye; B) inflammation of the ear; C) an over-growth of the bone of the inner ear that leads to inability of sound conduction to the inner ear; D) a fungus infection of the ear. Eustachian tube A) a tympany that is attached to the hammer and keeps he eardrum taut; B) a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose; C) a muscle, which is attached to the stirrup and stabilizes the connection between the stirrup and the oval window; D) three tiny bones that connect the eardrum to the inner ear. subcutaneous adipose layer A) a skin layer composed of connective tissue which specializes in the formation of fat; B) a living tissue composed of blood and lymph vessels and nerve fibers which lies directly below the external layer of the skin; C) a total name for all the three layers of the skin; D) the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. neutrophile A) a protein that interacts with the antigen; B) a cell of the lymphatic system; C) a large white blood cell that ingests microbes and antigens; D) an immunoglobulin. autoimmune reaction A) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; B) a reaction produced by treatment of both congenital and acquired immunodeficiency; C) malfunctioning of the immune system, misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; D) minor impairment of the immune system. hives A) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing; an itchy or runny nose; and irritated eyes; B) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals); C) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such as cold, sunlight, heart, or minor injury; D) a condition in which allergy is caused by physical exertion and produces vomiting and diarrhea. nasopharynx A) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; B) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; C) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passegeway for food from the mouth and air from the nose; D) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx. pyoptysis A) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract; B) the coughing up of white sputum; C) the expectoration of sputum containing pus; D) good, normal breathing. pulmonologist A) inflammation of the lungs; B) a specialist in blood diseases; C) resection of lung tissue; D) a specialist in lung diseases. alveoli A) clusters of air sacs at the end of the bronchioles; B) masses of lymphatic tissue located in the nasopharynx; C) a small flap of muscular tissue at the entrance to the larynx; D) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle separating the thoracic from abdominal cavity. fungal pneumonia A) inflammation of the lungs caused by a virus; B) inflammation of the bronchi caused by a virus; C) inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria; D) inflammation of the lungs caused by fungi. antibody A) post-mortem examination of the body; B) glycoprotein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign bodies; C) examination of tissue removed from the body to confirm the diagnosis; D) paralysis of one side of the body. rhinitis A) kidney inflammation; B) stomach inflammation; C) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose; D) inflammation of the body’s inner organs, namely bladder, gallbladder, liver, spleen, etc. hyperemia A) lack of blood; B) presence of excess of blood; C) resembling blood; D) abnormal tendency of bleeding. hypoglossal A) under the tongue; B) under the skin; C) on the tongue; D) on the skin. autonomic nervous system A) the system that consists of the brain and spinal cord; B) the nervous system that consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves, which carry impulses between the brain and the head and neck; C) the system of nerve fibers that carries impulses from the central nervous system to the glands, heart, blood vessels, and the involuntary muscles; D) the system that consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. neurasthenia A) physical condition characterized by general lassitude, irritability, and lack of concentration, worry, and hypochondria; B) a physician specializing in the field of neurology trained to diagnose, treat, and manage patients with neurological disorders; C) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve centre; D) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. encephaloma A) any disease of the brain; B) incision of part of the brain; C) inflammation of the brain; D) any swelling or tumour of the brain. tactition A) smell-one of the “chemical” senses; B) touch-sense of pressure perception; C) hearing-sense of sound perception; D) taste-the other “chemical” sense. retina A) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; B) a shin membrane in the eye; C) an area at the back of the eye on which the light is focused; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. pinna A) the external part of the ear; B) the external part of the eye; C) tympanic membrane; D) a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose. dermatology A) localized pain confined to the skin; B) inspection of the skin, usually with the aid of a lens; C) pertaining to the mucous membrane and the skin; D) the branch of medicine concerned with diagnosis and treatment of diseases and disorders of the skin. antibodies A) large white blood cells that ingest microbes and antigens; B) cells of the lymphatic system; C) proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes; D) 18 proteins which act in a cascade, with one protein activating the next protein. autohemotherapy A) serum prepared from the patient’s own blood; B) bleeding, haemorrhage; C) treatment by administration of the patient’s own blood; D) vaccine prepared from the patient’s own tissue or secretion. nasopharyngoscopy A) examination of the nose and throat by flexible or rigid optical instrument, or with a mirror; B) examination of the nose, voice box and ear with the help of rigid and flexible optical instrument; C) an instrument for inspection of the nose and voice box; D) an instrument for examining of the nose and throat. epiglottis A) fine hairs (cilia) in the nasal cavities that help to filter out foreign bodies; B) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle separating the thoracic from abdominal cavity; C) the smallest of the bronchial branches; D) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx that closes when swallowing, thus preventing food from entering the airways. pectoralgia A) good, normal breathing; B) difficult breathing; C) pertaining to the breast or chest; D) pain in the chest. immune system A) the interaction of organs and / or substances within human body that strictly pertain to reproduction; B) the system of organs that takes in food, digests it to extract energy and nutrients; C) the collection of mechanisms within an organism that protects against infection by identifying and killing; D) the system that coordinates the activity of muscles. malignant tumour A) a noncancerous neoplasm; B) a malfunction of the trigeminal nerve; C) a malfunction of the peripheral nerves; D) a cancerous neoplasm. hypothalamus A) a part of the brain which monitors the sensory stimuli we receive by suppressing some and magnifying others; B) a part of the brain located beneath the posterior part of the cerebrum; C) a part of the brain which contains neurons which control body temperature, sleep, appetite, and emotions; D) a part of the brain which literally means “bridge”. otorrhea A) discharge from the ear; B) discharge from the eye; C) a doctor qualified to treat ear diseases; D) a venereal disease. stroke A) the death of brain tissue resulting from the lack of blood flow and insufficient oxygen to the brain; B) a tumour originating in the cells of the meninges, which lines the brain and the spinal cord; C) the total or partial inability to recall recent or remote experiences; D) a chronic disease in which there is a scattered demyelination of the central nervous system. esthesiology A) study of the vision organs; B) study of the sense of smell and hearing; C) study of the sense organs; D) any factor causing senses. cyanosis A) yellow or even brown colouration of the skin; B) bluish colouration of the skin and mucous membranes; C) red or sometimes purple colour of the mucous membranes; D) subjective visual perception of the blue colour. finger clubbing A) a difficulty in breathing; B) any fracture of a finger or a toe because of low oxygen level in the blood; C) a familial but complicated reflex in which the lungs and airways are protected; D) an enlargement of the tips of fingers or toes caused by lung diseases. pharyngotomy A) a surgical procedure of making an incision into the throat to remove a tumour or anything obstructing the passage; B) a surgical procedure of removing part of the throat; C) plastic surgery of the throat; D) inflammation of both throat and voice box. thrombasthenia A) faulty nerve conduction characterized by weakness and quick fatigue of muscles; B) inherited weakness of blood platelets; C) psychoneurosis characterized by abnormal fatigability; D) weakness of the voice from fatigue. neurilemmoma A) a tumour of the myelinated sheaths of nerve fibers; B) surgical removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve; C) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; D) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. cerebrology A) examination of the brain; B) atrophy of the brain gray substance; C) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain; D) study of the structure and functions of the brain. thermoception A) the perception of pain; B) the perception of balance or acceleration; C) the sense of heat and cold; D) one of “chemical” senses. keratitis A) inflammation of the retina; B) blood in the retina; C) a toxin affecting eyes; D) inflammation of the retina and conjunctiva. the hammer A) one of the ossicles that is attached to the oval window; B) one of the ossicles that is attached to the eardrum; C) one of the ossicles that connects the malleus and stirrup; D) all three tiny bones, called ossicles. central nervous system A) the system that consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves; B) the system that consists of the brain and spinal cord; C) the system that carries impulses from the CNS to the glands, heart, blood vessels and the involuntary muscles; D) the system that consists of 31 pairs of spinal nerves, which carry messages between the spinal cord and the chest, abdomen, and extremities. neuralgia A) formation of the nervous tissue; B) trauma of the nervous system; C) acute paroxysmal pain along a peripheral sensory nerve; D) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve centre. polioencephalitis A) inflammation of the brain; B) inflammation of the spinal cord; C) atrophy of the brain gray substance; D) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain. taste A) gustation; B) olfaction; C) nociception; D) thermoception. pupil A) the circular, coloured area of the eye; B) the black area in the middle of the iris; C) the transparent dome on the surface of the eye; D) the white of the eye. auricle A) the external part of the eye; B) the external part of the ear; C) tympanic membrane; D) a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose. mucocutaneous A) ossification of the dermis; B) any skin eruption due to emotional stimuli; C) pertaining to or affecting the skin; D) pertaining to the mucous membrane and the skin. complement system A) large white blood cells that ingest microbes and antigens; B) the main cells of the lymphatic system which are relatively small; C) 18 proteins which act in a cascade, with one protein activating the next protein; D) messengers of the immune system secreted by cells of the immune system in response to stimulation. autointoxication A) treatment by administration of the patient’s own blood; B) chemical regulation of the body functions by means of own components of own tissues, i.e. by hormones; C) poisoning by toxins, generated in the body; D) toxin developed in the patient’s own blood. rhinorrhagia A) nose hemorrhage; B) pain in the nose; C) any disease of the nose; D) throat hemorrhage. bronchioles A) cluster of air sacs at the end of the bronchioles; B) the smallest of the bronchial branches; C) a double folded membrane enveloping each lung; D) fine hairs (cilia) in the nasal cavities that help to filter out foreign bodies. pneumonia A) inflammation of the bronchi usually caused by an infection; B) inflammation of the middle ear; C) infection of the cornea and pupil; D) infection of the lungs that involves alveoli and the tissues around them. anosmia A) the inability to taste; B) the inability to hear; C) the inability to smell; D) the inability to spell words property. eczema A) a cell that ingests fat; B) pathologic dryness of the mucous membrane; C) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; D) inflammation of the skin. innate immunity A) an obtained or gained immunity; B) an immunity a person is born with; C) an immunity which comes as a result of injected antiserum produced in another individual or animal; D) an immunity which comes about through natural processes that follow exposure to the infectious agent. adenoids A) masses of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx; B) hormones secreted by adenohypophysis; C) clusters of air sacs at she end of bronchioles; D) rounded masses of lymphatic tissue in the orolarynx. bronchoplasty A) originating from the bronchi; B) swelling of the mucosa of the bronchial tube; C) surgical alteration of the configuration of a bronchus; D) narrowing of the bronchus lumen. pleura A) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle, separating the thoracic from the abdominal cavity; B) a double-folded membrane enveloping each lung; C) a small flat of muscular tissue at the entrance of the larynx; D) fine hairs (cilia) that help to filter out foreign bodies from the nasal cavities. allergic rhinitis A) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; B) an allergic reaction to a particular food; C) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing; itchy, runny, or stuffy nose; and irritated eyes; D) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals). AIDS A) highly contagious disease caused by filterable virus and spread by droplets from the nose, mouth and throat of individuals in the infective stage; B) chronic autoimmune disease in which body’s own defense system attacks otherwise healthy tissue; C) fatal disease caused by rapidly mutating retrovirus that attacks the immune system and leaves the victim vulnerable to infections; D) failure of the organism to recognize its own constituent parts as “self”, which results in an immune response against its own cells and tissues. HIV A) the virus that can cause cancer; B) the virus that causes a sudden death; C) the virus that can cause AIDS; D) the virus that causes atherosclerosis. atopic disease A) gastro-intestinal tract disorder; B) an inherited allergic disease; C) a catching skin disease; D) a grave heart disease. hyposusceptibility A) the state of being pathologically too influenced, harmed or affected by a disease, infection, etc.; B) a pathological condition in which a person doesn’t feel any pain at all; C) a scientific study of a person’s susceptibility to a disease, infection, etc.; D) a medical condition in which susceptibility to infection, disease, etc. is much lower than normal. oncology A) a person qualified to treat tumours in the body; B) the scientific study of and treatment of tumours in the body; C) a specialized hospital for people suffering from tumours; D) the scientific study of and treatment of eye diseases. tumour A) a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or benign; B) an inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; D) a malfunction of the peripheral nerves. cerebrospinal fluid A) a fluid used in treatment of cerebrospinal disorders; B) a colourless acidic fluid located in the stomach, also often called as gastric juice; C) a watery fluid which flows throughout the brain and around the spinal cord and protects them from shock as might a cushion; D) the red liquid that flows through the bodies of humans and animals. pyorrhea A) discharge from the ear; B) discharge of pus; C) discharge of saliva; D) discharge from the eye. anticoagulant A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a substance that the body produces in the blood to fight disease; C) a substance that stops the blood from becoming thick and forming clots; D) a substance that enters the body and can cause a disease. anvil A) one of the ossicles, that is attached to the eardrum; B) all three tiny bones, called ossicles; C) one of the ossicles which is attacked to the oval window; D) one of the ossicles also called incus that connects the hammer and stirrup. angiasthenia A) weakness of the voice from fatigue; B) extreme strongness of blood vessels; C) paralysis of some blood vessels; D) fragility and weakness of blood vessels. neuritis A) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; B) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; C) inflammation of a peripheral nerve, often accompanied by degenerative changes in nervous tissue; D) physical condition characterized by general lassitude, irritability, and lack of concentration, worry, and hypochondria. knee jerk reflex A) an autonomic response to a stimulus; B) a reflex that demonstrates that the sensory nerve to the spinal cord, the nerve connections in the cord, and motor nerves back to the leg muscles are all functioning; C) a reflex which is tested by firmly stroking the outer border of the sole of the foot with a blunt object and in which the toes curl downward; D) a test in which a doctor asks a person to touch his nose with a forefinger, next to touch the doctor’s finger, and then to repeat these actions rapidly. equilibrioception A) the perception of balance or acceleration; B) the perception of pain; C) the sense of heat and cold; D) the sense of pressure perception, generally in the skin. osphresiometer A) instrument for measuring tactile sensitivity; B) olfactory nerve tumour; C) instrument for measuring smell sensitivity; D) a doctor trained to administer aneaesthesia. ophthalmologist A) a doctor trained to treat ear diseases; B) a doctor trained to treat eye diseases; C) study of the structure and functions of the eye; D) pertaining to eyes and face. diaphoresis A) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; B) dryness of the mouth from salivary gland dysfunction; C) pathologic dryness of the skin; D) condition in which painful areas of subcutaneous fat develop. antiperspirant A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a substance that the body produces in the blood to fight disease; C) a substance that stops the blood from becoming thick and forming clots; D) a substance that people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat. allergic conjunctivitis A) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing, itching and runny nose; B) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; C) an injury of the conjunctiva; D) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction. pneumoalveolography A) pertaining to the lungs and heart; B) a specialist in lung and alveoli diseases; C) x-ray examination of the air sacs of the lungs; D) resection of lung tissue. AIDS A) highly contagious disease caused by filterable virus and spread by droplets from the nose, mouth and throat of individuals in the infective stage; B) chronic autoimmune disease in which body’s own defense system attacks otherwise healthy tissue; C) fatal disease caused by rapidly matching retrovirus that attacks the immune system and leaves the victim vulnerable to infections; D) failure of the organism to recognize its own constituent parts as “self”, which results in an immune response against its own cells and tissues. tonsils A) masses of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx; B) rounded masses of lymphatic tissue in the orolarynx; C) cluster of air sacs at the end of bronchioles; D) the smallest of the bronchial branches. congenital immunodeficiency A) immunodeficiency that occurs later in life; B) immunodeficiency present from birth; C) autoimmune reaction of an adult organism; D) immune reaction in the genitals. rhinitis A) pain in the nose; B) nose hemorrhade; C) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose; D) inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose and voice box. cerebral angiography A) a technique used to detect blood vessels abnormalities in the brain; B) the procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid; C) a computer-enhanced scanning technique for analyzing X-ray pictures to detect a wide range of brain abnormalities; D) the procedure used to measure blood flow through the carotid arteries. presbyopia A) impairment of hearing due to old age; B) loss of feelings; C) impairment of vision due to old age; D) method of vision loss measuring. active immunity A) the immunity developed by means of injected antigens which are either vaccines or toxoids; B) various types of inherent, inborn resistance to infections and diseases; C) the body’s resistance to infections that comes about through natural processes which may follow exposure to the infectious agent; D) the immunity developed due to injection of antibodies against infectious agents produced by some individuals or by animals and thus given “ready-made” to the patient. AIDS A) a disease which destroys mental abilities of a person; B) an illness which causes inability of a person to think, to hear, to speak and to talk; C) an illness which attacks the body’s ability to resist infection and which usually causes death; D) a cardio-vascular disease which attacks elderly people and causes a sudden death. allergen A) a substance that improves allergic condition; B) a substance that causes allergic reaction; C) a substance that affects central nervous system; D) a substance that causes intracranial hemorrhage. dysfunction A) a state or act of working in a very satisfactory and successful way; B) the science of the forces involved in the movement; C) energy and enthusiasm to make new things happen or to make things succeed; D) a state or act of not working in a satisfactory and successful way. hypertension A) blood pressure that is higher than normal; B) blood pressure that is lower than normal; C) normal blood pressure; D) a doctor qualified to treat pathologic increase of blood pressure. coma A) a condition characterized by an abnormal increase and accumulation of fluid in the skull; B) a disturbance in brain function resulting from a temporary deficiency in the brain’s blood supply; C) malfunction of the peripheral nerves in the brain; D) a state of deep and prolonged unconsciousness caused by injury or disease; a condition of stupor and lethargy. epidermis A) the third skin layer which consists of interweaving loose bundles of connective tissue fibres which form a large-mesh network; B) a doctor qualified to treat skin, especially epidermis diseases; C) an external skin layer which consists of epithelial cells which possess great ability to multiply and replace the destroyed cells of this layer; D) the second layer of the skin which is located under the skin. stirrup A) one of the ossicles also called malleus attacked to the eardrum; B) one of the ossicles also called incus that connects the malleus and stapes; C) all three tiny bones connecting the eardrum to the inner ear; D) one of the ossicles also called stapes attached to the oval window at the entrance to the inner ear. ageusia A) the inability to hear; B) the inability to smell; C) the inability to taste; D) the inability to feel anything. suppository A) a small spherical or ovoid mass of a medicinal substance, intended to be swallowed whole; B) a flattish medicinal formulation made of a compressed powdered substance containing an active drug and excipients; C) a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles; D) an encapsulated or solid medication for insertion into the vagina, rectum, or urethra, where it melts and releases the active substance. lipoedema A) transformation of other types of cells into squamous cells; B) relating to both fatty and cellular tissue, or to connective tissue with many fat cells; C) oedema of subcutaneous fat, causing painful swellings, especially of the legs in women; D) a cell that ingests fat. antihistamine A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a drug used to treat allergies, especially hay fever; C) a substance that enters the body and can cause a disease; D) a substance the people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat. cataract A) a condition in which loss of vision occurs because of an abnormally high pressure in the eye; B) any opacity in the lense of the eye that results in blurred vision; C) paralysis of the iris sphincter; D) inflammation of the inner ear. pneumobilia A) pertaining to the lungs and heart; B) presence of air or other gas in the bile system; C) presence of air or some other gas in bronchoedema; D) changes of breathing process. perioral dermatitis A) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens; B) typically develops in areas where something, such as a tight garment, rubs or scratches the skin; C) may be a form of the skin disorder rosacea, adult acne or seborrheic dermatitis, involving the skin around the mouth or nose; D) can occur when fluid accumulates in the tissues just beneath the skin, and typically involves the lower leg. sclera A) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; B) a thin membrane in the eye; C) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. anaphylaxis A) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such as cold, sunlight, heat, or minor injury; B) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals); C) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; D) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction in a person who was previously sensitized by prior exposure to an allergen and who comes into contact with the same allergen again. cough A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; C) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially obstructed airways; D) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract. meninges A) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain, fills the ventricles and cushions the brain against injury; B) the three layers of tissue, the brain and the spinal cord are wrapped in; C) nerves at the front of the spinal cord, which carry information from the brain to the muscles; D) nerves at the back of the spinal cord, which carry sensory information from distant parts of the body to the brain. pharynx A) windpipe; B) voice box; C) trachea; D) throat. otosclerosis A) a progressive degenerative condition of the temporal bone which can result in hearing loss; B) an infection or inflammation of the middle ear; C) an inflammation or infection of the inner ear; D) discharge from the ear. adiposalgia A) condition in which painful areas of subcutaneous fat develop; B) relating to both fatty and cellular tissue, or to connective tissue with many fat cells; C) a cell that ingests fat; D) headache or pain in the ear. ear A) the organ of vision; B) the organ of tasting; C) the organ of hearing and balance; D) the gas we breathe in. ophthalmoplasty A) pertaining to eyes and face; B) plastic surgery of eyes; C) any disease of the eye; D) plastic surgery of the ears. esthesiometer A) instrument for measuring tactile sensitivity; B) method of measuring smell sensitivity; C) method of hearing loss measuring; D) instrument for measuring of the extend of feelings loss. quadriplegia A) paralysis affecting the lower extremities; B) paralysis affecting right or left side of the body; C) paralysis affecting all four extremities; D) lack of strength or a very slight paralysis of four extremities. dyspepsia A) eyesight impairment; B) science, sum of knowledge about gastro-intestinal tract; C) improvement of digestion; D) impairment of digestion. hyperacidity A) excess of acid in gastric juice; B) below normal amount of acid in gastric juice; C) extreme physical sensitivity to acid; D) normal amount of acid in gastric juice. Parkinson’s disease A) a tumour originating in the cells of the meninges, which lines the brain and the spinal cord; B) an inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; D) a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or benign. dermatitis A) a scientific study of skin diseases; B) an inflammation of skin that usually involves swollen, red and itchy skin; C) a doctor qualified to treat skin diseases; D) a medical condition that causes you react badly when you eat, smell or touch a particular substance. cerebellum A) a part of the brain which controls body temperature, sleep, appetite, and emotions; B) a part of the brain which monitors the sensory stimuli we receive by suppressing some and magnifying others; C) a part of the brain which contains nerve fiber tracts which connect the cerebellum and cerebrum with the rest of the brain; D) a part of the brain located beneath the posterior part of the cerebrum and aids in the coordination of voluntary movements and maintains balance and muscular tone. oropharynx A) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passageway for food from the mouth and air from the nose; B) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; C) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; D) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx. choroid A) a membranous lining inside the sclera that contains many blood vessels, which supply nutrients to the eye; B) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; C) the circular, coloured area of the eye; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. xerophthalmia A) pathologic dryness of the skin; B) dryness of the mouth from salivary gland dysfunction; C) oedema of the conjunctiva and cornea due to profuse perspiration; D) dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea due to vitamin A deficiency. cerebrospinal fluid A) nerves at the back of the spinal cord, which carry sensory information from distant parts of the body to the brain; B) the three layers of the brain and the spinal cord tissue are wrapped in; otherwise called as meninges; C) nerves at the front of the spinal cord carrying information from the brain to the muscles; D) fluid which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions it against sudden jarring and minor injury. stroke A) temporary disturbances of brain function caused by insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain for brief period; B) an insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain in which brain tissue die causing disabling neurologic damage; C) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system which is characterized by tremor, sluggish initiation of movements, and muscle rigidity; D) an inflammation of the meninges usually caused by a virus. anosmia A) the inability to taste; B) the inability to feel anything or almost anything; C) the inability to smell; D) the inability to see. otitis A) inflammation of the eye; B) inflammation of the ear; C) an over-growth of the bone of the inner ear that leads to inability of sound conduction to the inner ear; D) a fungus infection of the ear. vaccine A) misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; B) a substance made of weakened or killed microorganisms which is introduced into the body for prevention, improvement of the course or treatment of infectious diseases; C) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; D) the drug used in treatment of both congenital and acquired immunodeficiency. physical allergy A) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such a cold, sunlight, heat, or minor injury; B) acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction to airborne particle; C) an allergic reaction to a particular food; D) damage or injury of the body caused by physical force, that is a blow, hick, prick, etc. wheezing A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; C) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially obstructed airways; D) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract. pneumocardial A) presence of gas or air in the cardium; B) air-like tissue surrounding the heart; C) inflammation of the lungs and head; D) pertaining to the lungs and heart. subhepatic A) located below the lower jaw; B) under the tongue; C) located below the liver; D) under the skin. seborrheic dermatitis A) caused a red rash with a yellowish and somewhat “oily” scale; B) occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues just beneath the skin, and typically involves the lower leg; C) develops in areas where something rubs or scratches the skin; D) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens. cataract A) a painless clouding of the lens of the eye that may reduce a person’s vision; B) an increased intraocular tension, “hardening” of the eyeball; C) a decreased intraocular tension, “lightening” of the eyeball; D) a very painful but not dangerous to the eye-sight clouding of the lens and the pupil of the eye. antibiotic A) a drug used to treat allergies, especially hay fever; B) a substance that helps to reduce fever; C) a substance that can destroy or prevent the growth of bacteria and cure infections; D) a substance that the body produces in the blood to fight disease. autolesion A) erosion of skull bones in patients suffering from brain tumours; B) self-inflicted injury; C) serum prepared from the patient’s own tissue or secretion; D) toxin developed in the patient’s own blood. rhinalgia A) pain in the nose; B) pertaining to the nose and lip; C) allergic rhinitis; D) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose. bronchoedema A) narrowing of the bronchus lumen; B) swelling of the mucosa of the bronchial tube; C) originating from the bronchi; D) presence of air or other gas in the bile system. neurologist A) the branch of chemistry that studies chemical processes in the nervous system; B) the branch of anatomy that studies the anatomical organization of the nervous system; C) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; D) a physician specializing in the field of neurology and trained to diagnose, treat, and manage patients with neurological disorders. natural immunity A) the body’s resistance to infections that comes about through natural processes which may follow exposure to the infectious agent; B) various types of inherent, inborn resistance to infections and diseases; C) the body’s ability of being immortal; D) the immunity developed by means of injected antigens which are either vaccines or toxoids. HIV A) Higher Institution’s Victory; B) Human Infectious Venereal disease; C) Very Important Person; D) Human Immunodeficiency Virus. allergy A) a medical condition that causes you react badly or feel ill when you eat, smell or touch a particular substance; B) an illness that is caused by bacteria or a virus and that affects one part of the body; C) the act of discovering or identifying the exact cause of an illness or a problem; D) the chemical processes in living things that change food, etc. into energy and materials for growth. hyperglycemia A) lack of sugar in the blood; B) extreme physical sensitivity to sugar; C) excess of sugar in the blood; D) normal amount of sugar in the blood. dermatology A) a skin condition in which the skin becomes red, swollen and sore; B) a doctor who studies and treats skin diseases; C) the scientific study of skin diseases; D) a cosmetic cream applied to the skin. encephalitis A) kidney inflammation; B) an inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord; C) an inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; D) an inflammation of the meninges caused by a virus. retina A) the middle layer of the eye which is comprised of three parts: the choroids, ciliary body, and iris; B) the posterior cavity of the eye which is filled with a gel-like substance; C) the thick white outer layer that gives the eyeball its spherical shape; D) the inner layer of the eye which is responsible for receiving images projected through the cornea and lens. passive immunity A) the immunity developed due to injection of antibodies against infectious agents produced by some individuals or by animals and thus given “ready-made” to the patient; B) the body’s resistance to infections that comes about through natural processes which may follow exposure to the infectious agent; C) the immunity developed by means of injected antigens which are either vaccines or toxoids; D) various types of inherent, inborn resistance to infections and diseases. spinal cord A) a part of the CNS that lies beneath the cerebrum just above the brain stem and coordinates the body movements; B) the portion of the CNS enclosed in the vertebral column; C) the enlarged and highly developed mass of nervous tissue that forms the upper end of the CNS; D) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions the brain against sudden jarring. electroencephalography A) a simple, painless procedure in which 20 wires are pasted on the scalp to trace and record the electrical activity of the brain; B) in this procedure a needle is inserted into the spinal canal to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid that is examined under the microscope; C) a computer-enhanced scanning technique for analyzing x-ray pictures to detect a wide range of brain and spinal abnormalities; D) a technique used to detect blood vessels abnormalities in the brain, such as an aneurism, inflammation or a blocked blood vessel. deafness A) the inability to see; B) the ability to hear very well; C) the inability to hear; D) the inability to smell. hyperesthesia A) any factor causing senses; B) loss of feeling; C) excessive sensitiveness; D) olfaction impairment. capsule A) a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles; B) a medicinal tablet, usually oval in shape, coated in a soluble substance; C) alcoholic extract of a drug derived from a plant; D) a fatty medicated formulation applied to the skin or mucous membranes to heal or protect. otologist A) a specialist trained to treat ear diseases; B) a specialist trained to treat eye diseases; C) examination of the ear; D) inflammation of the Eustachian tube. epidermis A) a living tissue composed of blood and lymph vessels and nerve fibers, which lies directly below the external layer of the skin; B) a skin layer composed of connective tissue which specializes in the formation of fat; C) a total name for all the three layers of the skin; D) the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. macrophage A) a protein that interacts with the antigen; B) a cell of the lymphatic system; C) a large white blood cell that ingests microbes and antigens; D) an immunoglobulin. immunodeficiency disorders A) malfunctioning of the immune system, misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; B) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; C) disorders which have autoimmune cause, including lupus, myasthenia gravis, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, pemphigus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc; D) a disorder caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila, that accounts for 1 to 8 % of all pneumonias and about 4 % of fatal pneumonias. rhinoscope A) pain in the nose; B) an instrument for inspection of the nose; C) the procedure in which nose is inspected; D) nose tampon. hypopharynx A) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx; B) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; C) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; D) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passageway for food from the mouth and air from the nose. hemoptysis A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract; C) difficulty in breathing; D) a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from a inadequate amount of blood causes by lung diseases. pharyngitis A) inflammation of the throat; B) inflammation of the larynx; C) inflammation of the tonsils; D) inspection of the throat, larynx and tonsils. AIDS A) Acquired Infectious Diseased State; B) Acute Inflammatory Disease Syndrome; C) Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome; D) Acute Immune Deficiency Syndrome. antibody A) a substance, for example penicillin, that can destroy or prevent the growth of bacteria and cure infections; B) a substance that the body produces in the blood to fight disease; C) a substance that enters the body and can cause disease; D) a drug used to treat allergies. hypodermic A) on the skin; B) in the skin; C) above the skin; D) under the skin. cardiology A) a scientific study of eye diseases; B) a doctor who studies and treats heart diseases; C) a scientific study of heart diseases; D) a scientific study of gastro-intestinal tract disorders. amnesia A) the total or partial inability to recall recent or remote experiences; B) a state of deep and prolonged unconsciousness caused by injury or disease; C) a chronic disease in which there is a scattered demyelination of the central nervous system; D) bleeding inside the skull. brain A) a natural covering and inseparable part of the human body; B) the primary center for requesting and coordinating of body activities; C) a muscular partition which separates the thoracic from the abdominal cavity; D) a slippery membrane that helps the lungs move smoothly during each breath. otitis A) an infection or inflammation of the middle ear; B) any disease of the outer ear; C) surgical operation performed on the ear; D) discharge from the ear. otoscopy A) examination of the ear; B) a method of Eustachian tube examination; C) an instrument used while examining the ear; D) plastic surgery of the eardrum. dermopathy A) pain under the skin; B) any disease of the skin; C) inflammation of the skin; D) ossification of the dermis. sublingual A) inflammation of the tongue caused by harmful microorganisms; B) located below the lower jaw; C) located below the liver; D) under the tongue. pathogenesis A) the scientific study about general regularities of development, course and termination of diseases; B) medical treatment of injuries or diseases; C) a slight disorder of the brain that causes difficulty in reading and spelling, for example, but does not affect intelligence; D) pain caused by difficulty in digesting food. asthma A) a medical condition of the oral cavity that causes gingivitis; B) a respiratory disorder characterized by difficulty in breathing; C) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth; D) a doctor qualified to treat respiratory disorders. hypertrophy A) underdevelopment of an organ; B) overdevelopment of an organ; C) organ excision; D) organ incision. hyposecretion A) diminished secretion; B) increased secretion; C) normal secretion; D) extremely high secretion. intracranial hemorrhage A) the death of brain tissue; B) an abnormality of the facial nerve that leads to paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face; C) abdominal bleeding; D) bleeding inside the skull. osphresiology A) a scientific study which deals with the reception of sound vibration by the ear; B) a scientific study of visual sensory system; C) a science which deals with the study of odours and the sense of smell; D) a scientific study of tactile perception. glaucoma A) hypertension, blood pressure higher than normal; B) an increased intraocular tension, “hardening” of the eyeball; C) a disease of the middle ear; D) cloudiness of the lens of the eye. ophthalmometer A) an instrument for measuring the eye; B) an instrument for measuring the ear; C) a doctor qualified to treat ophthalmologic diseases; D) an instrument for measuring the blood pressure. cough A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) a crowing sound when breathing; C) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; D) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that result from partially obstructed airways. pharyngitis A) an inflammation of the bronchi caused by an infection; B) an infection of the lungs that involves alveoli and the tissues around them; C) an inflammation of the throat, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria; D) an inflammation of the voice box caused either by a virus or by bacteria. encephaloscopy A) study of the structure and functions of the brain; B) any disease of the brain; C) abnormal accumulation of fluid in the brain; D) examination of the brain. Parkinson’s disease A) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; B) inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord; D) a stroke or a transient ischemic attack causing disabling neurologic damage. tincture A) a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles; B) a medicinal tablet, usually oval in shape, coated in a soluble substance; C) alcoholic extract of a drug derived from a plant; D) a fatty medicated formulation applied to the skin or mucous membranes to heal or protect. tumour A) a pathologic new growth (neoplasm) that can be either malignant or benign; B) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; C) an inflammation of any organ or part of the body; D) a chronic disease characterized by speed defects, loss of muscular coordination, etc. hemiplegia A) fragility and weakness of blood vessels; B) paralysis affecting right or left side of the body; C) paralysis affecting all four extremities; D) slight paralysis affecting left side of the body. ear A) the organ of both hearing and balance; B) the organ of seeing; C) the smell organ; D) the organ of gastro-intestinal tract. xeroderma A) a cell that ingests fat; B) pathologic dryness of the skin; C) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; D) dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea due to vitamin A deficiency. salpingitis A) inflammation of the eardrum; B) method of Eustachian tube examination; C) inflammation of the Eustachian tube; D) a specialist trained to treat ear diseases. occulopathy A) a toxin affecting eyes; B) pertaining to eyes and face; C) any disease of eyes; D) plastic surgery of eyes. vision A) the sense of pressure perception, generally in the skin; B) the study of odours and the sense of smell; C) one of the two main “chemical” senses; D) the ability to detect electromagnetic waves within the visible range by the eye and the brain to interpret the images as sight. coma A) is an abnormality of the facial nerve that leads to sudden weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face; B) a disease of faulty nerve conduction characterisea by speech defects, loss of muscular coordination, etc.; C) a state of deep and prolonged unconsciousness caused by injury or disease; a condition of stupor and lethargy; D) is a genetically transmitted disease in which many soft, fleshy growths of abnormal nerve tissues appear in the skin. acquired immunity A) various types of inherent, inborn resistance to infections and diseases; B) the immunity developed by means of injected antigens which are either vaccines or toxoids; C) the body’s resistance to infections that comes about through natural processes which may follow exposure to the infectious agent; D) the immunity developed due to injection of antibodies against infectious agents produced by some individuals or by animals and thus given “ready-made” to the patient. sample A) a small amount of a substance taken from a larger amount and tested in order to obtain information about the substance; B) knowledge about the structure and behaviour of the natural and physical world, based on facts that you can prove; C) not complicated; easy to understand or do; D) something such as an object, a fact or a situation that shows, explains or supports what you say. hypersensivity A) a kind of treatment that uses hypnosis to help with physical or emotional problems; B) the practice of keeping yourself and your living and working areas clean in order to prevent illness and disease; C) blood pressure that is higher than normal; D) an extreme physical sensitivity to particular substances, medicines, light, etc. dystrophy A) a medical condition in which the muscles gradually become weaker; B) a medical condition in which the muscles gradually become stronger; C) pain caused by difficulty in digesting food; D) a slight disorder of the brain that causes difficulty in reading and spelling. encephalomyelitis A) an inflammation of the meninges caused by a virus; B) an inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) an inflammation of the lungs; D) an inflammation of the brain and the spinal cord. derma A) an external skin layer which consists of epithelial cells which possess great ability to multiply; B) the second layer of the skin which is located under the epidermis; C) the third skin layer which consists of interweaving loose bundles of connective tissue fibres which form a large-mesh network; D) a medical institution where dermatological diseases are treated. cornea A) the inner layer of the eye which is responsible for receiving images projected through the cornea and lens; B) the thick white outer layer that gives the eyeball its spherical shape; C) the transparent layer at the front of the eye which is responsible for refracting or bending light; D) the middle layer of the eye which is comprised of three parts: the choroids, ciliary body, and iris. calcification A) of, containing, or concerned with lime or calcium; B) a hormone secreted by the thyroid that inhibits the release of calcium from the skeleton and prevents a build-up of calcium in the blood; C) the most common nutritional deficiency in the world; D) the process of calcifying or becoming calcified. A tissue hardened by deposition of lime salts. trachea A) throat; B) voice box; C) windpipe; D) cilia. gustation A) taste – one of “chemical” senses; B) smell – the other “chemical” sense; C) hearing – the sense of sound perception; D) touch – the sense of pressure perception. HIV A) half intra-venous; B) Very Important Person; C) Human Infectious Viruses; D) Human Immunodeficiency Virus. bronchitis A) inflammation of the bronchi; B) an instrument used for inspecting bronchi; C) inflammation of the lungs; D) a doctor qualified to treat the diseases of the bronchi. iris A) the black area in the middle of the iris; B) the circular, coloured area of the eye; C) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; D) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye. dermatotherapy A) treatment of skin diseases; B) any skin eruption due to emotional stimuli; C) an instrument used for inspection of the skin; D) inspection of the skin, usually with the aid of a lens. encephalalgia A) inflammation of the brain; B) neoplasm of the spinal cord; C) examination of the brain; D) headache. neurectomy A) the branch of chemistry that studies chemical processes in the nervous system; B) surgical removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve; C) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; D) a tumour of the myelinated sheaths of nerve fibers. antibody A) post-mortem examination of the body; B) glycoprotein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign bodies; C) examination of tissue removed from the body to confirm the diagnosis; D) paralysis of one side of the body. cytokines A) large white blood cells that ingest microbes and antigens; B) proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes; C) 18 proteins which act in a cascade, with one protein activating the next protein; D) “the messengers” secreted by cells of the immune system in response to stimulation which amplify some aspects of the immune system and inhibit others. rhinology A) knowledge concerning throat; B) a doctor qualified to treat ear diseases; C) knowledge concerning the nose; D) pertaining to the nose and mouth. ossicles A) tympanic membrane; B) external auditory meatus; C) three tiny bones; D) small tubes that connect the middle ear with the bed of the nose. rhinology A) knowledge concerning the nose; B) a doctor qualified to treat nose diseases; C) inflammation of the nose membrane; D) a surgical operation performed on nose. hydrocephalus A) a condition characterized by an abnormal increase and accumulation of fluid in the skull, especially in young children, causing enlargement of the head and destruction of the brain; B) a state of deep and prolonged unconsciousness caused by injury or disease; C) a chronic disease in which there is a scattered demyelination of the central nervous system; D) is an abnormality of the facial nerve that leads to sudden weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face. hearing A) the sense of pressure perception; B) olfaction; C) gustation; D) the sense of sound perception. eardrum A) one of the three tiny bones (ossicles); B) a tympanic membrane; C) the Eustachian tube; D) the external part of the ear. subcutaneous A) under the skin; B) under the liver; C) inflammation of the skin; D) ossification of the dermis. autoimmune reaction A) a diverse condition in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; B) a condition in which the immune system malfunctions, misinterprets the body tissues as foreign, and attacks them; C) reaction to the treatment by administration of the patient’s own blood; D) vaccine prepared from the patient’s own tissue or secretion. myelitis A) inflammation of the brain; B) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain; C) inflammation of the spinal cord; D) any disease affecting the gray substance of the spinal cord. vitamins A) macronutrients needed by the body in large quantaties; B) components of many enzymes affecting important chemical reactions throughout the body; C) fragility and weakness of blood vessels; D) essential micronutrient, required by the body in small amounts for maintenance of metabolism. dermatalgia A) inflammation of the skin; B) ossification of the dermis; C) any disease of the skin; D) localized pain confined to the skin. nociception A) the perception of pain; B) the perception of balance or acceleration; C) the sense of cold and the absence of heat; D) the sense of pressure perception. major histocompatibility complex molecules A) secrete antibodies; B) kill certain microbes and cancer cells as soon as they are formed; C) initiate an immune response and send signal to mobilize neutrophiles to join them at a trouble spot; D) help the body to distinguish self from nonself. rhinallergosis A) pertaining to the nose and month; B) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose; C) allergic rhinitis; D) change in speech as a result of pathology in nose structures. oval window A) tympanic membrane; B) external auditory meatus; C) the entrance to the inner ear; D) a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose. alveoli A) clusters of air sacs at the end of the bronchioles; B) masses of lymphatic tissue located in the nasopharynx; C) a small flap of muscular tissue at the entrance to the larynx; D) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle separating the thoracic from abdominal cavity. iridectomy A) pertaining to eyes and face; B) excision of the iris thickened part; C) paralysis of the iris sphincter; D) bleeding from the iris. fungal pneumonia A) inflammation of the lungs caused by a virus; B) inflammation of the bronchi caused by a virus; C) inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria; D) inflammation of the lungs caused by fungi. neurology A) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; B) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; C) trauma of the nervous system; D) a physician specializing in the field of neurology and trained to diagnose, treat, and manage patients with neurological disorders. antibody A) post-mortem examination of the body; B) glycoprotein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign bodies; C) examination of tissue removed from the body to confirm the diagnosis; D) paralysis of one side of the body. AIDS A) acknowledged infection developing suddenly; B) acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; C) alcohol, insulin, drug screening; D) human immunodeficiency virus infection. thrombasthenia A) faulty nerve conduction characterized by weakness and quick fatigue of muscles; B) inherited weakness of blood platelets; C) psychoneurosis characterized by abnormal fatigability; D) weakness of the voice from fatigue. thermoception A) the perception of pain; B) the perception of balance or acceleration; C) the sense of heat and cold; D) one of “chemical” senses. cerebrology A) examination of the brain; B) atrophy of the brain gray substance; C) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain; D) study of the structure and functions of the brain. the hammer A) one of the ossicles that is attached to the oval window; B) one of the ossicles that is attached to the eardrum; C) one of the ossicles that connects the malleus and stirrup; D) all three tiny bones, called ossicles. innate immunity A) an obtained or gained immunity; B) an immunity a person is born with; C) an immunity which comes as a result of injected antiserum produced in another individual or animal; D) an immunity which comes about through natural processes that follow exposure to the infectious agent. allergic rhinitis A) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; B) an allergic reaction to a particular food; C) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing; itchy, runny, or stuffy nose; and irritated eyes; D) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals). eczema A) a cell that ingests fat; B) pathologic dryness of the mucous membrane; C) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; D) inflammation of the skin. adenoids A) masses of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx; B) hormones secreted by adenohypophysis; C) clusters of air sacs at the end of bronchioles; D) rounded masses of lymphatic tissue in the orolarynx. neurilemmoma A) a tumour of the myelinated sheaths of nerve fibers; B) surgical removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve; C) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; D) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. bronchoplasty A) originating from the bronchi; B) swelling of the mucosa of the bronchial tube; C) surgical alteration of the configuration of a bronchus; D) narrowing of the bronchus lumen. pleura A) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle, separating the thoracic from the abdominal cavity; B) a double-folded membrane enveloping each lung; C) a small flat of muscular tissue at the entrance of the larynx; D) fine hairs (cilia) that help to filter out foreign bodies from the nasal cavities. keratitis A) inflammation of the retina; B) blood in the retina; C) a toxin affecting eyes; D) inflammation of the retina and conjunctiva. knee jerk reflex A) an autonomic response to a stimulus; B) a reflex that demonstrates that the sensory nerve to the spinal cord, the nerve connections in the cord, and motor nerves back to the leg muscles are all functioning; C) a reflex which is tested by firmly stroking the outer border of the sole of the foot with a blunt object and in which the toes curl downward; D) a test in which a doctor asks a person to touch his nose with a forefinger, next to touch the doctor’s finger, and then to repeat these actions rapidly. pneumoalveolography A) pertaining to the lungs and heart; B) a specialist in lung and alveoli diseases; C) x-ray examination of the air sacs of the lungs; D) resection of lung tissue. equilibrioception A) the perception of balance or acceleration; B) the perception of pain; C) the sense of heat and cold; D) the sense of pressure perception, generally in the skin. osphresiometer A) instrument for measuring tactile sensitivity; B) olfactory nerve tumour; C) instrument for measuring smell sensitivity; D) a doctor trained to administer aneaesthesia. anvil A) one of the ossicles, that is attached to the eardrum; B) all three tiny bones, called ossicles; C) one of the ossicles which is attacked to the oval window; D) one of the ossicles also called incus that connects the hammer and stirrup. angiasthenia A) weakness of the voice from fatigue; B) extreme strongness of blood vessels; C) paralysis of some blood vessels; D) fragility and weakness of blood vessels. antiperspirant A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a substance that the body produces in the blood to fight disease; C) a substance that stops the blood from becoming thick and forming clots; D) a substance that people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat. diaphoresis A) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; B) dryness of the mouth from salivary gland dysfunction; C) pathologic dryness of the skin; D) condition in which painful areas of subcutaneous fat develop. allergic conjunctivitis A) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing, itching and runny nose; B) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; C) an injury of the conjunctiva; D) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction. ophthalmologist A) a doctor trained to treat ear diseases; B) a doctor trained to treat eye diseases; C) study of the structure and functions of the eye; D) pertaining to eyes and face. tonsils A) masses of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx; B) rounded masses of lymphatic tissue in the orolarynx; C) cluster of air sacs at the end of bronchioles; D) the smallest of the bronchial branches. neuritis A) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; B) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; C) inflammation of a peripheral nerve, often accompanied by degenerative changes in nervous tissue; D) physical condition characterized by general lassitude, irritability, and lack of concentration, worry, and hypochondria. suppository A) a small spherical or ovoid mass of a medicinal substance, intended to be swallowed whole; B) a flattish medicinal formulation made of a compressed powdered substance containing an active drug and excipients; C) a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles; D) an encapsulated or solid medication for insertion into the vagina, rectum, or urethra, where it melts and releases the active substance. ageusia A) the inability to hear; B) the inability to smell; C) the inability to taste; D) the inability to feel anything. antihistamine A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a drug used to treat allergies, especially hay fever; C) a substance that enters the body and can cause a disease; D) a substance the people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat. sclera A) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; B) a thin membrane in the eye; C) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. meninges A) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain, fills the ventricles and cushions the brain against injury; B) the three layers of tissue, the brain and the spinal cord are wrapped in; C) nerves at the front of the spinal cord, which carry information from the brain to the muscles; D) nerves at the back of the spinal cord, which carry sensory information from distant parts of the body to the brain. stirrup A) one of the ossicles also called malleus attacked to the eardrum; B) one of the ossicles also called incus that connects the malleus and stapes; C) all three tiny bones connecting the eardrum to the inner ear; D) one of the ossicles also called stapes attached to the oval window at the entrance to the inner ear. lipoedema A) transformation of other types of cells into squamous cells; B) relating to both fatty and cellular tissue, or to connective tissue with many fat cells; C) oedema of subcutaneous fat, causing painful swellings, especially of the legs in women; D) a cell that ingests fat. cough A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; C) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially obstructed airways; D) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract. cataract A) a condition in which loss of vision occurs because of an abnormally high pressure in the eye; B) any opacity in the lense of the eye that results in blurred vision; C) paralysis of the iris sphincter; D) inflammation of the inner ear. pneumobilia A) pertaining to the lungs and heart; B) presence of air or other gas in the bile system; C) presence of air or some other gas in bronchoedema; D) changes of breathing process. anaphylaxis A) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such as cold, sunlight, heat, or minor injury; B) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals); C) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; D) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction in a person who was previously sensitized by prior exposure to an allergen and who comes into contact with the same allergen again. pharynx A) windpipe; B) voice box; C) trachea; D) throat. perioral dermatitis A) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens; B) typically develops in areas where something, such as a tight garment, rubs or scratches the skin; C) may be a form of the skin disorder rosacea, adult acne or seborrheic dermatitis, involving the skin around the mouth or nose; D) can occur when fluid accumulates in the tissues just beneath the skin, and typically involves the lower leg. stroke A) temporary disturbances of brain function caused by insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain for brief period; B) an insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain in which brain tissue die causing disabling neurologic damage; C) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system which is characterized by tremor, sluggish initiation of movements, and muscle rigidity; D) an inflammation of the meninges usually caused by a virus. anosmia A) the inability to taste; B) the inability to feel anything or almost anything; C) the inability to smell; D) the inability to see. cerebrospinal fluid A) nerves at the back of the spinal cord, which carry sensory information from distant parts of the body to the brain; B) the three layers of the brain and the spinal cord tissue are wrapped in; otherwise called as meninges; C) nerves at the front of the spinal cord carrying information from the brain to the muscles; D) fluid which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions it against sudden jarring and minor injury. choroid A) a membranous lining inside the sclera that contains many blood vessels, which supply nutrients to the eye; B) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; C) the circular, coloured area of the eye; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. otitis A) inflammation of the eye; B) inflammation of the ear; C) an over-growth of the bone of the inner ear that leads to inability of sound conduction to the inner ear; D) a fungus infection of the ear. wheezing A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; C) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially obstructed airways; D) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract. subhepatic A) located below the lower jaw; B) under the tongue; C) located below the liver; D) under the skin. vaccine A) misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; B) a substance made of weakened or killed microorganisms which is introduced into the body for prevention, improvement of the course or treatment of infectious diseases; C) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; D) the drug used in treatment of both congenital and acquired immunodeficiency. xerophthalmia A) pathologic dryness of the skin; B) dryness of the mouth from salivary gland dysfunction; C) oedema of the conjunctiva and cornea due to profuse perspiration; D) dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea due to vitamin A deficiency. physical allergy A) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such a cold, sunlight, heat, or minor injury; B) acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction to airborne particle; C) an allergic reaction to a particular food; D) damage or injury of the body caused by physical force, that is a blow, hick, prick, etc. pneumocardial A) presence of gas or air in the cardium; B) air-like tissue surrounding the heart; C) inflammation of the lungs and head; D) pertaining to the lungs and heart. oropharynx A) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passageway for food from the mouth and air from the nose; B) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; C) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; D) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx. seborrheic dermatitis A) caused a red rash with a yellowish and somewhat “oily” scale; B) occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues just beneath the skin, and typically involves the lower leg; C) develops in areas where something rubs or scratches the skin; D) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens. electroencephalography A) a simple, painless procedure in which 20 wires are pasted on the scalp to trace and record the electrical activity of the brain; B) in this procedure a needle is inserted into the spinal canal to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid that is examined under the microscope; C) a computer-enhanced scanning technique for analyzing x-ray pictures to detect a wide range of brain and spinal abnormalities; D) a technique used to detect blood vessels abnormalities in the brain, such as an aneurism, inflammation or a blocked blood vessel. epidermis A) a living tissue composed of blood and lymph vessels and nerve fibers, which lies directly below the external layer of the skin; B) a skin layer composed of connective tissue which specializes in the formation of fat; C) a total name for all the three layers of the skin; D) the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. deafness A) the inability to see; B) the ability to hear very well; C) the inability to hear; D) the inability to smell. capsule A) a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles; B) a medicinal tablet, usually oval in shape, coated in a soluble substance; C) alcoholic extract of a drug derived from a plant; D) a fatty medicated formulation applied to the skin or mucous membranes to heal or protect. otologist A) a specialist trained to treat ear diseases; B) a specialist trained to treat eye diseases; C) examination of the ear; D) inflammation of the Eustachian tube. pharyngitis A) inflammation of the throat; B) inflammation of the larynx; C) inflammation of the tonsils; D) inspection of the throat, larynx and tonsils. hyperesthesia A) any factor causing senses; B) loss of feeling; C) excessive sensitiveness; D) olfaction impairment. spinal cord A) a part of the CNS that lies beneath the cerebrum just above the brain stem and coordinates the body movements; B) the portion of the CNS enclosed in the vertebral column; C) the enlarged and highly developed mass of nervous tissue that forms the upper end of the CNS; D) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions the brain against sudden jarring. macrophage A) a protein that interacts with the antigen; B) a cell of the lymphatic system; C) a large white blood cell that ingests microbes and antigens; D) an immunoglobulin. immunodeficiency disorders A) malfunctioning of the immune system, misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; B) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; C) disorders which have autoimmune cause, including lupus, myasthenia gravis, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, pemphigus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc; D) a disorder caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila, that accounts for 1 to 8 % of all pneumonias and about 4 % of fatal pneumonias. rhinoscope A) pain in the nose; B) an instrument for inspection of the nose; C) the procedure in which nose is inspected; D) nose tampon. hemoptysis A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract; C) difficulty in breathing; D) a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from a inadequate amount of blood causes by lung diseases. hypopharynx A) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx; B) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; C) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; D) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passageway for food from the mouth and air from the nose. hypertrophy A) underdevelopment of an organ; B) overdevelopment of an organ; C) organ excision; D) organ incision. hyposecretion A) diminished secretion; B) increased secretion; C) normal secretion; D) extremely high secretion. osphresiology A) a scientific study which deals with the reception of sound vibration by the ear; B) a scientific study of visual sensory system; C) a science which deals with the study of odours and the sense of smell; D) a scientific study of tactile perception. encephaloscopy A) study of the structure and functions of the brain; B) any disease of the brain; C) abnormal accumulation of fluid in the brain; D) examination of the brain. glaucoma A) hypertension, blood pressure higher than normal; B) an increased intraocular tension, “hardening” of the eyeball; C) a disease of the middle ear; D) cloudiness of the lens of the eye. asthma A) a medical condition of the oral cavity that causes gingivitis; B) a respiratory disorder characterized by difficulty in breathing; C) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth; D) a doctor qualified to treat respiratory disorders. ophthalmometer A) an instrument for measuring the eye; B) an instrument for measuring the ear; C) a doctor qualified to treat ophthalmologic diseases; D) an instrument for measuring the blood pressure. intracranial hemorrhage A) the death of brain tissue; B) an abnormality of the facial nerve that leads to paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face; C) abdominal bleeding; D) bleeding inside the skull. pharyngitis A) an inflammation of the bronchi caused by an infection; B) an infection of the lungs that involves alveoli and the tissues around them; C) an inflammation of the throat, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria; D) an inflammation of the voice box caused either by a virus or by bacteria. Parkinson’s disease A) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system; B) inflammation of the brain caused by a virus; C) inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord; D) a stroke or a transient ischemic attack causing disabling neurologic damage. tincture A) a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles; B) a medicinal tablet, usually oval in shape, coated in a soluble substance; C) alcoholic extract of a drug derived from a plant; D) a fatty medicated formulation applied to the skin or mucous membranes to heal or protect. pathogenesis A) the scientific study about general regularities of development, course and termination of diseases; B) medical treatment of injuries or diseases; C) a slight disorder of the brain that causes difficulty in reading and spelling, for example, but does not affect intelligence; D) pain caused by difficulty in digesting food. neurectomy A) the branch of chemistry that studies chemical processes in the nervous system; B) surgical removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve; C) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; D) a tumour of the myelinated sheaths of nerve fibers. encephalalgia A) inflammation of the brain; B) neoplasm of the spinal cord; C) examination of the brain; D) headache. epilepsy A) the total or partial inability to recall recent or remote experiences; B) the death of brain tissue resulting from the lack of blood flow and insufficient oxygen to the brain; C) bleeding inside the skull; D) a disorder characterized by the tendency to have recurring seizures. gustation A) taste – one of “chemical” senses; B) smell – the other “chemical” sense; C) hearing – the sense of sound perception; D) touch – the sense of pressure perception. iris A) the black area in the middle of the iris; B) the circular, coloured area of the eye; C) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; D) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye. ossicles A) tympanic membrane; B) external auditory meatus; C) three tiny bones; D) small tubes that connect the middle ear with the bed of the nose. dermatotherapy A) treatment of skin diseases; B) any skin eruption due to emotional stimuli; C) an instrument used for inspection of the skin; D) inspection of the skin, usually with the aid of a lens. cytokines A) large white blood cells that ingest microbes and antigens; B) proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes; C) 18 proteins which act in a cascade, with one protein activating the next protein; D) “the messengers” secreted by cells of the immune system in response to stimulation which amplify some aspects of the immune system and inhibit others. HIV A) half intra-venous; B) Very Important Person; C) Human Infectious Viruses; D) Human Immunodeficiency Virus. rhinology A) knowledge concerning throat; B) a doctor qualified to treat ear diseases; C) knowledge concerning the nose; D) pertaining to the nose and mouth. trachea A) throat; B) voice box; C) windpipe; D) cilia. bronchitis A) inflammation of the bronchi; B) an instrument used for inspecting bronchi; C) inflammation of the lungs; D) a doctor qualified to treat the diseases of the bronchi. antibody A) post-mortem examination of the body; B) glycoprotein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign bodies; C) examination of tissue removed from the body to confirm the diagnosis; D) paralysis of one side of the body. neurology A) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; B) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; C) trauma of the nervous system; D) a physician specializing in the field of neurology and trained to diagnose, treat, and manage patients with neurological disorders. myelitis A) inflammation of the brain; B) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain; C) inflammation of the spinal cord; D) any disease affecting the gray substance of the spinal cord. phonasthenia A) slight paralysis affecting either right or left side of the body; B) inherited weakness of blood platelets; C) fragility and weakness of blood vessels; D) weakness of the voice from fatigue. nociception A) the perception of pain; B) the perception of balance or acceleration; C) the sense of heart and the absence of heat; D) the sense of pressure perception. iridectomy A) pertaining to eyes and face; B) excision of the iris thickened part; C) paralysis of the iris sphincter; D) bleeding from the iris. oval window A) tympanic membrane; B) external auditory meatus; C) the entrance to the inner ear; D) a small tube that connects the middle ear with the back of the nose. dermatalgia A) inflammation of the skin; B) ossification of the dermis; C) any disease of the skin; D) localized pain confined to the skin. major histocompatibility complex molecules A) secrete antibodies; B) kill certain microbes and cancer cells as soon as they are formed; C) initiate an immune response and send signal to mobilize neutrophiles to join them at a trouble spot; D) help the body to distinguish self from nonself. AIDS A) acknowledged infection developing suddenly; B) acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; C) alcohol, insulin, drug screening; D) human immunodeficiency virus infection. rhinallergosis A) pertaining to the nose and month; B) inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose; C) allergic rhinitis; D) change in speech as a result of pathology in nose structures. alveoli A) clusters of air sacs at the end of the bronchioles; B) masses of lymphatic tissue located in the nasopharynx; C) a small flap of muscular tissue at the entrance to the larynx; D) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle separating the thoracic from abdominal cavity. fungal pneumonia A) inflammation of the lungs caused by a virus; B) inflammation of the bronchi caused by a virus; C) inflammation of the lungs caused by bacteria; D) inflammation of the lungs caused by fungi. antibody A) post-mortem examination of the body; B) glycoprotein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign bodies; C) examination of tissue removed from the body to confirm the diagnosis; D) paralysis of one side of the body. neurilemmoma A) a tumour of the myelinated sheaths of nerve fibers; B) surgical removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve; C) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; D) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. cerebrology A) examination of the brain; B) atrophy of the brain gray substance; C) inflammation of the gray substance of the brain; D) study of the structure and functions of the brain. thrombasthenia A) faulty nerve conduction characterized by weakness and quick fatigue of muscles; B) inherited weakness of blood platelets; C) psychoneurosis characterized by abnormal fatigability; D) weakness of the voice from fatigue. thermoception A) the perception of pain; B) the perception of balance or acceleration; C) the sense of heat and cold; D) one of “chemical” senses. keratitis A) inflammation of the retina; B) blood in the retina; C) a toxin affecting eyes; D) inflammation of the retina and conjunctiva. the hammer A) one of the ossicles that is attached to the oval window; B) one of the ossicles that is attached to the eardrum; C) one of the ossicles that connects the malleus and stirrup; D) all three tiny bones, called ossicles. eczema A) a cell that ingests fat; B) pathologic dryness of the skin; C) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; D) inflammation of the skin. innate immunity A) an obtained or gained immunity; B) an immunity a person is born with; C) an immunity which comes as a result of injected antiserum produced in another individual or animal; D) an immunity which comes about through natural processes that follow exposure to the infectious agent. allergic rhinitis A) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; B) an allergic reaction to a particular food; C) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing; itchy, runny, or stuffy nose; and irritated eyes; D) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals). adenoids A) masses of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx; B) hormones secreted by adenohypophysis; C) clusters of air sacs at she end of bronchioles; D) rounded masses of lymphatic tissue in the orolarynx. pleura A) a bell-shaped sheet of muscle, separating the thoracic from the abdominal cavity; B) a double-folded membrane enveloping each lung; C) a small flat of muscular tissue at the entrance of the larynx; D) fine hairs (cilia) that help to filter out foreign bodies from the nasal cavities. bronchoplasty A) originating from the bronchi; B) swelling of the mucosa of the bronchial tube; C) surgical alteration of the configuration of a bronchus; D) narrowing of the bronchus lumen. neuritis A) a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system; B) a group of nerve cells forming a nerve center; C) inflammation of a peripheral nerve, often accompanied by degenerative changes in nervous tissue; D) physical condition characterized by general lassitude, irritability, and lack of concentration, worry, and hypochondria. knee jerk reflex A) an autonomic response to a stimulus; B) a reflex that demonstrates that the sensory nerve to the spinal cord, the nerve connections in the cord, and motor nerves back to the leg muscles are all functioning; C) a reflex which is tested by firmly stroking the outer border of the sole of the foot with a blunt object and in which the toes curl downward; D) a test in which a doctor asks a person to touch his nose with a forefinger, next to touch the doctor’s finger, and then to repeat these actions rapidly. angiasthenia A) weakness of the voice from fatigue; B) extreme strongness of blood vessels; C) paralysis of some blood vessels; D) fragility and weakness of blood vessels. equilibrioception A) the perception of balance or acceleration; B) the perception of pain; C) the sense of heat and cold; D) the sense of pressure perception, generally in the skin. osphresiometer A) instrument for measuring tactile sensitivity; B) olfactory nerve tumour; C) instrument for measuring smell sensitivity; D) a doctor trained to administer aneaesthesia. ophthalmologist A) a doctor trained to treat ear diseases; B) a doctor trained to treat eye diseases; C) study of the structure and functions of the eye; D) pertaining to eyes and face. anvil A) one of the ossicles, that is attached to the eardrum; B) all three tiny bones, called ossicles; C) one of the ossicles which is attacked to the oval window; D) one of the ossicles also called incus that connects the hammer and stirrup. diaphoresis A) perspiration, especially profuse perspiration; B) dryness of the mouth from salivary gland disfunction; C) pathologic dryness of the skin; D) condition in which painful areas of subcutaneous fat develop. antiperspirant A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a substance that the body produces in the blood to fight disease; C) a substance that stops the blood from becoming thick and forming clots; D) a substance that people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat. allergic conjunctivitis A) an allergy to airborne particles that causes sneezing, itching and runny nose; B) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; C) an injury of the conjunctiva; D) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction. tonsils A) masses of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx; B) rounded masses of lymphatic tissue in the orolarynx; C) clucter of air sacs at the end of bronchioles; D) the smallest of the bronchial branches. pneumoalveolography A) pertaining to the lungs and heart; B) a specialist in lung and alveoli diseases; C) x-ray examination of the air sacs of the lungs; D) resection of lung tissue. meninges A) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain, fills the ventricles and cushions the brain against injury; B) the three layers of tissue, the brain and the spinal cord are wrapped in; C) nerves at the front of the spinal cord, which carry information from the brain to the muscles; D) nerves at the back of the spinal cord, which carry sensory information from distant parts of the body to the brain. transient ishemic attack A) an insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain in which brain tissues die causing disabling neurologic damage; B) a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or benign; C) an inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord; D) temporary disturbances of brain function caused by insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain for brief period. ageusia A) the inability to hear; B) the inability to smell; C) the inability to taste; D) the inability to feel anything. sclera A) the front relatively tough white outer layer of the eye; B) a thin membrane in the eye; C) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. cataract A) a condition in which loss of vision occurs because of an abnormally high pressure in the eye; B) any opacity in the lense of the eye that results in blurred vision; C) paralysis of the iris sphincter; D) inflammation of the inner ear. stirrup A) one of the ossicles also called malleus attacked to the eardrum; B) one of the ossicles also called incus that connects the malleus and stapes; C) all three tiny bones connecting the eardrum to the inner ear; D) one of the ossicles also called stapes attached to the oval window at the entrance to the inner ear. lipoedema A) transformation of other types of cells into squamous cells; B) relating to both fatty and cellular tissue, or to connective tissue with many fat cells; C) oedema of subcutaneous fat, causing painful swellings, especially of the legs in women; D) a cell that ingests fat. antihistamine A) a substance that helps to prevent infection in wounds by killing bacteria; B) a drug used to treat allergies, especially hay fever; C) a substance that enters the body and can cause a disease; D) a substance the people use, especially in their armpits, to prevent or reduce sweat. anaphylaxis A) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such as cold, sunlight, heat, or minor injury; B) also called urticaria, a reaction in the skin characterized by small, pale or reddened swelling (wheals); C) an allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva; D) an acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction in a person who was previously sensitized by prior exposure to an allergen and who comes into contact with the same allergen again. pharynx A) windpipe; B) voice box; C) trachea; D) throat. cough A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; C) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially obstructed airways; D) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract. pneumobilia A) pertaining to the lungs and heart; B) presence of air or other gas in the bile system; C) presence of air or some other gas in bronchoedema; D) changes of breathing process. perioral dermatitis A) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens; B) typically develops in areas where something, such as a tight garment, rubs or scratches the skin; C) may be a form of the skin disorder rosacea, adult acne or seborrheic dermatitis, involving the skin around the mouth or nose; D) can occur when fluid accumulates in the tissues just beneath the skin, and typically involves the lower leg. cerebrospinal fluid A) nerves at the back of the spinal cord, which carry sensory information from distant parts of the body to the brain; B) the three layer of tissue the brain and the spinal cord are wrapped in; otherwise called as meninges; C) nerves at the front of the spinal cord carrying information from the brain to the muscles; D) fluid which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions it against sudden jarring and minor injury. stroke A) temporary disturbances of brain function caused by insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain for brief period; B) an insufficient blood supply to parts of the brain in which brain tissue die causing disabling neurologic damage; C) a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system which is characterized by tremor, sluggish initiation of movements, and muscle rigidity; D) an inflammation of the meninges usually caused by a virus. anosmia A) the inability to taste; B) the inability to feel anything or almost anything; C) the inability to smell; D) the inability to see. choroid A) a membranous lining inside the sclera that contains many blood vessels, which supply nutrients to the eye; B) a transparent dome on the surface of the eye; C) the circular, coloured area of the eye; D) the black area in the middle of the iris. otitis A) inflammation of the eye; B) inflammation of the ear; C) an over-growth of the bone of the inner ear that leads to inability of sound conduction to the inner ear; D) a fungus infection of the ear. xerophthalmia A) pathologic dryness of the skin; B) dryness of the mouth from salivary gland dysfunction; C) oedema of the conjunctiva and cornea due to profuse perspiration; D) dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea due to vitamin A deficiency. subhepatic A) located below the lower jaw; B) under the tongue; C) located below the liver; D) under the skin. vaccine A) misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; B) a substance made of weakened or killed microorganisms which is introduced into the body for prevention, improvement of the course or treatment of infectious diseases; C) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; D) the drug used in treatment by both congenital and acquired immunodeficiency. physical allergy A) a condition in which allergic symptoms develop in response to a physical stimulus, such a cold, sunlight, heat, or minor injury; B) acute, generalized, potentially severe and life-threatening allergic reaction to airborne particle; C) an allergic reaction to a particular food; D) damage or injury of the body caused by physical force, that is a blow, hick, prick, etc. oropharynx A) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passegeway for food from the mouth and air from the nose; B) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; C) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; D) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx. wheezing A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the unpleasant sensation of difficulty in breathing; C) a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially obstructed airways; D) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract. pneumocardial A) presence of gas or air in the cardium; B) air-like tissue surrounding the heart; C) inflammation of the lungs and head; D) pertaining to the lungs and heart. seborrheic dermatitis A) caused a red rash with a yellowish and somewhat “oily” scale; B) occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues just beneath the skin, and typically involves the lower leg; C) develops in areas where something rubs or scratches the skin; D) results from direct contact with one of many irritants or allergens. spinal cord A) a part of the CNS that lies beneath the cerebrum just above the brain stem and coordinates the body movements; B) the portion of the CNS enclosed in the vertebral column; C) the enlarged and highly developed mass of nervous tissue that forms the upper end of the CNS; D) fluid, which flows over the surface of the brain between the meninges, fills internal spaces within the brain, and cushions the brain against sudden jarring. electroencephalography A) a simple, painless procedure in which 20 wires are pasted on the scalp to trace and record the electrical activity of the brain; B) in this procedure a needle is inserted into the spinal canal to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid that is examined under the microscope; C) a computer-enhanced scanning technique for analyzing x-ray pictures to detect a wide range of brain and spinal abnormalities; D) a technique used to detect blood vessels abnormalities in the brain, such as an aneurism, inflammation or a blocked blood vessel. deafness A) the inability to see; B) the ability to hear very well; C) the inability to hear; D) the inability to smell. hyperesthesia A) any factor causing senses; B) loss of feeling; C) excessive sensitiveness; D) olfaction impairment. glaucoma A) any opacity in the lens of the eye that results in blurred vision; B) a condition in which loss of vision occurs because of an abnormally high pressure in the eye; C) any disease of the eye; D) inflammation of the retina and conjunctiva. otologist A) a specialist trained to treat ear diseases; B) a specialist trained to treat eye diseases; C) examination of the ear; D) inflammation of the Eustachian tube. epidermis A) a living tissue composed of blood and lymph vessels and nerve fibers, which lies directly below the external layer of the skin; B) a skin layer composed of connective tissue which specializes in the formation of fat; C) a total name for all the three layers of the skin; D) the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. macrophage A) a protein that interacts with the antigen; B) a cell of the lymphatic system; C) a large white blood cell that ingests microbes and antigens; D) an immunoglobulin. immunodeficiency disorders A) malfunctioning of the immune system, misinterpretation of the body tissues and attacking them by the immune system; B) a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately; C) disorders which have autoimmune cause, including lupus, myasthenia gravis, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, pemphigus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc; D) a disorder caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila, that accounts for 1 to 8 % of all pneumonias and about 4 % of fatal pneumonias. hypopharynx A) a small flap of muscular tissue covering the entrance to the larynx; B) the first division of the throat that is the nearest to the nasal cavities; C) the second division of the throat below nasopharynx and closer to the mouth; D) the third division of the pharynx serving as a common passegeway for food from the mouth and air from the nose. hemoptysis A) a sudden explosive movement of air that tends to clear material from the airways; B) the coughing up of blood from the respiratory tract; C) difficulty in breathing; D) a bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from a inadequate amount of blood causes by lung diseases. Вставте пропущене слово чи словосполучення: The ... is the organ of sight. A) ear; B) eye; C) nose; D) mouth. The ... contains nerve fiber tracts that connect the cerebellum and cerebrum with the rest of the brain. A) pons; B) neuron; C) tissue; D) vessels. A relatively simple, highly accurate ... test can be used to screen people for HIV infection. A) eye; B) mucous; C) blood; D) head. ... is a column of nervous tissue. A) brain; B) spinal cord; C) neuron; D) nerve fibres. ... is the mechanical process of breathing. A) hearing; B) respiration; C) inoculation; D) inflammation. The ... is a natural covering and an inseparable part of human body. A) tissue; B) skin; C) hair; D) heart. ... can degenerate, causing Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease. A) Cells; B) Tissues; C) Nerves; D) Blood. ... is an inflammation of both the brain and the spinal cord. A) Encephalitis; B) Encephalomyelitis; C) Parkinson’s disease; D) Stroke. ... is the exchange of gases in the cells and the tiny capillary blood vessels which surround them. A) Internal respiration; B) External respiration; C) Expiration; D) Inspiration. Only four basic tastes can be distinguished: sweet, sour, salty and ... . A) delicious; B) greasy; C) bitter; D) cold. The ... is the organ of sight. A) ear; B) eye; C) nose; D) mouth. The ... contains nerve fiber tracts that connect the cerebellum and cerebrum with the rest of the brain. A) pons; B) neuron; C) tissue; D) vessels. If you can’t smell or taste your …, you may eat too much and gain weight. A) foot; B) tooth; C) food; D) feet. The cornea helps in focusing light on the … at the back of the eye. A) pupil; B) sclera; C) retina; D) conjunctiva. The ear serves as an organ of both … and balance. A) vision; B) division; C) lesion; D) hearing. The epidermis is the … layer of the skin forming the protective wrap of the body surface. A) outermost; B) innermost; C) liquid; D) middle. Anti-infective agents … the skin from different viral, bacterial, and fungal infections. A) infect; B) protect; C) injure; D) operate. Macrophages and neutrophiles are … that ingest microbes and antigens. A) minute white blood cells; B) large white blood cells; C) tiny red blood cells; D) very big red blood cells. Learned immunity is subdivided into acquired immunity, … and active immunity. A) innate immunity; B) immunodeficienty; C) autoimmunity; D) passive immunity. A relatively simple, highly accurate ... test can be used to screen people for HIV infection. A) eye; B) mucous; C) blood; D) head. The lymph nodes swell because the lymphatic vessels drain the infection by carrying it to the nearest area where an … can be organized. A) immunodeficiency disorder; B) allergic reaction; C) autoimmune reaction; D) immune response. … are a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately, so infections are more common. A) Immunodeficiency disorders; B) Autoimmune reactions; C) Respiratory symptoms; D) Eye diseases. The tonsils, two rounded masses of lymphatic tissue, are located in the … . A) nasopharynx; B) oropharynx; C) hypopharynx; D) lungs. The healthy person breathes … during exercise and at high altitudes. A) slower; B) faster; C) longer; D) shorter. In most cases, the diagnosis of pneumonia is confirmed with a … . A) urinanalysis; B) ophthalmoscopy; C) tympanometry; D) chest x-ray. The cerebrum is divided into the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal … . A) lobes; B) quarters; C) extremities; D) hemispheres. The inability to feel anything or almost anything is called … . A) thermoception; B) nociception; C) equilibrioception; D) paresthesia. ... is a column of nervous tissue. A) brain; B) spinal cord; C) neuron; D) nerve fibres. ... is the mechanical process of breathing. A) hearing; B) respiration; C) inoculation; D) inflammation. The ... is a natural covering and an inseparable part of human body. A) tissue; B) skin; C) hair; D) heart. ... can degenerate, causing Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease. A) Cells; B) Tissues; C) Nerves; D) Blood. Reactions of the immune system in which normal body tissue is injured are called ... . A) allergens; B) atopic reactions; C) anaphylaxis; D) allergic reactions. The ... coordinates the body movements. A) hypothalamus; B) thalamus; C) cerebrum; D) cerebellum. One of the primary functions of the respiratory system is to bring … into the lungs. A) carbon dioxide; B) oxygen; C) nitrogen; D) hydrogen. The cerebrum is divided into the frontal, parietal, …, and temporal lobes. A) occipital; B) pituitary; C) cerebral; D) back. The immune system is composed of … and soluble substances. A) nerves; B) sense organs; C) respiration; D) cells. … is an infection by one of two viruses that progressively destroys white blood cells, causing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and other diseases that result from the impaired immunity. A) HIV infection; B) AIDS; C) Allergic reaction; D) Lower respiratory tract infection. The … is a natural covering and an inseparable part of the human body. A) skin; B) hair; C) nail; D) shin. The corium layer, directly …, is also called dermis. A) below the subcutaneous adipose layer; B) above the epidermis; C) above the corneum layer of the skin; D) below the epidermis. The ear serves a dual purpose as an organ of both … and balance. A) vision; B) smell; C) hearing; D) taste. The lens is located … the iris. A) before; B) behind; C) to the right of; D) in the middle of. The … to taste is called ageusia. A) ability; B) inability; C) super ability; D) likelihood. Headaches are among the … medical problems. A) rare; B) least common; C) most common; D) gravest. The brain has three major anatomic components: …, the brain stem, and … . A) the spinal cord, the meninges; B) the forehead, the temples; C) the cerebrum, the cerebellum; D) pia mater, dura mater. The third division of the … is the hypopharynx. A) larynx; B) pharynx; C) mouth; D) hypophysis. Dyspnea … the amount of exercises that can be performed. A) expands; B) enlarges; C) limits; D) increases. Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the …, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria. A) middle ear; B) bronchi; C) larynx; D) throat. The brain and its meninges are contained in a tough, bony protective structure, the … . A) skull; B) skin; C) school; D) vertebrae. The inability … anything or almost anything is called paresthesia. A) to smell; B) to see; C) to hear; D) to feel. ... typically develops in areas where something, such as a tight garment, rubs or scratches your skin. A) Atopic dermatitis; B) Stasis dermatitis; C) Perioral dermatitis; D) Neurodermatitis. The function of the immune system is … the body against microbes, cancer cells, transplanted tissues and organs. A) to invade; B) to harm; C) to hurt; D) to defend. Everyone is born with … immunity. A) innate; B) learned; C) passive; D) active. Interruption of … for only a few minutes by suffocation or strangulation causes death. A) hearing; B) seeing; C) breathing; D) smelling. Among the most common symptoms of … are a cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, wheezing, stridor, hemoptysis, and respiratory failure. A) nervous disorders; B) respiratory disorders; C) ophthalmic disorders; D) immune disorders. A person suffering from bronchitis may … sputum, which may be yellow or green. A) digest; B) breath; C) inhale; D) cough up. The … consists of the brain and spinal cord. A) central nervous system; B) peripheral nervous system; C) autonomic nervous system; D) nervous system. Sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch are considered to be the major human …. A) organs; B) tissues; C) senses; D) parts. ... are individual nerve cells of microscopic structure. A) Neurons; B) Nerves; C) Tissues; D) Vessels. The exchange of gases in the cells within the organs of the body is called ... . A) inspiration; B) expiration; C) external respiration; D) internal respiration. A ... is a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or benign. A) tissue; B) tumour; C) cell; D) nerve. The ... is next under the epidermis. A) papillary layer; B) reticular layer; C) derma; D) adipose layer. The function of the … is to defend the body against invades (microbes, cancer cells, transplanted tissues and organs). A) respiratory system; B) nervous system; C) sense organs; D) immune system. … is a suspension of dead, attenuated, or otherwise modified microorganisms for inoculation to produce immunity to a disease. A) Antihistamine; B) Vaccine; C) Antibiotic; D) Blood. Air enters the body through the … . A) ear; B) blood; C) nose; D) lungs. A cough is a sudden explosive movement of … that tends to clear material from the airways. A) blood; B) air; C) saliva; D) urine. Pneumonia is an infection of the … that involves alveoli and the tissues around them. A) trachea; B) pharynx; C) bronchi; D) lungs. The … consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. A) central nervous system; B) peripheral nervous system; C) autonomic nervous system; D) nervous system. Almost 90 % of the information is supplied to the brain through … . A) ears; B) eyes; C) nose; D) throat. We can see, think, hear, respond to pain, temperature, touch, etc. thanks to the activities of the body controlled by the ... . A) respiratory system; B) nervous system; C) sensory system; D) immune system. ... occurs when the protective material, specific for a given infectious agent, is produced in another individual and given thus “ready-made” to the patient. A) Natural immunity; B) Acquired immunity; C) Passive immunity; D) Active immunity. Soft growths of abnormal nerve tissue are called … . A) tumours; B) neurofibromas; C) neoplasm; D) tissues. The ... is located beneath the posterior part of the cerebrum. A) cerebellum; B) thalamus; C) hypothalamus; D) pons. When a person is caused to develop his own antibodies, it is an example of ... . A) natural immunity; B) acquired immunity; C) passive immunity; D) active immunity. The most important muscle used for breathing is the ... . A) lung; B) pleura; C) trachea; D) diaphragm. The skin is intimately connected with the central ... . A) digestive system; B) immune system; C) nervous system; D) respiratory system. On its way to the lungs, air passes from the larynx to the ... . A) nasal cavity; B) trachea; C) alveolus; D) diaphragm. Senses are the physiological methods of … . A) nociception; B) perception; C) tactition; D) gustation. The … can be seen at work when a wound or an infection in a fingertip leads to an enlarged lymph node at the elbow. A) respiratory system; B) nervous system; C) sense organs; D) immune system. Sometimes the immune system malfunctions, misinterprets the body tissues as foreign, and attacks them, resulting in an … . A) autoimmune reaction; B) immune reaction; C) cough and sneezing; D) vision impairment. The nasopharynx is the first division of the …, and is the nearest to the nasal cavities. A) larynx; B) pharynx; C) adenoids; D) nose. Coughing is one way in which the … are protected. A) eyes and ears; B) lungs and airways; C) stomach and duodenum; D) brain and spinal cord. Common symptoms of … are a cough that produces sputum, chest pain, chills, fever, and shortness of breath. A) Parkinson’s disease; B) headache; C) glaucoma; D) pneumonia. The … has three major anatomic components: the cerebrum, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. A) spinal cord; B) nervous system; C) CNS; D) brain. The taste receptors on the … detect sweet, salt, sour, and bitter . A) nose; B) throat; C) tongue; D) eye. The ..., the largest unit of the respiratory system, look like large pink sponges that almost fill the chest. A) heart; B) lungs; C) nose; D) liver. Dermatitis is also called ... . A) inborn resistance; B) epidermis; C) eczema; D) stimulus. A ... is an abnormal mass anywhere in the body. A) tissue; B) tumour; C) cell; D) nerve. Almost 90 % of the information is supplied to the brain through ... . A) eyes; B) ears; C) mouth; D) blood. The ear comprises three sections: the outer ear, the middle ear and the ... . A) eardrum; B) inner ear; C) ear canal; D) pinna. Acquired partial or complete protection against certain infectious diseases is called ... . A) natural immunity; B) acquired immunity; C) passive immunity; D) active immunity. The major cells of the immune system are the … . A) nervous cells; B) red blood cells; C) erythrocytes; D) white blood cells. The … can be seen at work when a throat infection causes the lymph nodes under the jaw to swell. A) respiratory system; B) nervous system; C) sense organs; D) immune system. Such disorders as lupus, myasthenia gravis, Graves’ disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, pemphigus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, Sjögren’s syndrome, and pernicious anemia have … cause. A) autoimmune; B) allergic; C) neurological; D) ophthalmic. Below the nasopharynx and closer to the mouth is the second division of the …, the orolarynx. A) larynx; B) pharynx; C) mouth; D) nose. Shortness of breath is the … sensation of difficulty in breathing. A) pleasant; B) unpleasant; C) wonderful; D) nice. When a person appears to have pneumonia, a doctor listens to the chest with a … to evaluate the condition. A) laryngoscope; B) bronchoscope; C) stethoscope; D) sterile rubber glove. The cerebrum consists of dense, convoluted masses of tissue divided into the left and the right cerebral … . A) quarters; B) extremities; C) hemispheres; D) nerves. It is the … that performs olfactory response and detects smells by means of the specialized olfactory nerve ending. A) throat; B) tongue; C) nose; The transmission of HIV requires contact with contaminated … such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, cerebrospinal fluid, and breast milk. A) body fluid; B) human hair; C) toenails; D) body bone. The entrance to the larynx is covered by a … called epiglottis. A) mucous membrane; B) fluid-containing sac; C) small flap of muscular tissue; D) clusters of air sacs. Pleuritic pain, a sharp pain arising from an irritation in the lining of the lungs, is made … by deep breathing and coughing. A) better; B) more pleasant; C) worse; D) enjoyable. … is a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles. A) Ointment; B) Tablet; C) Tincture; D) Powder. The spinal cord is protected by the … that make up the spinal column. A) vertebrae; B) skull; C) skin; D) spleen. The lacrimal nerve of the eye stimulates the tear glands to produce … . A) blood; B) mucous; C) saliva; D) tears. ... is an infection by one or two viruses that destroys white blood cells causing diseases that result from the impaired immunity. A) HIV; B) AIDS; C) IgE; D) ME. The upper and lower ... protect the outer surface of the eye. A) jaws; B) eyelids; C) limbs; D) lips. Respiration is the mechanical process of ... . A) eating; B) speaking; C) breathing; D) coughing. The ... system includes: neurons, nerves, brain, and meninges. A) respiratory; B) nervous; C) sensory; D) immune. The ... is the primary center for regulating and coordinating of body activities. A) heart; B) lungs; C) brain; D) neck. There are 5 main human senses, they are: sight, hearing, smell, taste and ... . A) perception; B) touch; C) breathing; D) talking. Derma is located under the ... . A) epidermis; B) true skin; C) subcutaneous adipose layer; D) epithelial cells. The smallest of the bronchial branches are called ... . A) alveoli; B) bronchioles; C) erythrocytes; D) capillaries. Dermatitis is an inflammation of ... . A) lungs; B) skin; C) ear; D) eye. The ... is the centre of regulations and coordination of body activities. A) heart; B) lungs; C) brain; D) neurons. Nervous system contains 100 billion or more ... . A) tumours; B) nerve cells; C) vessels; D) tissues. ... deals with the study of odors and the sense of smell. A) osphresiology; B) ophthalmology; C) otolaryngology; D) cardiology. The largest part of the brain is ... . A) pons; B) cerebellum; C) cerebrum; D) spinal cord. Air enters through the ... and passes through nasal cavities. A) ear; B) hairs; C) nose; D) cells. Human immunodeficiency virus infection is an infection by one or two viruses that progressively destroys white blood cells called ... causing AIDS. A) thrombocytes; B) lymphocytes; C) granulocytes; D) erythrocytes. The size of the pupil is controlled by the …, which opens and closed the iris. A) aqueous humor; B) retina; C) sclera; D) papillary sphincter muscle. ... is an inflammation of brain caused by a virus. A) Encephalitis; B) Encephalomyelitis; C) Parkinson’s disease; D) Tumour. ... is the process when air is expelled out of the lungs to equalize the pressure. A) Inspiration; B) Expiration; C) Respiration; D) Accumulation. ... protects the brain and spinal cord from shock as might a cushion. A) Muscle tissue; B) Cerebrospinal fluid; C) Mucus; D) Skull. The ... is a column of nervous tissue. A) brain; B) eyes; C) spinal cord; D) nerve. The ... can be subdivided into the following strata: corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum and basale. A) epidermis; B) derma; C) corium layer; D) subcutaneous adipose layer. ... is inborn resistance to specific diseases which individuals may possess. A) Natural immunity; B) Acquired immunity; C) Passive immunity; D) Active immunity. Macrophages and neutrophils are large … that ingest microbes and antigens. A) nervous cells; B) red blood cells; C) erythrocytes; D) white blood cells. In the region of mediastinum, the … divides into two branches called bronchi. A) nose; B) pharynx; C) trachea; D) epiglottis. … is an inflammation of the voice box. A) Tonsillitis; B) Pharyngitis; C) Bronchitis; D) Laryngitis. ... may include headaches, pain, weakness, poor coordination, diminished or abnormal sensations, fainting, and confusion. A) Neurologic symptoms; B) Respiratory symptoms; C) Dermatologic disorders; D) Gustation symptoms. Allergic reactions are reactions of the … in which normal body tissue is injured. A) immune system; B) respiratory system; C) nervous system; D) sense organs. Wheezing is a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially … airways. A) expanded; B) increased; C) obstructed; D) enlarged. The … consists of the eardrum and a small air-filled chamber containing a chain of three ossicles. A) outer ear; B) middle ear; C) inner ear; D) labyrinth. The most common cause of recurring wheezing is … . A) leukemia; B) cataract; C) asthma; D) otitis. The … consists of the pinna or auricle and the external auditory meatus. A) outer ear; B) middle ear; C) inner ear; D) labyrinth. An … can be almost anything – dust, plant pollen, a drug, or food – that acts as an antigen to stimulate an immune response. A) allergen; B) antihistamine; C) antibody; D) illness. At the end of the bronchioles there are … called alveoli. A) mucous membranes; B) fluid-containing sacs; C) small flaps of muscular tissue; D) clusters of air sacs. The lower leg jerks when the tendon below the kneecap is gently tapped with a small rubber … . A) glove; B) hammer; C) bronchoscope; D) injection. The accumulation of neutrophils and killing and digesting of microbes leads to the formation of … . A) gas; B) saliva; C) blood; D) pus. … is an inflammation of the membrane lining a sinus, especially a nasal sinus. A) Tonsillitis; B) Pharyngitis; C) Laryngitis; D) Sinusitis. … (also called immunoglobulins) are proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes. A) White blood cells; B) Red blood cells; C) Allergens; D) Antibodies. … an allergen is better than trying to treat an allergic reaction. A) Avoiding; B) Subjecting; C) Exposing; D) Eating. The … of the bronchial branches are called bronchioles. A) broadest; B) largest; C) smallest; D) biggest. A doctor usually is able to detect wheezing by listening with a … as the person breathes. A) laryngoscope; B) bronchoscope; C) stethoscope; D) sterile rubber glove. Nerve cells collected into bundles called nerves carry … all over the body. A) electrical messages; B) external stimuli; C) internal chemicals; D) electronic calculations. Parkinson’s disease is a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the … . A) nervous system; B) immune system; C) respiratory system; D) gastro-intestinal system. The … is the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. A) epidermis; B) dermis; C) corium layer; D) subcutaneous adipose layer. There are 5 classes of …: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, and IgD. A) white blood cells; B) red blood cells; C) allergens; D) antibodies. … are the drugs most commonly used for treating allergies. A) Antihistamines; B) Antibiotics; C) Aspirin; D) Analgesics. Each lung is enveloped in a … called pleura. A) small flap of muscular tissue; B) cluster of air sacs; C) double-folded membrane; D) thin fluid. Bronchitis is an … of the bronchi usually caused by an infection. A) irritation; B) inspection; C) inflammation; D) inoculation. The nervous system can be classified into two major divisions: … and the peripheral nervous system. A) the middle nervous system; B) the spinal cord; C) the autonomic nervous system; D) the central nervous system. A tumour is a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or … . A) benign; B) cancerous; C) neoplasm; D) ligament. The subcutaneous adipose layer of the skin is a connective tissue layer which specializes in the formation of … . A) tears; B) sweat; C) hair; D) fat. The ... is the organ of sight. A) ear; B) eye; C) nose; D) mouth. The ... contains nerve fiber tracts that connect the cerebellum and cerebrum with the rest of the brain. A) pons; B) neuron; C) tissue; D) vessels. A relatively simple, highly accurate ... test can be used to screen people for HIV infection. A) eye; B) mucous; C) blood; D) head. ... is a column of nervous tissue. A) Brain; B) Spinal cord; C) Neuron; D) Nerve fibers. ... is the mechanical process of breathing. A) Hearing; B) Respiration; C) Inoculation; D) Inflammation. The ... is a natural covering and an inseparable part of human body. A) tissue; B) skin; C) hair; D) heart. ... can degenerate, causing Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease. A) Ears; B) Skin; C) Nerves; D) Blood. The tonsils, two rounded masses of lymphatic tissue, are located in the … . A) nasopharynx; B) oropharynx; C) hypopharynx; D) lungs. In most cases, the diagnosis of pneumonia is confirmed with a … . A) urinanalysis; B) ophthalmoscopy; C) tympanometry; D) chest x-ray. … are a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately, so infections are more common. A) Immunodeficiency disorders; B) Autoimmune reactions; C) Respiratory symptoms; D) Eye diseases. The lymph nodes swell because the lymphatic vessels drain the infection by carrying it to the nearest area where an … can be organized. A) immunodeficiency disorder; B) allergic reaction; C) autoimmune reaction; D) immune response. The cerebrum is divided into the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal … . A) lobes; B) quarters; C) extremities; D) hemispheres. The inability to feel anything or almost anything is called … . A) thermoception; B) nociception; C) equilibrioception; D) paresthesia. The healthy person breathes … during exercise and at high altitudes. A) slower; B) faster; C) longer; D) shorter. The inability … anything or almost anything is called paresthesia. A) to smell; B) to see; C) to hear; D) to feel. … is an infection by one of two viruses that progressively destroys white blood cells, causing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and other diseases that result from the impaired immunity. A) HIV infection; B) AIDS; C) Allergic reaction; D) Lower respiratory tract infection. Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the …, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria. A) middle ear; B) bronchi; C) larynx; D) throat. The third division of the … is the hypopharynx. A) larynx; B) pharynx; C) mouth; D) hypophysis. Dyspnea … the amount of exercises that can be performed. A) expands; B) enlarges; C) limits; D) increases. The immune system is composed of … and soluble substances. A) nerves; B) sense organs; C) respiration; D) cells. The brain and its meninges are contained in a tough, bony protective structure, the … . A) skull; B) skin; C) school; D) vertebrae. The entrance to the larynx is covered by a … called epiglottis. A) mucous membrane; B) fluid-containing sac; C) small flap of muscular tissue; D) clusters of air sacs. The lacrimal nerve of the eye stimulates the tear glands to produce … . A) blood; B) mucous; C) saliva; D) tears. The transmission of HIV requires contact with contaminated … such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, cerebrospinal fluid, and breast milk. A) body fluid; B) human hair; C) toenails; D) body bone. The spinal cord is protected by the … that make up the spinal column. A) vertebrae; B) skull; C) skin; D) spleen. Pleuritic pain, a sharp pain arising from an irritation in the lining of the lungs, is made … by deep breathing and coughing. A) better; B) more pleasant; C) worse; D) enjoyable. … is a medicinal preparation consisting of a mixture of two or more drugs in the form of fine particles. A) Ointment; B) Tablet; C) Tincture; D) Powder. The major cells of the immune system are the … . A) nervous cells; B) red blood cells; C) erythrocytes; D) white blood cells. Allergic reactions are reactions of the … in which normal body tissue is injured. A) immune system; B) respiratory system; C) nervous system; D) sense organs. ... may include headaches, pain, weakness, poor coordination, diminished or abnormal sensations, fainting, and confusion. A) Neurologic symptoms; B) Respiratory symptoms; C) Dermatologic disorders; D) Gustation symptoms. Wheezing is a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially … airways. A) expanded; B) increased; C) obstructed; D) enlarged. … is an inflammation of the voice box. A) Tonsillitis; B) Pharyngitis; C) Bronchitis; D) Laryngitis. In the region of mediastinum, the … divides into two branches called bronchi. A) nose; B) pharynx; C) trachea; D) epiglottis. The … consists of the eardrum and a small air-filled chamber containing a chain of three ossicles. A) outer ear; B) middle ear; C) inner ear; D) labyrinth. Macrophages and neutrophils are large … that ingest microbes and antigens. A) nervous cells; B) red blood cells; C) erythrocytes; D) white blood cells. An … can be almost anything – dust, plant pollen, a drug, or food – that acts as an antigen to stimulate an immune response. A) allergen; B) antihistamine; C) antibody; D) illness. The lower leg jerks when the tendon below the kneecap is gently tapped with a small rubber … . A) glove; B) hammer; C) bronchoscope; D) injection. The most common cause of recurring wheezing is … . A) leukemia; B) cataract; C) asthma; D) otitis. The accumulation of neutrophils and killing and digesting of microbes leads to the formation of … . A) gas; B) saliva; C) blood; D) pus. At the end of the bronchioles there are … called alveoli. A) mucous membranes; B) fluid-containing sacs; C) small flaps of muscular tissue; D) clusters of air sacs. … is an inflammation of the membrane lining a sinus, especially a nasal sinus. A) Tonsillitis; B) Pharyngitis; C) Laryngitis; D) Sinusitis. The … consists of the pinna or auricle and the external auditory meatus. A) outer ear; B) middle ear; C) inner ear; D) labyrinth. … an allergen is better than trying to treat an allergic reaction. A) Avoiding; B) Subjecting; C) Exposing; D) Eating. The … of the bronchial branches are called bronchioles. A) broadest; B) largest; C) smallest; D) biggest. A doctor usually is able to detect wheezing by listening with a … as the person breathes. A) laryngoscope; B) bronchoscope; C) stethoscope; D) sterile rubber glove. Nerve cells collected into bundles called nerves carry … all over the body. A) electrical messages; B) external stimuli; C) internal chemicals; D) electronic calculations. … (also called immunoglobulins) are proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes. A) White blood cells; B) Red blood cells; C) Allergens; D) Antibodies. The … is the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. A) epidermis; B) dermis; C) corium layer; D) subcutaneous adipose layer. Parkinson’s disease is a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the … . A) nervous system; B) immune system; C) respiratory system; D) gastro-intestinal system. … are the drugs most commonly used for treating allergies. A) Antihistamines; B) Antibiotics; C) Aspirin; D) Analgesics. A tumour is a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or … . A) benign; B) cancerous; C) neoplasm; D) ligament. Each lung is enveloped in a … called pleura. A) small flap of muscular tissue; B) cluster of air sacs; C) double-folded membrane; D) thin fluid. There are 5 classes of …: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, and IgD. A) white blood cells; B) red blood cells; C) allergens; D) antibodies. The nervous system can be classified into two major divisions: … and the peripheral nervous system. A) the middle nervous system; B) the spinal cord; C) the autonomic nervous system; D) the central nervous system. The subcutaneous adipose layer of the skin is a connective tissue layer which specializes in the formation of … . A) tears; B) sweat; C) hair; D) fat. Bronchitis is an … of the bronchi usually caused by an infection. A) irritation; B) inspection; C) inflammation; D) inoculation. A relatively simple, highly accurate ... test can be used to screen people for HIV infection. A) eye; B) mucous; C) blood; D) head. ... is the mechanical process of breathing. A) Hearing; B) Respiration; C) Inoculation; D) Inflammation. The ... is the organ of sight. A) ear; B) eye; C) nose; D) mouth. The ... is a natural covering and an inseparable part of human body. A) tissue; B) skin; C) hair; D) heart. The ... contains nerve fiber tracts that connect the cerebellum and cerebrum with the rest of the brain. A) pons; B) neuron; C) tissue; D) vessels. ... can degenerate, causing Alzheimer’s disease or Parkinson’s disease. A) Ears; B) Skin; C) Nerves; D) Blood. ... is a column of nervous tissue. A) Brain; B) Spinal cord; C) Neuron; D) Nerve fibres. The lymph nodes swell because the lymphatic vessels drain the infection by carrying it to the nearest area where an … can be organized. A) immunodeficiency disorder; B) allergic reaction; C) autoimmune reaction; D) immune response. … are a group of diverse conditions in which the immune system doesn’t function adequately, so infections are more common. A) Immunodeficiency disorders; B) Autoimmune reactions; C) Respiratory symptoms; D) Eye diseases. The tonsils, two rounded masses of lymphatic tissue, are located in the … . A) nasopharynx; B) oropharynx; C) hypopharynx; D) lungs. The healthy person breathes … during exercise and at high altitudes. A) slower; B) faster; C) longer; D) shorter. In most cases, the diagnosis of pneumonia is confirmed with a … . A) urinanalysis; B) ophthalmoscopy; C) tympanometry; D) chest x-ray. The cerebrum is divided into the frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal … . A) lobes; B) quarters; C) extremities; D) hemispheres. The inability to feel anything or almost anything is called … . A) thermoception; B) nociception; C) equilibrioception; D) paresthesia. The immune system is composed of … and soluble substances. A) nerves; B) sense organs; C) respiration; D) cells. … is an infection by one of two viruses that progressively destroys white blood cells, causing acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and other diseases that result from the impaired immunity. A) HIV infection; B) AIDS; C) Allergic reaction; D) Lower respiratory tract infection. The third division of the … is the hypopharynx. A) larynx; B) pharynx; C) mouth; D) hypophysis. Dyspnea … the amount of exercise that can be performed. A) expands; B) enlarges; C) limits; D) increases. Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the …, usually caused by a virus but also commonly caused by bacteria. A) middle ear; B) bronchi; C) larynx; D) throat. The brain and its meninges are contained in a tough, bony protective structure, the … . A) skull; B) skin; C) school; D) vertebrae. The inability … anything or almost anything is called paresthesia. A) to smell; B) to see; C) to hear; D) to feel. The major cells of the immune system are the … . A) nervous cells; B) red blood cells; C) erythrocytes; D) white blood cells. The transmission of HIV requires contact with contaminated … such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, cerebrospinal fluid, and breast milk. A) body fluid; B) human hair; C) toenail; D) body bone. The entrance to the larynx is covered by a … called epiglottis. A) mucous membrane; B) fluid-containing sac; C) small flap of muscular tissue; D) clusters of air sacs. Pleuritic pain, a sharp pain arising from an irritation in the lining of the lungs, is made … by deep breathing and coughing. A) better; B) more pleasant; C) worse; D) enjoyable. Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the palatine …, causing enlargement, occasionally to the extent that they nearly touch one another. A) larynx; B) pharynx; C) bronchi; D) tonsils. The spinal cord is protected by the … that make up the spinal column. A) vertebrae; B) skull; C) skin; D) spleen. The lacrimal nerve of the eye stimulates the tear glands to produce … . A) blood; B) mucous; C) saliva; D) tears. Macrophages and neutrophils are large … that ingest microbes and antigens. A) nervous cells; B) red blood cells; C) erythrocytes; D) white blood cells. Allergic reactions are reactions of the … in which normal body tissues is injured. A) immune system; B) respiratory system; C) nervous system; D) sense organs. In the region of mediastinum, the … divides into two branches called bronchi. A) nose; B) pharynx; C) trachea; D) epiglottis. Wheezing is a whistling, musical sound during breathing that results from partially … airways. A) expanded; B) increased; C) obstructed; D) enlarged. … is an inflammation of the voice box. A) Tonsillitis; B) Pharyngitis; C) Bronchitis; D) Laryngitis. ... may include headaches, pain, weakness, poor coordination, diminished or abnormal sensations, fainting, and confusion. A) Neurologic symptoms; B) Respiratory symptoms; C) Dermatologic disorders; D) Gustation symptoms. The … consists of the eardrum and a small air-filled chamber containing a chain of three ossicles. A) outer ear; B) middle ear; C) inner ear; D) labyrinth. The accumulation of neutrophils and killing and digesting of microbes leads to the formation of … . A) gas; B) saliva; C) blood; D) pus. An … can be almost anything – dust, plant pollen, a drug, or food – that acts as an antigen to stimulate an immune response. A) allergen; B) antihistamine; C) antibody; D) illness. At the end of the bronchioles there are … called alveoli. A) mucous membranes; B) fluid-containing sacs; C) small flaps of muscular tissue; D) clusters of air sacs. The most common cause of recurring wheezing is … . A) leukemia; B) cataract; C) asthma; D) otitis. … is an inflammation of the membrane lining a sinus, especially a nasal sinus. A) Tonsillitis; B) Pharyngitis; C) Laryngitis; D) Sinusitis. The lower leg jerks when the tendon below the kneecap is gently tapped with a small rubber … . A) glove; B) hammer; C) bronchoscope; D) injection. The … consists of the pinna or auricle and the external auditory meatus. A) outer ear; B) middle ear; C) inner ear; D) labyrinth. … (also called immunoglobulins) are proteins that interact with the antigen that initially stimulated the B lymphocytes. A) White blood cells; B) Red blood cells; C) Allergens; D) Antibodies. … an allergen is better than trying to treat an allergic reaction. A) Avoiding; B) Subjecting; C) Exposing; D) Eating. The … of the bronchial branches are called bronchioles. A) broadest; B) largest; C) smallest; D) biggest. A doctor usually is able to detect wheezing by listening with a … as the person breathes. A) laryngoscope; B) bronchoscope; C) stethoscope; D) sterile rubber glove. Nerve cells collected into bundles called nerves carry … all over the body. A) electrical messages; B) external stimuli; C) internal chemicals; D) electronic calculations. Parkinson’s disease is a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the … . A) nervous system; B) immune system; C) respiratory system; D) gastro-intestinal system. The … is the outermost, totally cellular layer of the skin forming the waterproof, protective wrap of the body surface. A) epidermis; B) dermis; C) corium layer; D) subcutaneous adipose layer. There are 5 classes of …: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, and IgD. A) white blood cells; B) red blood cells; C) allergens; D) antibodies. … are the drugs most commonly used for treating allergies. A) Antihistamines; B) Antibiotics; C) Aspirin; D) Analgesics. Each lung is enveloped in a … called pleura. A) small flap of muscular tissue; B) cluster of air sacs; C) double-folded membrane; D) thin fluid. Bronchitis is an … of the bronchi usually caused by an infection. A) irritation; B) inspection; C) inflammation; D) inoculation. The nervous system can be classified into two major divisions: … and the peripheral nervous system. A) the middle nervous system; B) the spinal cord; C) the autonomic nervous system; D) the central nervous system. A tumour is a pathologic new growth that can be either malignant or … . A) benign; B) cancerous; C) neoplasm; D) ligament. The subcutaneous adipose layer of the skin is a connective tissue layer which specializes in the formation of … . A) tears; B) sweat; C) hair; D) fat. Вставте присудок у правильному часі і стані: The professor … just … the students about different nervous system tumours. A) is … told; B) has … told; C) does … tell; D) are … telling. The patient … blood transfusion before the surgeon entered the operating room. A) was performed; B) was being performed; C) had been performed; D) had been performing. The pulmonary abscess usually … via the bronchus. A) was being drained; B) had been drained; C) is drained; D) drain. The patient … from constant pain in the ear for several weeks before he visited a doctor. A) suffered; B) was suffering; C) had been suffering; D) had suffered. In some days, when the body temperature is normal, the patient … to walk a little. A) will allow; B) will be allowed; C) will be allowing; D) will have allowed. … purulent discharge already … into the external auditory canal? A) Has … poured; B) Was … poured; C) Had … poured; D) Does … pour. By 3 o’clock the professor … the lecture for half an hour already. A) will deliver; B) will have delivered; C) will be delivering; D) will have been delivering. The newborn … HIV infection from his mother suffering from AIDS. A) had acquired; B) acquired; C) was acquired; D) had been acquired. … an otolaryngologist easily … among other surgeons by the head mirror he wears attached to his forehead? A) Does … recognize; B) Is … recognized; C) Is …recognizing; D) Did …recognize. The doctor … this case for three weeks by the end of the year. A) is investigating; B) will be investigating; C) will have been investigated; D) will have been investigating. A week before the admission to the hospital the patient … bronchitis after which his condition did not improve. A) has had; B) had had; C) was having; D) had. What … the patient … about when the students entered the doctor’s consulting room? A) were … being asked; B) are … asked; C) was … being asked; D) were … asked. The patient … numerous foci of inflammation in the left lung before he underwent the streptomycin treatment. A) had; B) had had; C) was having; D) has. Don’t worry. The doctor … here to give help if it … . A) will be, is needed; B) will be, will be needed; C) will is, will needs; D) shall, shall be needed. I … the paragraph on types of immunity for half an hour already. A) have read; B) am reading; C) have been reading; D) have been read. The nurse … busy this morning, hasn’t she? A) have been; B) was; C) is; D) has been. The professor was tired as he … on the rate of AIDS spread in Ukraine for about an hour. A) had reported; B) had been reporting; C) was reporting; D) had been reported. The patient with pharyngolaryngitis … antibiotics now. A) is being injected; B) is injecting; C) was injected; D) will be injecting. Coughing episodes … recently … by chest pain. A) did … accompany; B) has … accompanied; C) have … been accompanied; D) was … accompanied. The lecturer told us that a day later we … a test on the anatomy of the brain and spinal cord. A) will write; B) would write; C) write; D) are writing. The patient … blood transfusion before the surgeon entered the operating room. A) was performed; B) was being performed; C) had been performed; D) had been performing. The pulmonary abscess usually … via the bronchus. A) was being drained; B) had been drained; C) is drained; D) drain. The patient … from constant pain in the ear for several weeks before he visited a doctor. A) suffered; B) was suffering; C) had been suffering; D) had suffered. In some days, when the body temperature is normal, the patient … to walk a little. A) will allow; B) will be allowed; C) will be allowing; D) will have allowed. … purulent discharge already … into the external auditory canal? A) Has … poured; B) Was … poured; C) Had … poured; D) Does … pour. By 3 o’clock the professor … the lecture for half an hour already. A) will deliver; B) will have delivered; C) will be delivering; D) will have been delivering. A man … unconscious for a few minutes before an ambulance arrived. A) were; B) has been; C) had been; D) was. The patient … for the doctor since seven o’clock. A) waited; B) had waited; C) has been waiting; D) is waiting. She … for her stethoscope since she came to the hospital. A) looks; B) had looked; C) is looking; D) has been looking. Usually I … coffee in the morning. I … from hypertension. A) don’t have / suffer; B) haven’t / am suffering; C) am not having / suffer; D) have / suffer. I … as a doctor at this hospital for five years. A) has worked; B) have been working; C) was worked; D) am working. John … for his examination in Anatomy for an hour and a half already. A) was preparing; B) has been preparing; C) is preparing; D) has prepared. Why … she … tired? – She … all night. A) is … look / didn’t sleep; B) do … look / don’t slept; C) will … look / isn’t sleeping; D) does … look / hasn’t been sleeping. The operation … for half an hour by the time the intern entered the operating room. A) had been lasting; B) was lasting; C) had lasted; D) lasted. The patients with allergies … usually … with antihistamines. A) do … treat; B) is … treated; C) are … treating; D) are … treated. The doctor was not sure so a chest x-ray … to be really sure the patient … pneumonia. A) needed / develops; B) needs / have developed; C) was needing / was developing; D) was needed / had developed. The students … the problem of HIV and AIDS prevention for twenty minutes when I entered the class-room. A) was discussing; B) had been discussing; C) will be discussing; D) had discussed. They … married for five years when Tom got to know that he suffered from congenital immunodeficiency disorder. A) are; B) had been; C) has been; D) was. That patient suffering from cough … by 9 o’clock. A) won’t have been examined; B) will be examined; C) will be examining; D) won’t have examined. People who … very sick … at home. A) isn’t / treats; B) aren’t / are treated; C) wasn’t / treated; D) hasn’t been / is treating. The newborn … HIV infection from his mother suffering from AIDS. A) had acquired; B) acquired; C) was acquired; D) had been acquired. Recently our medicine … great progress in different skin diseases treatment. A) made; B) has made; C) is making; D) had made. The neurologist … electromyography and nerve conducting velocity tests from 9 till 10 tomorrow. A) will perform; B) will be performing; C) will have performed; D) will be performed. He said that the professor … the students about different ear, nose and throat disorders for an hour and a half. A) had been telling; B) has told; C) will have been telling; D) has been telling. Miotic drugs … in the eye by that time. A) won’t be instilled; B) won’t be instilling; C) won’t have been instilled; D) won’t instill. John … in hospital since October. A) is; B) were; C) are; D) has been. Prof. Shevchuk … Anatomy at our university since 1984. A) is teaching; B) was teaching; C) had taught; D) has been teaching. The students … the effectiveness of vaccine usage in preventing of some types of influenza since eight o’clock. A) discussed; B) had discussed; C) are discussing; D) have been discussing. Beth … already … some case histories and … four patients this morning. A) was written / was received; B) has written / received; C) has written / receives; D) have written / received. … prof. Shevchuk … at this hospital for 20 years before retirement? A) Has … worked; B) Had ... been working; C) Did … work; D) Is … working. The patient with pharyngolaryngitis … antibiotics now. A) is being injected; B) is injecting; C) is injected; D) has injected. The patient … by pulmonologist at the moment. A) is being examined; B) is examining; C) has been examined; D) is examined. There … four nurses and an old doctor in the polyclinic. A) was; B) is; C) were; D) did. How long … you … English? A) has … learnt; B) are … learning; C) have … been learning; D) is … learnt. The outstanding physician Dick White … at his reference book in Immunology for two years already. A) is working; B) has been working; C) was working; D) had worked. What … they … now? – They … a very important problem of autoimmune reactions and immunodeficiency disorders treatment. A) do … do / have discussed; B) did … do / discuss; C) are … doing / are discussing; D) is … done / is discussed. The patients … for the doctor for a quarter of an hour before appeared at the polyclinic, had they? A) weren’t waiting; B) wasn’t waiting; C) hadn’t been waiting; D) hasn’t waited. … the patient … antibiotics by the nurse when the doctor entered the ward? A) Was … injecting; B) Was … being injected; C) Was …injected; D) Were … being injected. Antibiotics … for patients with preexisting lung disease. A) is being used; B) are used; C) uses; D) was using. Some years ago cerebral studies … by means of electrodes. A) were carried out; B) was carried out; C) carried out; D) had been carried out. This patient has developed severe complications that’s why he … from the hospital tomorrow. A) won’t discharge; B) won’t be discharged; C) shan’t be discharged; D) won’t be discharging. I … for the findings of my blood analysis for an hour already. A) have been waiting; B) is waiting; C) wait; D) have waited. Barbara … a nurse for 20 years in this clinic and she is still working here. A) have been; B) were; C) has been; D) was. Only two fat-soluble vitamins … in the body to any extent. A) are storing; B) was stored; C) stores; D) are stored. I … for the doctor since 8 o’clock. I can’t wait any more as I have fever and pain in the chest. A) have waited; B) have been waiting; C) am waiting; D) waited. John … for the results of ELISA test for two days when the laboratory assistant said it was negative. A) waited; B) has waited; C) is waiting; D) had been waiting. The doctors were almost sure that infectious bronchitis in this patient … by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. A) caused; B) had been caused; C) causes; D) were being caused. Last year antibiotics … me as the infection … by a virus. A) didn’t help / was caused; B) don’t help / is caused; C) hasn’t helped / has been caused; D) was helping / was causing. The diagnosis of atopic dermatitis … usually … after several visits to the dermatologist. A) is … established; B) is … establishing; C) were … established; D) had … been established. At this time yesterday the nerve conducting velocity test …by the doctor to recognize chronic polyneuropathy. A) was performed; B) had been performing ; C) was being performed; D) had been performed. … you ever … any injury of the ear? A) Did … have; B) Have … had; C) Had …had; D) Do … have. By the time you come back the apparatus for blood transfusion … by the nurse. A) will be preparing; B) will be prepared; C) will have been prepared; D) will have been preparing. Two years ago a slowly progressing degenerative disorder of the nervous system … in this patient. A) was diagnosed; B) diagnosed; C) had been diagnosed; D) has been diagnosed. While the patient …, the nurse was filling in the case history. A) was being examined; B) was examined; C) examined; D) are being examined. The patient with encephalomyelitis … severe complications because he was timely diagnosed and adequately treated. A) wasn’t developed; B) didn’t develop; C) didn’t developed; D) haven’t developed. A variety of symptoms and complications … before the doctor made a correct diagnosis. A) analyzed; B) had analyzed; C) had been analyzed; D) were analyzed. The dentist … the tooth by the time we come. A) will fill; B) had filled; C) will have filled; D) was filling. I … the paragraph on types of immunity for half an hour. A) have been reading; B) read; C) am reading; D) am read. She … the lecture on autoimmune reactions for twenty minutes already. A) is studying; B) was studying; C) had studied; D) has been studying. The scientists … the problem of autoimmune reactions and immunodeficiency disorders treatment for several hours; but they … the agreement yet. A) are discussing / don’t reach; B) was discussing / didn’t reach; C) has discussed / hasn’t reached; D) have been discussing / haven’t reached. I … an interesting article on strategies for an AIDS vaccine for half an hour when the librarian said they were going to close. A) read; B) was reading; C) had read; D) had been reading. The patient suffering from dyspnea … just … . A) has … examined; B) have … been examined; C) has … been examined; D) was examined. Deep-breathing exercises … by my granny the whole evening yesterday in order to prevent pneumonia. A) was performed; B) we performing; C) were being performed; D) has been performed. At this time on Tuesday the patient … by the doctor to obtain the medical history. A) was interviewing; B) was being interviewed; C) had been interviewed; D) had interviewed. The patient with pneumonia … 1 gr of norsulphasol every six hours for the following 10 days already when he began to feel better. A) was receiving; B) received; C) had been received; D) had been receiving. Tomorrow an ophthalmologist … the conjunctival sac with disinfectant solution. A) will be washing out; B) will wash out; C) will be washed out; D) will have washed out. All tomorrow morning the doctor … diagnostic tests and procedures to confirm neurologic disorder suggested by the medical history. A) will perform; B) will be performed; C) will be performing; D) will have been performed. … a blockage in the blood supply to the brain … a stroke yesterday or the day before yesterday? A) Had …caused; B) Did … cause; C) Was… causing; D) Did … caused. The current symptoms … by the patient now. A) are described; B) are being described; C) are describing; D) have been described. My sister’s state of health … since she was discharged from the hospital. A) didn’t change; B) isn’t changed; C) hasn’t changed; D) wasn’t changed. The patient has lost a considerable amount of blood, that’s why he … a blood transfusion now. A) gives; B) is giving; C) is being given; D) had been given. All our nurses … rather reliable, … they? A) is / are; B) aren’t / aren’t; C) are / aren’t; D) will be / aren’t. How long … you … in the hospital? A) have … been staying; B) had … stayed; C) are … staying; D) does … stay. This little boy … special immunostimulator drugs since he injured his eye. A) took; B) takes; C) have been taking; D) has been taking. Samantha dared to tell Derek about her HIV contamination, as she … him for many years. A) had known; B) had been knowing; C) was known; D) were known. My friend … chest surgery this week so it’s not a surprise he … pneumonia some minutes ago. A) had / diagnosed; B) had / has been diagnosed; C) has had / was diagnosed; D) was having / was being diagnosed. Enlarged adenoids in this child repeatedly … recurring infections last year. A) provokes; B) provoked; C) will provoke; D) was provoked. Don’t phone Tom from 5 to 7. He … English. A) will have had; B) will have; C) has; D) will be having. She … the test in Histology for ten minutes. A) is written; B) has been writing; C) is writing; D) writes. I … to understand your report on the immune response for half an hour. A) tried; B) try; C) have been trying; D) has tried. The professor was tired as he … on the rate of AIDS spread in Ukraine for about an hour. A) has been reporting; B) reported; C) is reporting; D) reports. Olga … in hospital for a week already when her boyfriend called on. A) were; B) will be; C) had been; D) have been. … the patient with chest pain … before the nurse entered the ward? A) Was … examined; B) Was … examining; C) Have … been examined; D) Had … been examined. That newborn with pneumonia … mechanical respiratory support yesterday but it … now. A) needed / doesn’t need; B) has needed / don’t need; C) was needed / isn’t needing; D) needs / didn’t need. The dermatologist … that red crusted rash on my face … by atopic dermatitis. A) had said / had been causing; B) said / is caused; C) said / was caused; D) say / is causing. When … you … your last asthma attack? A) will … have; B) did … have; C) are … having; D) had … had. The cranial nerves, motor nerves, sensory nerves, and reflexes of this patient … now. A) are being examined; B) examined; C) will be examined; D) have examined. To improve the patient’s sleep and the condition of his nervous system he … bromide during the whole course of the disease until he was discharged from the hospital. A) had been taken; B) had been taking; C) was taken; D) took. This patient … fully because he suffers from AIDS. A) won’t cure; B) won’t be curing; C) won’t be cured; D) won’t have been cured. While the patient … by the physician he said that a dry cough had developed two days before. A) was asking; B) asked; C) was being asked; D) has been asked. When all the received stimuli … the brain sends orders through the nerve fibers in the spinal cord to different parts of the human body. A) has been analyzed; B) have been analyzed; C) is analyzed; D) is analyzing. By 3 o’clock on Monday the professor … the lecture on the immunity for half an hour already. A) was delivering; B) will deliver; C) will be delivering; D) will have been delivering. Before the lesson was over all the students … the final test on the last modulus. A) had written; B) had been written; C) has been written; D) was writing. All morning the doctor … diagnostic tests and procedures to confirm nuerologic disorder suggested by the medical history. A) will perform; B) will be performed; C) will be performing; D) will performing. Diseases of the inner ear … often … with deafness. A) are … associated; B) is … associated; C) are … associating; D) are … being associated. Henry usually wears glasses and now he … sunglasses. A) wears; B) has worn; C) wore; D) is wearing. They … the operation since nine o’clock. A) perform; B) have been performing; C) had performed; D) will be performing. This patient … by the ophthalmologist five days ago. A) were treated; B) was treating; C) is treated; D) was treated. Doctor Kovalenko was tired and angry, as nurses on duty … him all night to report on his patients’ state of health. A) had rang; B) were ringing; C) had been ringing; D) rang. An old man suffering from pneumonia … by 8 a.m. tomorrow. He … intravenous antibiotics. A) had been hospitalized / was given; B) have been hospitalized / are giving; C) is hospitalizing / has given; D) will have been hospitalized / will be given. Infectious bronchitis often … with symptoms of a common cold. A) are started; B) is starting; C) has been started; D) starts. My grandmother … by the dermatologist now. The doctor … thorough examination of her skin for a quarter of an hour. A) is examining / has performed; B) was examining / had performed; C) is examined / has performed; D) is being examined / has been performing. Before admission to the hospital the patient aged 48 … lobular pneumonia gradually for weeks. A) developed; B) were developing; C) had been developing; D) had developed. When … HIV infection first … in this patient with pneumonia? A) was … detected; B) did … detect; C) was … being detected; D) had … detected. The students … lectures on eye diseases since the professor went to Kyiv. A) didn’t attend; B) wasn’t attended; C) haven’t attended; D) hadn’t attended. At that moment a needle … in the spinal canal to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid. A) was inserted; B) inserted; C) had been inserted; D) was being inserted. The patient … difficulty in breathing yesterday. A) didn’t have; B) wasn’t having; C) hadn’t had; D) doesn’t have. When the nurse entered the doctor’s consulting room, the patient … by the neurologist. A) is being examined; B) was being examined; C) is examining; D) was examining . When … the vaccine … subcutaneously to produce a more active resistance of the protective mechanisms of the body? A) will … inject; B) will … be injected; C) will … be injecting; D) will … have been injecting. The doctor … the patient closely for serious complications for half an hour already. A) examines; B) have examined; C) is examining; D) has been examining. In Parkinson’s disease nerve cells in basal ganglia usually …, resulting in lower production of dopamine. A) degenerates; B) are degenerating; C) degenerate; D) have degenerated. The scientist … immunologic measurements in people with AIDS with those of healthy people all morning on Monday. A) will compare; B) will be compared; C) will be comparing; D) will have been compared. X-ray image of the spinal cord … by the doctor now to detect abnormalities within the spinal column. A) is taking; B) has taken; C) is being taken; D) has been taken. What … this laboratory assistant … here since morning? A) are … doing; B) was … doing; C) has been … doing; D) will be … doing. The teacher … a lecture on different types of immunity by 9 a.m. A) had started; B) was starting; C) has started; D) started. Don’t disturb him. He … at his report on immunoglobulins. A) is working; B) was working; C) works; D) have worked. The nurse … the leg of the patient with dermatitis for some minutes when the doctor … the ward. A) was dressing / was entered; B) had been dressing / entered; C) has been dressed / had entered; D) was dressed / was entered. I am out of breath. I … for almost thirty minutes. A) run; B) am running; C) have been running; D) has run. Irritative bronchitis … usually … by various kinds of dust. A) is … causing; B) were … caused; C) is … caused; D) was … being caused. The airways … obstructed by the time you take some expectorant. A) shall be; B) will have been; C) is; D) was. He … nightmares before he saw that horror-film. A) hasn’t; B) hadn’t had; C) haven’t had; D) hasn’t had. I can’t answer your question now, I … everything about lymphocytes. A) remember not; B) am not remembering; C) don’t remember; D) hasn’t remembered. How many months … they … this polyclinic? A) has … built; B) is … building; C) will … have built; D) have … been building. The mother … since the pediatrician said that her daughter had congenital immunodeficiency. A) is crying; B) has been crying; C) has cried; D) cries. Small amount of white sputum … just … by the patient suffering from bronchitis. A) has been … coughed out; B) were … coughed out; C) is … coughing out; D) will … cough out. This patient usually … from dermatitis of the hands and feet in autumn. A) is suffering; B) was suffering; C) have suffered; D) suffers. By that time the doctor … already … the patient treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. A) was … administered; B) had … administered; C) were … administering; D) has … been administered. Tom … well recently. A) doesn’t feel; B) hasn’t felt; C) isn’t feeling; D) haven’t felt. The student knew the paragraph on lymphatic vessels by heart when she … it several times. A) had read; B) will read; C) was reading; D) has read. I … this patient suffering from beriberi two years ago. A) have seen; B) saw; C) will see; D) am seeing. Her sister … at district polyclinic № 4 since 1995. A) is working; B) has been working; C) had worked; D) will have worked. My granny … from the hospital the day before yesterday. A) discharges; B) will be discharged; C) is being discharged; D) was discharged. Tomorrow the diagnosis of bronchitis … by the doctor even on the basis of your symptoms only. A) will make; B) will be making; C) will be made; D) is being made. Dry skin … common in people after 40 past middle age. A) were; B) have been; C) is; D) will have been. The patient … blood transfusion before the surgeon entered the operating room. A) were performing; B) being performed; C) had been performed; D) have been performing. The pulmonary abscess usually … via the bronchus. A) was being drained; B) had been drained; C) is drained; D) drain. The patient … from constant pain in the ear for several weeks before he visited a doctor. A) suffered; B) were suffering; C) had been suffering; D) have suffered. In some days, when the body temperature is normal, the patient … to walk a little. A) will allow; B) will be allowed; C) will be allowing; D) will have allowed. … purulent discharge already … into the external auditory canal? A) Has … poured; B) Was … poured; C) Had … poured; D) Does … pours. By 3 o’clock the professor … the lecture for half an hour already. A) deliver; B) shall have delivered; C) will be delivered; D) will have been delivering. The newborn … HIV infection from his mother suffering from AIDS. A) have acquired; B) acquired; C) was acquired; D) had been acquired. The patient … for the doctor since seven o’clock. A) waited; B) had waited; C) has been waiting; D) is waiting. They … married for five years when Tom got to know that he suffered from congenital immunodeficiency disorder. A) are; B) had been; C) has been; D) was. A man … unconscious for a few minutes before an ambulance arrived. A) were; B) has been; C) had been; D) was. The students … the problem of HIV and AIDS prevention for twenty minutes when I entered the class-room. A) was discussing; B) had been discussing; C) will be discussing; D) had discussed. That patient suffering from cough … by 9 o’clock. A) won’t have been examined; B) will be examined; C) will be examining; D) won’t have examined. People who … very sick … at home. A) isn’t / treats; B) aren’t / are treated; C) wasn’t / treated; D) hasn’t been / is treating. She … for her stethoscope since she came to the hospital. A) looks; B) had looked; C) is looking; D) has been looking. I … for the doctor since 8 o’clock. I can’t wait any more as I have fever and pain in the chest. A) have waited; B) have been waiting; C) am waiting; D) waited. The diagnosis of atopic dermatitis … usually … after several visits to the dermatologist. A) is … established; B) is … establishing; C) were … established; D) had … been established. John … for the results of ELISA test for two days when the laboratory assistant said it was negative. A) waited; B) has waited; C) is waiting; D) had been waiting. Barbara … a nurse for 20 years in this clinic and she is still working here. A) have been; B) were; C) has been; D) was. The doctors were almost sure that infectious bronchitis in this patient … by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. A) caused; B) had been caused; C) causes; D) were being caused. Last year antibiotics … me as the infection … by a virus. A) didn’t help / was caused; B) don’t help / is caused; C) hasn’t helped / has been caused; D) was helping / was causing. Only two fat-soluble vitamins … in the body to any extent. A) are storing; B) was stored; C) stores; D) are stored. How long … you … in the hospital? A) have … been staying; B) had … stayed; C) are … staying; D) does … stay. Enlarged adenoids in this child repeatedly … recurring infections last year. A) provokes; B) provoked; C) will provoke; D) was provoked. Ann dared to tell John about her HIV contamination, as she … him for many years. A) had known; B) had been knowing; C) was known; D) were known. All our nurses … rather reliable, … they? A) is / are; B) aren’t / aren’t; C) are / aren’t; D) will be / aren’t. My friend … chest surgery this week so it’s not a surprise he … pneumonia some minutes ago. A) had / diagnosed; B) had / has been diagnosed; C) has had / was diagnosed; D) was having / was being diagnosed. The dermatologist … that red crusted rash on my face … by atopic dermatitis. A) had said / had been causing; B) said / is caused; C) said / was caused; D) say / is causing. This little boy … special immunostimulator drugs since he injured his eye. A) took; B) takes; C) have been taking; D) has been taking. They … the operation since nine o’clock. A) perform; B) have been performing; C) had performed; D) will be performing. Infectious bronchitis often … with symptoms of a common cold. A) are started; B) is starting; C) has been started; D) starts. Doctor Kovalenko was tired and angry, as nurses on duty … him all night to report on his patients’ state of health. A) had rang; B) were ringing; C) had been ringing; D) rang. An old man suffering from pneumonia … by 8 a.m. tomorrow. He … intravenous antibiotics. A) had been hospitalized / was given; B) have been hospitalized / are giving; C) is hospitalizing / has given; D) will have been hospitalized / will be given. Henry usually wears glasses and now he … sunglasses. A) wears; B) has worn; C) wore; D) is wearing. My grandmother … by the dermatologist now. The doctor … thorough examination of her skin for a quarter of an hour. A) is examining / has performed; B) was examining / had performed; C) is examined / has performed; D) is being examined / has been performing. This patient … by the ophthalmologist five days ago. A) were treated; B) was treating; C) is treated; D) was treated. The teacher … a lecture on different types of immunity by 9 a.m. A) had started; B) was starting; C) has started; D) started. The nurse … the leg of the patient with dermatitis for some minutes when the doctor … the ward. A) was dressing / was entered; B) had been dressing / entered; C) has been dressed / had entered; D) was dressed / was entered. What … this laboratory assistant … here since morning? A) are … doing; B) was … doing; C) has been … doing; D) will be … doing. Irritative bronchitis … usually … by various kinds of dust. A) is … causing; B) were … caused; C) is … caused; D) was … being caused. I am out of breath. I … for almost thirty minutes. A) run; B) am running; C) have been running; D) has run. Don’t disturb him. He … at his report on immunoglobulins. A) is working; B) was working; C) works; D) have worked. The airways … obstructed by the time you take some expectorant. A) shall be; B) will have been; C) is; D) was. I can’t answer your question now, I … everything about lymphocytes. A) remember not; B) am not remembering; C) don’t remember; D) hasn’t remembered. This patient usually … from dermatitis of the hands and feet in autumn. A) is suffering; B) was suffering; C) have suffered; D) suffers. How many months … they … this polyclinic? A) has … built; B) is … building; C) will … have build; D) have … been building. The mother … since the pediatrician said that her daughter had congenital immunodeficiency. A) is crying; B) has been crying; C) has cried; D) cries. By that time the doctor … already … the patient treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. A) was … administered; B) had … administered; C) were … administering; D) has … been administered. He … nightmares before he saw that horror-film. A) hasn’t; B) hadn’t had; C) haven’t had; D) hasn’t had. Small amount of white sputum … just … by the patient suffering from bronchitis. A) has been … coughed out; B) were … coughed out; C) is … coughing out; D) will … cough out. He knew the paragraph on lymphatic vessels by heart when she … it several times. A) had read; B) will read; C) was reading; D) has read. I am sure that tomorrow the diagnosis of bronchitis … by the doctor even on the basis of your symptoms only. A) will make; B) will be making; C) will be made; D) is being made. Her sister … at district polyclinic № 4 since 1995. A) is working; B) has been working; C) had worked; D) will have worked. Tom … well recently. A) doesn’t feel; B) hasn’t felt; C) isn’t feeling; D) haven’t felt. My granny … from the hospital the day before yesterday. A) discharges; B) will be discharged; C) is being discharged; D) was discharged. I … this patient suffering from beriberi two years ago. A) have seen; B) saw; C) will see; D) am seeing. Dry skin … common in people after 40 past middle age. A) were; B) have been; C) is; D) will have been. The pulmonary abscess usually … via the bronchus. A) was being drained; B) had been drained; C) is drained; D) drain. The newborn … HIV infection from his mother suffering from AIDS. A) have acquired; B) acquired; C) was acquired; D) had been acquired. In some days, when the body temperature is normal, the patient … to walk a little. A) will allow; B) will be allowed; C) will be allowing; D) will have allowed. … purulent discharge already … into the external auditory canal? A) Has … poured; B) Was … poured; C) Had … poured; D) Does … pours. The patient … from constant pain in the ear for several weeks before he visited a doctor. A) suffered; B) were suffering; C) had been suffering; D) have suffered. The patient … blood transfusion before the surgeon entered the operating room. A) were performing; B) being performed; C) had been performed; D) have been performing. By 3 o’clock the professor … the lecture for half an hour already. A) deliver; B) shall have delivered; C) will be delivered; D) will have been delivering. A man … unconscious for a few minutes before an ambulance arrived. A) were; B) has been; C) had been; D) was. The patient … for the doctor since seven o’clock. A) waited; B) had waited; C) has been waiting; D) is waiting. She … for her stethoscope since she came to the hospital. A) looks; B) had looked; C) is looking; D) has been looking. The students … the problem of HIV and AIDS prevention for twenty minutes when I entered the class-room. A) was discussing; B) had been discussing; C) will be discussing; D) had discussed. They … married for five years when Tom got to know that he suffered from congenital immunodeficiency disorder. A) are; B) had been; C) has been; D) was. That patient suffering from cough … by 9 o’clock. A) won’t have been examined; B) will be examined; C) will be examining; D) won’t have examined. People who … very sick … at home. A) isn’t / treats; B) aren’t / are treated; C) wasn’t / treated; D) hasn’t been / is treating. Barbara … a nurse for 20 years in this clinic and she is still working here. A) have been; B) were; C) has been; D) was. He … English since 1991. A) have taught; B) was taught; C) is teaching; D) has been teaching. I … for the doctor since 8 o’clock. I can’t wait any more as I have fever and pain in the chest. A) have waited; B) have been waiting; C) am waiting; D) waited. John … for the results of ELISA test for two days when the laboratory assistant said it was negative. A) waited; B) has waited; C) is waiting; D) had been waiting. The doctors were almost sure that infectious bronchitis in this patient … by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. A) caused; B) had been caused; C) causes; D) were being caused. Last year antibiotics … me as the infection … by a virus. A) didn’t help / was caused; B) don’t help / is caused; C) hasn’t helped / has been caused; D) was helping / was causing. The diagnosis of atopic dermatitis … usually … after several visits to the dermatologist. A) is … established; B) is … establishing; C) were … established; D) had … been established. All our nurses … rather reliable, … they? A) is / are; B) aren’t / aren’t; C) are / aren’t; D) will be / aren’t. How long … you … in hospital? A) have … been staying; B) had … stayed; C) are … staying; D) does … stay. This little boy … special immunostimulator drugs since he injured his eye. A) took; B) takes; C) have been taking; D) has been taking. Samantha dared to tell Derek about her HIV contamination, as she … him for many years. A) had known; B) had been knowing; C) was known; D) were known. My friend … chest surgery this week so it’s not a surprise he … pneumonia some minutes ago. A) had / diagnosed; B) had / has been diagnosed; C) has had / was diagnosed; D) was having / was being diagnosed. Enlarged adenoids in this child repeatedly … recurring infections last year. A) provokes; B) provoked; C) will provoke; D) was provoked. The dermatologist … that red crusted rash on my face … by atopic dermatitis. A) had said / had been causing; B) said / is caused; C) said / was caused; D) say / is causing. Henry usually wears glasses and now he … sunglasses. A) wears; B) has worn; C) wore; D) is wearing. They … the operation since nine o’clock. A) perform; B) have been performing; C) had performed; D) will be performing. The student … through the medical journals since early morning. He wants to find something concerning autoimmune reactions. A) looks; B) is looking; C) have been looking; D) has been looking. Doctor Kovalenko was tired and angry, as nurses on duty … him all night to report on his patients’ state of health. A) had rang; B) were ringing; C) had been ringing; D) rang. An old man suffering from pneumonia … by 8 a.m. tomorrow. He … intravenous antibiotics. A) had been hospitalized / was given; B) have been hospitalized / are giving; C) is hospitalizing / has given; D) will have been hospitalized / will be given. Infectious bronchitis often … with symptoms of a common cold. A) is started; B) is starting; C) has been started; D) starts. My grandmother … by the dermatologist now. The doctor … thorough examination of her skin for a quarter of an hour. A) is examining / has performed; B) was examining / had performed; C) is examined / has performed; D) is being examined / has been performing. Don’t disturb him. He … at his report on immunoglobulins. A) is working; B) was working; C) works; D) have worked. The teacher … a lecture on different types of immunity by 9 a.m. A) had started; B) was starting; C) has started; D) started. What … this laboratory assistant … here since morning? A) is … doing; B) was … doing; C) has been … doing; D) will be … doing. I am out of breath. I … for almost thirty minutes. A) run; B) am running; C) have been running; D) has run. Irritative bronchitis … usually … by various kinds of dust. A) is … causing; B) will … be caused; C) is … caused; D) was … being caused. The airways … obstructed by the time you take some expectorant. A) shall be; B) will have been; C) is; D) was. The nurse … the leg of the patient with dermatitis for some minutes when the doctor … the ward. A) was dressing / was entered; B) had been dressing / entered; C) has been dressing / had entered; D) was dressed / was entered. He … nightmares before he saw that horror-film. A) hasn’t; B) hadn’t had; C) haven’t had; D) hasn’t had. I can’t answer your question now, I … everything about lymphocytes. A) remember not; B) am not remembering; C) don’t remember; D) hasn’t remembered. How many months … they … this polyclinic? A) has … built; B) is … building; C) will … have built; D) have … been building. The mother … since the pediatrician said that her daughter had congenital immunodeficiency. A) is crying; B) has been crying; C) has cried; D) cries. Small amount of white sputum … just … by the patient suffering from bronchitis. A) has been … coughed out; B) were … coughed out; C) is … coughing out; D) will … cough out. The patient … from chronic dermatitis of the hands and feet since 1998. A) is suffering; B) was suffering; C) have suffered; D) has been suffering. By that time the doctor … already … the patient treatment for seborrheic dermatitis. A) was … administered; B) had … administered; C) were … administering; D) has … been administered. Tom … well recently. A) doesn’t feel; B) hasn’t felt; C) isn’t feeling; D) hadn’t felt. The student knew the paragraph on lymphatic vessels by heart when she … it several times. A) had read; B) will read; C) was reading; D) has read. I … this patient for years. A) hasn’t seen; B) haven’t seen; C) didn’t saw; D) won’t have seen. Her sister … at district polyclinic № 4 since 1995. A) is working; B) has been working; C) had worked; D) will have worked. My granny … from Graves’ disease and rheumatoid arthritis for several years already. A) suffers; B) suffered; C) is suffering; D) has been suffering. Вставте потрібну форму інфінітиву: The endocrine system is known … many and varied functions of an organism by means of hormones. A) to regulate; B) to be regulated; C) to have been regulated; D) to be regulating. The patient is likely … his teeth some years ago. A) to lose; B)to be lost; C)to have lost; D) to have been lost. We watched the dentist … full dental examination. A) perform; B) to perform; C) to have been performing; D) be performed. It was necessary … that tooth. A) to extract; B) to be extracted; C) to be extracting; D) to have extracted. I hope a new denture … very quickly. A) to be making; B) to be made; C) to have made; D) make. The teacher was glad … with the students now. A) to be working; B) to work; C) to have worked; D) to have been working The doctor was satisfied … an adequate treatment for the patient suffering from immunodeficiency disorder. A) to be administered; B) to have been administered; C) to have administered; D) to have been administering. Scientists believe the thymus … a certain role in the immune processes in the body. A) play; B) to play; C) to be played; D) be playing. This infertile woman was the first … the embryo grown in the laboratory in her uterus. A) to implant; B) to have been implanting; C) to be implanting; D) to be implanted. Auditory brain stem response is the test that can … between sensory and neural hearing loss. A) to distinguish; B) distinguish; C) be distinguished; D) to be distinguishing. She seems … as a nurse at the neurological department some years ago. A) to work; B) to be working; C) to have worked; D) to have been worked. The professor let the students … home. A) go; B) to go; C) to be going; D) be gone. The doctor considers the tumour … by the last year's brain injury. A) to have been caused; B) to be caused; C) to be causing; D) have caused. The student must … on the methods of HIV prevention now. A) have been answered; B) to be answered; C) to have been answering; D) be answering. Otosclerosis is known … hardening of the bony tissue of the labyrinth. A) be; B) to be; C) to is; D) been. To determine the cause of encephalitis, a doctor considers whether the patient may … to a source of infection. A) to have been exposed; B) have been exposed; C) have exposed; D) to have exposed. My mother is happy … at this department for many years. A) to have been working; B) to work; C) to have been worked; D) to be worked. The students watched the neurologist … the physical examination. A) to perform; B) perform; C) to have performed; D) to be performing. He bought some expectorants … to his wife. A) to give B) be giving C) have given D) have been given He seems … a report for two hours already. A) to write B) to be writing C) to have written D) to have been writing The nurse is glad … the patient last week. A) to have helped; B) to help; C) be helping; D) has helped. The doctor made a list of procedures … . A) to be doing; B) to have done; C) to be done; D) to have been done. Mother made me … in bed as I was ill. A) to lie; B) to be lain; C) have lain; D) lie. He considered severe headaches … by the brain tumour. A) to cause; B) to be caused; C) to be causing; D) have caused. The fluid drainage is certainly … the patient with a conductive hearing loss. A) to help; B) to be helped; C) help; D) be helping. At the moment the otolaryngologist must … the wax plug by a dry method with the aid of a tube. A) take out; B) be taking out; C) to be taken out; D) to be taking out. I saw him … fresh leafy green vegetables: spinach, broccoli, cabbage and lettuce. A) to eat B) eat C) to be eating D) to have been eating Every medical student knows receptors … on the tongue to detect sweet, salt, sour, and bitter. A) to locate; B) to be locating; C) to be located; D) to have located. Auditory brain stem response is the test that can … between sensory and neural hearing loss. A) to distinguish; B) distinguish; C) be distinguished; D) to be distinguishing. The students were glad … the examinations. A) to have passed; B) to pass; C) to be passed; D) to be passing. Drinking much coffee can … teeth staining. A) to cause; B) cause; C) be caused; D) to be caused. The dentist recommended me … porcelain dental braces. A) to be chosen; B) to have chosen; C) to choose; D) to be choosing. All the patients suffering bronchitis are … deep-breathing exercises. A) to do; B) to be done; C) to be doing; D) to have done. Doctors consider his pneumonia … by Hemophilus influenza. A) to cause; B) to have caused; C) to be caused; D) to be causing. While being examined by the neurologist you must … your nose with forefingers. A) to touch; B) touch; C) be touching; D) to have been touched. These drugs are believed … already the patient. A) to be helping; B) help; C) to have helped; D) to have been helped. She is proud … the problem now with this well-known scientist. A) to discuss; B) have discussed; C) to be discussing; D) to have been discussed. The pulmonologist prescribed him antibiotics … for a week. A) to take; B) to be taking; C) to be taken; D) have been taking. I was unlikely … to the conference. A) to be sent; B) to send; C) send; D) to have sent. Ann seems … as a periodontist at our local clinic for a year. A) to have worked; B) to have been working; C) to work; D) to be working. She seems … as a nurse at the neurological department some years ago. A) to work; B) to be working; C) to have worked; D) to have been worked. I know that these medicines may … teeth and … tooth enamel. a) to discolour / to harm; b) discolour / harm; c) to have discoloured / to have harmed; d) be discoloured / be harmed. My sister is happy … at this laboratory for 10 years already. a) to have been worked; b) to work; c) to have been working; d) to be worked. Her mother seems … from rickets in her early childhood. a) to have suffered; b) to have been suffered; c) to be suffered; d) to be suffering. The patient is certain … from the hospital tomorrow. A) to discharge; B) to be discharged; C) to be discharging; D) to have discharged. The incidence of lung disorders appears … recently. A) to be increasing; B) increase; C) to have been increasing; D) to have been increased. The physician supposed the standard blood test … the infection. A) have revealed; B) to reveal; C) to have been revealed; D) be revealing. The patient suffering from seborrheic dermatitis should … a specific shampoo. A) to use; B) to be used; C) use; D) be using. Pneumonic patients are … with antibiotics. A) to treat; B) to be treated; C) be treated; D) have been treating. The doctor made the patient … to bland diet. A) to keep; B) to be keeping; C) keep; D) be keeping. The professor let the students … home. A) go; B) to go; C) to be going; D) be gone. This procedure is unlikely … with wax plug removal. A) be helping; B) to help; C) have been helped; D) to have been helping. The student heard the teacher … a lecture on the most common eye disorders. A) to have been delivered; B) have delivered; C) to deliver; D) be delivering. Laser procedures should … to correct near-sightedness. A) to perform; B) to be performed; C) be performed; D) perform. He is known … chest surgery, that’s why the doctor administered therapy to prevent pneumonia. A) to be having; B) have; C) to have had; D) to have been having. The patient’s condition was too severe … to the other hospital. A) to be transporting; B) to be transported; C) to have transported; D) to transport. The students are very glad … to a very interesting lecture now. A) to listen; B) to be listening; C) to have listened; D) to have been listened. The doctor considers the tumour … by the last year's brain injury. A) to have been caused; B) to be caused; C) to be causing; D) have caused. The student must … on the methods of HIV prevention now. A) have been answered; B) to be answered; C) to have been answering; D) be answering. Otosclerosis is known … hardening of the bony tissue of the labyrinth. A) be; B) to be; C) to is; D) been. The ophthalmologist believes his blindness … by brain tumour. A) be caused; B) have caused; C) to have been caused; D) to be causing. The doctor made a list of drugs … at the chemist’s shop. A) to buy; B) to be buying; C) to be bought; D) have been bought. Disinfecting agents are known … by nurses or doctors to sterilize their skin. A) to be used; B) have been used; C) to be using; D) to have been using. Usually a doctor can … the cause of a headache from the patient’s medical history. A) be determined; B) determine; C) to determine; D) to be determined. The patient is happy … from severe pneumonia. A) to have been recovered; B) to be recovered; C) be recovering; D) to have recovered. At that moment I was very happy … to my professor. A) to speak; B) have spoken; C) to be speaking; D) have been spoken. The cochlea is known … a hollow tube coiled in the shape of a snail’s shell. A) are; B) am; C) be; D) to be. The immunologist must … the patient at the moment. A) have questioned; B) to question; C) to be questioning; D) be questioning. Mary seems … as a dentist at our local clinic a year ago. A) to have been working; B) to be working; C) to work; D) to have worked. Antihistamines are known … for treating allergies. A) to use; B) to be using; C) to be used; D) to have used. He was so upset … from bronchitis for the whole week. A) be suffering; B) to have been suffering; C) to be suffered; D) have suffered. Her perioral dermatitis is likely … by makeup. A) to cause; B) to be causing; C) to have been caused; D) to have been causing. Motor nerves are known … the voluntary muscles. A) to be activated; B) to activate; C) to have been activated; D) have been activating. When a person suffers from severe headaches a doctor may … a tumour. A) to suspect; B) suspect; C) to be suspecting; D) be suspecting. … a correct diagnosis the doctor performed examination with a slit lamp. A) To make; B) To be made; C) To be making; D) To have made. The dentist let me … full dental examination. A) to perform; B) perform; C) be performed; D) has performed. It is important … to a regular regime of teeth brushing. A) to keep; B) keep; C) to be kept; D) be kept. Dendrites are known … information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. A) to be received; B) to receive; C) to have received; D) to be receiving. To determine the cause of pneumonia, a doctor considers whether a patient may … to a source of infection. A) to be exposed; B) have been exposed; C) to have been exposing; D) be exposing. Some of the autonomic nerves are known … sympathetic nerves. A) to call; B) to be calling; C) to be called; D) to have been calling. This patient’s condition didn’t seem … after the course of treatment. A) be improved; B) to have been improved; C) to be improving; D) have improved. The best way … skin infections is by careful washing the skin with soap or water. A) to have prevented; B) to have been prevented; C) to prevent; D) to be prevented. Neurofibromas can … peripheral nerves as well as nerve roots in the spine. A) be damaged; B) to be damaged; C) damage; D) to be damaging. My friend is satisfied … this experiences surgeon for two days. A) to assist; B) to be assisting; C) to have been assisted; D) to have been assisting. The speed at which motor nerves conduct impulses can … with nerve conduction study. A) to measure; B) measure; C) be measured; D) to be measuring. The drugs … did not relieve symptoms. A) to have been using; B) to be used; C) to be using; D) to have used. The patient seemed … to the doctor’s advice very attentively now. A) listen; B) to be listening; C) have listened; D) to have been listened. The student could … the material dealing with eye diseases much better. A) to be learning; B) have learnt; C) to have been learning; D) be learnt. My grandmother is old enough … good eyesight. A) have; B) to have; C) to have had; D) to be having. He wanted his son … by our stomatologist. A) to have examined; B) to be examined; C) to examine; D) examine. The patient is certain … now. A) to sleep; B) to be sleeping; C) to have slept; D) to have been sleeping. He is unlikely … soon. A) to have recovered; B) to recover; C) recover; D) be recovering. Could the patient … such a bad pain in the stomach after taking this drugs? A) to develop; B) have developed; C) to be developing; D) have been developed. It was impossible … a neurologist as the patient’s condition was very severe. A) not to be consulting; B) not consult; C) not have consulted; D) not to consult. The doctor pulled out a chair and made the patient … down. A) to sit; B) to have sat; C) sit; D) have been sitting. Additional flavours can … because of combination of taste sense with the sense of smell. A) to be determining; B) to have determined; C) be determined; D) have been determined. The students saw the doctor … neurologic examination to detect any abnormality. A) to be performing; B) perform; C) have performed; D) to have been performing. Any cancer elsewhere in the body are known sometimes … the nervous system. A) to be caused; B) to cause; C) to have been caused; D) to be causing. The stroke in this patient is supposed … disabling neurologic damage. A) to have caused; B) cause; C) to have been caused; D) be causing. They are proud of their son … as a neurologist for many years. A) to work; B) to be working; C) to have been worked; D) to have been working. An abnormality of the autonomic nervous system may … such problems as fall in blood pressure, lack of sweating, etc. A) to be caused; B) cause; C) to be causing; D) to have been caused. The doctors hardly expect him … consciousness, it was a terrible stroke. A) to be recovered; B) to have been recovering; C) to recover; D) to have recovered. This work must … by students as soon as possible. A) to do; B) to be done; C) do; D) be done. It was a real pleasure … in the sea on such a hot day. A) swim; B) to be swum; C) to be swimming; D) to have been swum. The patient remembered in what way … this medicine. A) to have used; B) to have been used; C) to use; D) be used. Scientists believe some birth defects … by spontaneous and unexplained changes in genes. A) to cause; B) have been caused; C) to be caused; D) to have been causing. This patient suffering from autoimmune reaction must … two day ago. A) to have been hospitalized; B) have been hospitalized; C) to have hospitalized; D) have hospitalized. The main point is … the cause of fever by asking the patient about present and previous symptoms. A) to determine; B) to be determined; C) to be determining; D) to have determined. The nurse is glad … patients since morning. A) to be helped; B) to have been helped; C) to have been helping; D) help. They wanted the professor … a lecture on the human sensory system. A) deliver; B) be delivered; C) to be delivered; D) to deliver. It was a pleasure … to an interesting lecture delivered by the professor of immunology. A) to be listened; B) to be listening; C) to have been listened; D) have listened. The nurse is glad … this patient now. A) to be helping; B) to have helped; C) to have been helped; D) to be helped. The patient suffering from paresthesia hopes … completely … . A) to have been … curing; B) to be … curing; C) to … cure; D) to be … cured. The operation on trachea was too difficult … . A) to be performed; B) to perform; C) to be performing; D) to have performed. This doctor is said … at the maternity home for 20 years. A) to be working; B) to work; C) to have been worked; D) to have been working. Medical students know some antibiotics … loss of taste. A) to be caused; B) be causing; C) to cause; D) to have been caused. Nobody likes … from any disease. A) to be suffered; B) be suffering; C) to suffer; D) to have been suffered. Consumption of fluid must … by patients with bronchitis. A) to increase; B) be increasing; C) be increased; D) to have increased. He seemed … what the teacher explained. A) not to be understood; B) not to have understood; C) to not understand; D) not be understanding. Now the student pretends … to the lecturer. A) to listen; B) to be listened; C) to be listening; D) to have been listened. Almost 90 % of information is known … to the brain through eyes. A) to be supplying; B) to be supplied; C) to have been supplying; D) to have been supplied. The general practitioner made all students … the patients in order to obtain their medical histories. A) to have been interviewing B) to interview C) be interviewed D) interview Will this patient with allergy agree … with antihistamines? A) to treat B) to be treated C) to have been treated D) to have treated The dispensing pharmacist looks happy … advice to an old woman now. A) to give B) to have given C) to be given D) to be giving He wants me… him advice on his wisdom tooth treatment. A) to be giving B) to give C) give D) to have given The patient was glad to…by this experienced doctor last year. A) to have been treated B) to be treated C) to treat D) to have treated The dentist noticed the patient’s gum … A) to bleed B) to have bled C) to be bleeding D) bleed Diseases of oral cavity can...by unbalanced diet . A) to cause B) to be caused C) cause D) be caused The dentist let the patient … . A) to get up B) get up C) to be getting up D) can get up The surgeon ordered some tests … to confirm the diagnosis. A) to do; B) to be done; C) to have done; D) to be doing. The students heard the patient … in the doctor’s consulting room. A) to cry; B) to have cried; C) cry; D) have cried. The size of the pupil is known … by the papillary sphincter muscle. A) to control; B) to be controlled; C) to be controlling; D) to have controlled. The doctor suspected her allergic reaction … by seasonal fruits. A) to have caused; B) to have been causing; C) to have been caused; D) to be causing. People can’t … some allergens. A) to be avoided; B) to be avoiding; C) avoid; D) have avoided. She seemed … the doctor’s recommendations. A) to be forgotten; B) to be forgetting; C) to have forgotten; D) to have been forgetting. The doctor gave a patient with pneumonia permission … a little. A) to be walked; B) to walk; C) be walked; D) have been walked. The nurse turned out … procedures administered by doctors since the early morning. A) to perform; B) to be performed; C) to have been performed; D) to have been performing. The nurse is always glad … a patient. A) to be helping; B) to have helped; C) to have been helping; D) to help. We know diphtheria … one of the leading causes of death among children years ago. A) to have been; B) to be; C) be; D) have been. This patient suffering from some infection is the first … by the infectionist. A) to be examining; B) to have examined; C) to examine; D) to be examined. The surgeons must … the operation at the moment. A) to be performing; B) to perform; C) be performing; D) have performed. The students saw the doctor … magnetic resonance imaging to detect abnormalities of the cerebellum. A) carry out; B) to carry out; C) to be carried out; D) to have been carried out. His deafness is supposed … by the hereditary disease. A) to be causing; B) to cause; C) to be caused; D) be caused. The student tried … the right answer. A) to be found; B) to have been found; C) to have been finding; D) to find. Neural hearing loss is known … by brain tumours. A) to cause; B) to be causing; C) to be caused; D) have been caused. Immune system can … at work when a wound in a fingertip leads to an enlarged node at the elbow. A) to see; B) to be seen; C) see; D) be seen. She ought … the doctor’s advice. A) to have asked; B) have asked; C) to have been asked; D) have been asked. The doctors seem … a very important problem now. A) to discuss; B) to be discussed; C) to be discussing; D) to have discussed. The patient noticed his doctor … the operating room. A) to be entering; B) to enter; C) enter; D) have been entered. We know penicillin … an effective antibiotic in the treatment of inflammations. A) are; B) to be; C) be; D) have been. He is likely … problem with this wisdom tooth. A) to be having B) to have C) have D) to have had The patient was glad to…by this experienced doctor last year. A) to have been helped B) to be helped C) help D) to have helped The student observed the dentist … the implant to the patient. A) to anchor B) anchor C) to be anchoring D) to be anchored Unbalanced diet can… diseases of oral cavity. A) to cause B) to be caused C) cause D) be caused The doctor wanted her … x-rays before placing fixed denture. a) to take B) to be taken C) to have been taken D) can be taken The tubercle bacillus was known … by Robert Koch. A) to discover; B) to be discovered; C) to have discovered; D) to be discovering. The patient is glad … by the nurse. A) to be helping; B) to help; C) to have been helping; D) to have been helped. Auditory brain stem response is the test that can … between sensory and neural hearing loss. A) to distinguish; B) distinguish; C) be distinguished; D) to be distinguishing. She seems … as a nurse at the neurological department some years ago. A) work; B) to be working; C) to have worked; D) to have been worked. The professor let the students … home. A) go; B) to go; C) to be going; D) gone. The doctor considers the tumour … by the last year's brain injury. A) to have been caused; B) to be causing; C) be causing; D) have caused. The student must … on the methods of HIV prevention now. A) have been answered; B) to be answered; C) to have been answering; D) be answering. Otosclerosis is known … hardening of the bony tissue of the labyrinth. A) be; B) to be; C) to is; D) been. We know the retina … the nerves that sense light and the blood supply that nourishes them. A) to contain; B) to be containing; C) to be contained; D) to have been contained. Neural hearing loss is likely … by brain tumours. A) cause; B) to cause; C) to be caused; D) be causing. The laboratory assistant must … blood analysis at the moment. A) to perform; B) to be performing; C) be performing; D) have been performing. Neurosurgeons want this device … during the operation on the brain. A) to use; B) to be using; C) to be used; D) to have used. The patient suffering from autoimmune reaction is satisfied … yesterday. A) to be examined; B) to be examining; C) to have examined; D) to have been examined. Laser procedures should … to correct near-sightedness. A) to perform; B) to be performed; C) be performed; D) perform. He is known … chest surgery, that’s why the doctor administered therapy to prevent pneumonia. A) to be having; B) have; C) to have had; D) to have been having. This procedure is unlikely … with wax plug removal. A) be helping; B) to help; C) have been helped; D) to have been helping. The student heard the teacher … a lecture on the most common eye disorders. A) to have been delivered; B) have delivered; C) to deliver; D) be delivering. The students are very glad … to a very interesting lecture now. A) to listen; B) to be listening; C) to have listened; D) to have been listened. The patient’s condition was too severe … to the other hospital. A) to be transporting; B) to be transported; C) to have transported; D) to transport. The laboratory assistant can … common blood test count now. A) be performing; B) to be performing; C) to perform; D) have been performed. He seems …at this problem now. A) to be working B) to work C) work D) to be worked The dentist was satisfied …the aesthetic smile of the patient. A) to have improved B) to be improved C) improve D) to have been improved The nurse watched the dentist …injection to the patient. A) give B) be given C) to give D) to be given Cigarette smoking can…gum disease. A) to cause B) to be caused C) cause D) be caused The doctor ordered x-rays ….before treating root canal. A) to take B) to be taken C) to have been taken D) to be taking We expect this child with influenza … soon. A) recover; B) to recover; C) to be recovered; D) to have recovered. The professor made us … at the laboratory. A) work; B) to work; C) to be worked; D) be worked. Her perioral dermatitis is likely … by makeup. A) to cause; B) to be causing; C) to have been caused; D) to have been causing. Motor nerves are known … the voluntary muscles. A) to be activated; B) to activate; C) to have been activated; D) have been activating. Antihistamines are known … for treating allergies. A) to use; B) to be using; C) to be used; D) to have used. He was so upset … from bronchitis for the whole week. A) be suffering; B) to have been suffering; C) to be suffered; D) have suffered. … a correct diagnosis the doctor performed examination with a slit lamp. A) To make; B) To be made; C) To be making; D) To have made. When a person suffers from severe headaches a doctor may … a tumour. A) to suspect; B) suspect; C) to be suspecting; D) be suspecting. We saw the patient … after the operation. A) to sleep; B) sleep; C) to be slept; D) sleeps. His teeth turned out … because of fluorosis. A) to stain B) to be stained С) to have been stained D) to be staining They wanted the professor … a lecture. A) to deliver B) to be delivered С) to have delivered D) to be delivering He expects good results … with the use of fixed braces. A) to achieve B) to be achieved С) to have achieved D) achieved This patient is glad … . A) to have been helped B) to help С) to helped D) to have helped The professor made us … at the dental laboratory. A) to work B) work С) to have worked D) to have been worked The students watched the dentist … tooth extraction. A) perform B) be performed C) to have been performed D) to have been performing The doctor wanted the patient … his dental office next Friday. A) to be visited B) to visit C) be visiting D) have been visited Bill’s teeth discolouration is likely … by coffee, tea and smoking. A) to have been caused B) to cause C) to be causing D) have caused Unbalanced diet can … diseases of oral cavity. A) to cause B) to be caused C) cause D) be caused The patient was glad … by this experienced doctor last year. A) to have been helped B) to be helping C) help D) to have helped The student observed the dentist … the implant to the patient. A) to anchor B) anchor C) to have been anchored D) to be anchored He seems … at this problem now. A) to be working B) to have worked C) work D) to be worked The nurse watched the dentist … injection to the patient. A) give B) be given C) to give D) to be given The doctor ordered x-rays … before treating root canal. A) to take B) to be taken C) to have been taken D) be taking My grandmother is old enough … good eyesight. A) have; B) to have; C) to have had; D) to be having. The drugs … did not relieve symptoms. A) to have been using; B) to be used; C) to be using; D) to have used. The patient seemed … to the doctor’s advice very attentively now. A) listen; B) to be listening; C) have listened; D) to have been listened. The speed at which motor nerves conduct impulses can … with nerve conduction study. A) to measure; B) measure; C) be measured; D) to be measuring. The student could … the material dealing with eye diseases much better. A) to be learning; B) have learnt; C) to have been learning; D) be learnt. Dendrites are known … information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. A) to be received; B) to receive; C) to have received; D) to be receiving. He wants me … him a piece of advice on his wisdom tooth treatment. A) to be given B) to give C) give D) to have given The patient was glad … by this experienced doctor last year. A) to have been treated B) to be treated C) to treat D) to have treated Diseases of oral cavity can ... by unbalanced diet. A) to cause B) to be causing C) cause D) be caused He seems … as a cosmetic dentist at the regional clinic. A) to work B) be working С) to be worked D) to have been worked The doctor pulled out a chair and made the patient … down. A) to sit; B) to have sat; C) sit; D) have been sitting. It was impossible … a neurologist as the patient’s condition was very severe. A) not to be consulting; B) not consult; C) not have consulted; D) not to consult. It was a real pleasure … in the sea on such a hot day. A) swim; B) to be swum; C) to be swimming; D) to have been swum. The patient remembered in what way … this medicine. A) to have used; B) to have been used; C) to use; D) be used. The doctors hardly expect him … consciousness, it was a terrible stroke. A) to be recovered; B) to have been recovering; C) to recover; D) to have recovered. This work must … by students as soon as possible. A) to do; B) to be done; C) do; D) be done. Cigarette smoking can … gum disease. A) to cause B) to have caused С) cause D) to have been caused We watched the dentist … full dental examination. A) perform B) to perform C) to have been performing D) to be performed My father is happy … as a cosmetic dentist for ten years. A) to have been working B) be working С) to work D) work The patient with some dental defects hopes … almost model-perfect teeth. A) to have made B) to be made С) be making D) to have been made The dentist thinks brace breakage … by eating tough-to-bite food. A) to cause B) be caused С) to have been caused D) to be causing Consumption of fluid must … by patients with bronchitis. A) to increase; B) be increasing; C) be increased; D) to have increased. Medical students know some antibiotics … loss of taste. A) to be caused; B) be causing; C) to cause; D) to have been caused. Nobody likes … from any disease. A) to be suffered; B) be suffering; C) to suffer; D) to have been suffered. He seemed … what the teacher explained. A) not to be understood; B) not to have understood; C) to not understand; D) not be understanding. Almost 90 % of information is known … to the brain through eyes. A) to be supplying; B) to be supplied; C) to have been supplying; D) to have been supplied. Now the student pretends … to the lecturer. A) to listen; B) to be listened; C) to be listening; D) to have been listened. The patient was advised … his retainer once a week. A) disinfect; B) to be disinfected; C) to disinfect; D) to have disinfected. We watched the dentist … an electronic image of the upper teeth. A) make; B) to make; C) to have been making; D) to have made. The doctor wanted all my teeth … . A) extract; B) to be extracted; C) to be extracting; D) to have extracted. The students were glad … with this outstanding dentist for two months. A. to have been working; B. work; C. to be worked; D. to have been worked. Drinking much coffee can … teeth staining. A. to cause; B. cause; C. be caused; D. to be caused. I’m sorry … the thermometer. A. to have been breaking; B. to be broken; C. to have broken; D. to have been broken. Cigarette smoking can … gum disease. A) to cause B) to have caused C) cause D) to be causing The student was glad … to the international students’ conference. A) to have been sent B) have been sent C) be sending D) to have been sending The dental nurse ordered them … in the hall. A) to have been waiting B) to wait C) to have been waited D) to be waited Computer-aided technology helps the orthodontist … ideal tooth positions. A) to be creating B) be created C) to create D) to have created People can’t … some allergens. A) to be avoided; B) to be avoiding; C) avoid; D) have avoided. The doctor gave a patient with pneumonia permission … a little. A) to be walked; B) to walk; C) be walked; D) have been walked. The doctor suspected her allergic reaction … by seasonal fruits. A) to have caused; B) to have been causing; C) to have been caused; D) to be causing. The nurse turned out … procedures administered by doctors since the early morning. A) to perform; B) to be performed; C) to have been performed; D) to have been performing. She seemed … the doctor’s recommendations. A) to be forgotten; B) to be forgetting; C) to have forgotten; D) to have been forgetting. The size of the pupil is known … by the papillary sphincter muscle. A) to control; B) to be controlled; C) to be controlling; D) to have controlled. The student is sorry … hard all these years. A) not to have been working B) not to work C) not to be worked D) not to have been worked The doctor said that my bad breath is certain … by poor oral hygiene. A) to cause B) have caused C) to be causing D) to be caused The dentist made a list of procedures … . A) do B) to have been doing C) have been doing D) to be done The professor let the students … in the dental laboratory. A) work B) to work C) to have worked D) to be working Neural hearing loss is known … by brain tumours. A) to cause; B) to be causing; C) to be caused; D) have been caused. The doctors seem … a very important problem now. A) to discuss; B) to be discussed; C) to be discussing; D) to have discussed. The student tried … the right answer. A) to be found; B) to have been found; C) to have been finding; D) to find. She ought … the doctor’s advice. A) to have asked; B) have asked; C) to have been asked; D) have been asked. Immune system can … at work when a wound in a fingertip leads to an enlarged node at the elbow. A) to see; B) to be seen; C) see; D) be seen. The patient noticed his doctor … the operating room. A) to be entering; B) to enter; C) enter; D) have been entered. Tooth enamel wearing away is believed … by overzealous use of over-thecounter home bleaching products. A) be causing B) to have been caused C) cause D) to cause The patient with broken and crooked teeth was the first … . a) to examine b) to have examined c) to be examined d) to be examining The dentist projected an image of the patient’s teeth on a computer monitor … his teeth on the screen. a) to modify b) to be modified c) to have been modified d) to be modifying The stomatologist made a list of procedures … . a) to have been doing b) to have done c) to do d) to be done My father is happy … as a cosmetic dentist in this famous dental clinic for five years. a) to work b) to be working c) to have been working d) to have been worked The patient with some dental defects hopes … perfect teeth. a) to have been made b) to be making c) to be made d) to have been making The cosmetic dentist used composite bonding … a healthy and bright smile. a) to be creating b) to have been created c) to have created d) to create His teeth turned out ... because of fluorosis. a) to stain b) to be stained c) have been stained d) to be staining They wanted the professor ... a lecture. a) to deliver b) to be delivered c) to have delivered d) be delivering This patient is glad ... by this experienced orthodontist. a) to help b) help c) to have helped d) to have been helped He expects good results ... with the use of fixed braces. a) to achieve b) to be achieved c) to have achieved d) achieve The professor made us ... at the dental laboratory. a) to work b) work c) to have worked d) to have been worked The teacher was glad ... with the students now. a) to be working b) to work c) have worked d) have been working It is very important … the antipyretic for lowering the body temperature. a) to have taken b) take c) to be taken d) to take The doctor made a list of powders and pills… . a) to be bought b) to be buying c) to have bought d) buy The teacher made me … a lot about the main routes of drug administration. a) to be learnt b) to be learning c) to learn d) learn This doctor is always ready … his patients. a) to help b) to be helping c) to have been helping d) to be helped The patient with allergic rhinitis is satisfied … by this experienced allergologist. a) to have been examining b) to be examining c) to have been examined d) to have examined The pharmacist made us … the dosage of insulin attentively. a) to read b) read c) to be reading d) to have read The dermatologist made a list of topical medications … to the skin and mucous membranes. a) to be applied b) to apply c) to be applying d) to have been applying My mother is happy…..at this chemist’s for many years. a) to be worked b) work c) be working d) to have been working She seems … as a nurse at the neurological department some years ago. A) work; B) to be working; C) to have worked; D) to have been worked. Otosclerosis is known … hardening of the bony tissue of the labyrinth. A) be; B) to be; C) to is; D) been. The doctor considers the tumour … by the last year's brain injury. A) to have been caused; B) to be causing; C) be causing; D) have caused. The student must … on the methods of HIV prevention now. A) have been answered; B) to be answered; C) to have been answering; D) be answering. The professor let the students … home. A) go; B) to go; C) to be going; D) gone. Auditory brain stem response is the test that can … between sensory and neural hearing loss. A) to distinguish; B) distinguish; C) be distinguished; D) to be distinguishing. I heard the baby …because of severe earache the whole evening yesterday. A) to have cried B) be crying C) to be crying D) to cry The doctor draw blood … it for the presence of the pathogenic microorganisms. A) to be testing; B) to test; C) to have been tested; D) to have tested. The pharmacist will explain the consumer how … antimycotic ointment. A) to have used; B) to be using; C) to use; D) to be used. Hot weather makes me … uncomfortable. A) to feel; B) feel; C) to be felt; D) to have felt. Antibiotics can … infections caused by bacteria. a) to treat b) to have treated c) treat d) be treated This article on antihistamines is unlikely … next month. a) to print b) to be printed c) to have been printed d) to have been printing The doctor was happy … the operation successfully. a) to have performed b) to be performed c) to have been performed d) perform This procedure is unlikely … with wax plug removal. A) be helping; B) to help; C) have been helped; D) to have been helping. The student heard the teacher … a lecture on the most common eye disorders. A) to have been delivered; B) have delivered; C) to deliver; D) be delivering. Laser procedures should … to correct near-sightedness. A) to perform; B) to be performed; C) be performed; D) perform. He is known … chest surgery, that’s why the doctor administered therapy to prevent pneumonia. A) to have; B) have; C) to have had; D) to have been having. The patient’s condition was too severe … to the other hospital. A) to be transporting; B) to be transported; C) to have transported; D) to transport. The students are very glad … to a very interesting lecture now. A) to listen; B) to be listening; C) to have listened; D) to have been listened. Antihistamines are known … for treating allergies. A) to use; B) to be using; C) to be used; D) to have used. He was so upset … from bronchitis for the whole week. A) be suffering; B) to have been suffering; C) to be suffered; D) have suffered. Her perioral dermatitis is likely … by makeup. A) to cause; B) to be causing; C) to have been caused; D) to have been causing. Motor nerves are known … the voluntary muscles. A) to be activated; B) to activate; C) to have been activated; D) have been activating. When a person suffers from severe headaches a doctor may … a tumour. A) to suspect; B) suspect; C) to be suspecting; D) be suspecting. … a correct diagnosis the doctor performed examination with a slit lamp. A) to make; B) to be made; C) to be making; D) to have made. Dendrites are known … information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. A) to be received; B) to receive; C) to have received; D) to be receiving. The speed at which motor nerves conduct impulses can … with nerve conduction study. A) to measure; B) measure; C) be measured; D) to be measuring. The drugs … did not relieve symptoms. A) to use; B) to be used; C) to be using; D) to have used. The patient seemed … to the doctor’s advice very attentively. A) listen; B) to be listening; C) have listened; D) to have been listened. The student could … the material dealing with eye diseases much better. A) to be learning; B) have learnt; C) to have been learning; D) be learnt. My grandmother is old enough … good eyesight. A) have; B) to have; C) to have had; D) to be having. It was impossible … a neurologist as the patient’s condition was very severe. A) not to be consulting; B) not consult; C) not have consulted; D) not to consult. The doctor pulled out a chair and made the patient … down. A) to sit; B) to have sat; C) sit; D) have been sitting. The doctors hardly expect him … consciousness, it was a terrible stroke. A) to be recovered; B) to have been recovering; C) to recover; D) to have recovered. This work must … by students as soon as possible. A) to do; B) to be done; C) do; D) be done. It was a real pleasure … in the sea on such a hot day. A) swim; B) to be swum; C) to be swimming; D) to have been swum. The patient remembered in what way … this medicine. A) to have used; B) to have been used; C) to use; D) be used. Nobody likes … from any disease. A) to be suffered; B) to be suffering; C) to suffer; D) to have been suffered. Consumption of fluid must … by patients with bronchitis. A) to increase; B) be increasing; C) be increased; D) to have increased. Almost 90 % of information is known … to the brain through eyes. A) to be supplying; B) to be supplied; C) to have been supplying; D) to have been supplied. He seemed … what the teacher explained. A) not to be understood; B) not to have understood; C) not understand; D) not be understanding. Now the student pretends … to the lecturer. A) to listen; B) to be listened; C) to be listening; D) to have been listened. Medical students know some antibiotics … loss of taste. A) to be caused; B) to be causing; C) to cause; D) to have been caused. The size of the pupil is known … by the papillary sphincter muscle. A) to control; B) to be controlled; C) to be controlling; D) to have controlled. The doctor suspected her allergic reaction … by seasonal fruits. A) to have caused; B) to have been causing; C) to have been caused; D) to be causing. People can’t … some allergens. A) to be avoided; B) to be avoiding; C) avoid; D) have avoided. She seemed … the doctor’s recommendations. A) to be forgotten; B) to be forgetting; C) to have forgotten; D) to have been forgetting. The doctor gave a patient with pneumonia permission … a little. A) to be walking; B) to walk; C) be walked; D) have been walked. The nurse turned out … procedures administered by doctors since the early morning. A) to perform; B) to be performed; C) to have been performed; D) to have been performing. The student tried … the right answer. A) to be found; B) to have been found; C) to have been finding; D) to find. Neural hearing loss is known … by brain tumours. A) to cause; B) to be causing; C) to be caused; D) have been caused. Immune system can … at work when a wound in a fingertip leads to an enlarged nodes at the elbow. A) to see; B) to be seen; C) see; D) be seen. The doctors seem … a very important problem now. A) to discuss; B) to be discussed; C) to be discussing; D) to have discussed. The patient noticed his doctor … the operating room. A) to be entering; B) to enter; C) enter; D) have been entered. Трансформуйте наступні речення у активний стан: My granny has been advised by her orthodontist to keep the dentures in place overnight. A temporary dental filling will be used by the dentist in this emergency dental treatment. The students were being taught by the teacher how to distinguish between different types of immunity during the whole lesson on Monday. The antibiotics have already been administered to the patients by doctors for combating an infection. My sister is being extracted a bad tooth by your father at the moment. The impressions have already been sent to the laboratory. The symptoms of asthma will be studied by the students next time. The problem of AIDS in our country is being discussed by the students at the moment. The patient has been advised by the dentist to keep the dentures in place overnight. He is being examined by the dentist now. Anaphylactic shock has been studied by this prominent scientist for two years already. They will be explained the use of the Present Perfect Tense by the teacher tomorrow. Amalgam fillings are commonly used by dentists nowadays. A permanent filling is being put by the dentist now. Allergic reactions haven’t been investigated by the students yet. The lungs are separated from the abdomen by the diaphragm. The student was being asked by the professor when I came. The patient has just been advised by the dentist to brush his teeth twice a day. A small post made of titanium is being inserted into the patient’s bone socket by the dentist now. Each alveolus is surrounded by a dense network of capillaries. This book was being read by him at this time yesterday. The symptoms of this disease will have been studied by the surgeon by the beginning of autumn. The impressions will be sent to the laboratory by the denturist tomorrow. Some sedative drug is being given to the patient by the dentist now. Peter is being examined by the doctor now. Operations are usually performed by the surgeon in the morning. The patient has been advised by the dentist to keep the dentures in place overnight. Veneers are mainly placed on front teeth. The interesting article about AIDS has already been written by our teacher. The student hasn’t been told about different nervous system tumors by teacher yet. Metabolic processes are regulated by the central nervous system. A small post is being inserted by the dentist at the moment. Teeth enamel discolouration was caused by chemical damage to teeth. The patient is being operated on the spinal cord by the famous surgeon now. New method of examining patients is being developed by scientists at the moment. Ann will have already been discharged from the hospital by the doctor by this time tomorrow. The patient’s state of the oral cavity will be improved by the stomatologist next week. His bad breath has been detected by his sister today. Brace breakage has been caused by eating tough-to-bite food. Jack is being performed a prophylactic check-up by the dentist at the moment. The secretory function of the skin is performed by the sweat and sebaceous glands. The patient’s lungs and heart have already been listened to by the therapeutist. Ann will be administered an injection by the doctor tomorrow. Wards are being cleaned and aired by the nurses now. These drugs were prescribed by the doctor. At the moment a very interesting article on deterioration of dental implants is being read by my father. A hole in the top or back of tooth is made by the dentist to get to the root. The patient will have been treated by this dental orthopedist by 5 p.m. tomorrow. Composite veneers were performed in a single visit to the dentist. A cobalt-chrome frame has been constructed around the remaining teeth. Many dental disorders are caused by poor hygiene. Temporary veneers will have been removed before the dentist installs them with dental cement. The patient has just been injected antibiotic by this pretty nurse. By evening the toothache will have been reduced by this new pill. Some natural teeth had been extracted by the dentist before he inserted immediate dentures. Veneers were invented by Charles Pincus in California. Jack is being examined by the dentist at the moment. Oral hygiene has never been observed by the patient adequately. My sister is being operated on by your father at the moment. Veneers are placed mainly on the front teeth. Veneers were permanently cemented to the teeth by the dentist yesterday. The drugs are being made by the pharmacist at the moment. The patient has just been advised by the dentist to brush his teeth twice a day. Amalgam filling had been put by the dentists by that time yesterday. The impressions will be sent to the laboratory by the denturist tomorrow. Some sedative drug is being given to the patient by the dentist now. Amalgam fillings are commonly used by the dentists nowadays. The impressions have already been sent to the laboratory. A permanent filling is being put by the dentist now. Absent teeth have already been substituted by bridgework. Veneers are mainly used to correct colour of the teeth. A small post made of titanium is being inserted into the patient’s bone socket by the dentist now. Veneers were invented by a dentist Charles Pincus. He is being examined by the dentist now. The patient has been advised to keep the dentures in place overnight until the adjustment period is over. Small amounts of white sputum have just been coughed up by the patient. The patient suffering from dermatitis is being examined by the dermatologist now. Antibiotics are used by patients with preexisting lung diseases. Ann will be administered an injection by the doctor tomorrow. Wards are being cleaned and aired by the nurses now. The patient’s lungs and heart have already been listened to by the therapeutist. Dandelion roots were used by me as a drug for better digestion. With dyspnea, the faster breathing has lately been accompanied by the sensation of running out of air. The lungs are being listened to by the doctor now. The pleura is moistened with a serous secretion. An inspiration had urgently been needed by the patient, before expiration was completed. The paragraph on autoimmune reactions is being read by the students now. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal by the diaphragm. The chest pain will have been reduced by keeping the chest wall still by 8 o’clock. The paragraph on the immune system wasn’t being read by the students when the teacher entered the class-room. Wheezing has been caused by the narrowing of the airways. These tablets were bought by my younger brother. Will the paragraph on eye diseases be read by the students next week? Pulmonary function testing has been needed by the doctor to assess the benefits of treatment. The physician was waited for by his patients. My sister is being examined by the ophthalmologist at the moment. The debilitated is cared for well by the nurse. The district doctor has already been sent for by us. The patient suffering from cataract was being examined by the ophthalmologist when the nurse entered the doctor’s consulting room. The patient suffering from dermatitis is being examined by the dermatologist now. Antibiotics are used by patients with preexisting lung diseases. Small amounts of white sputum have just been coughed up by the patient. The patient’s lungs and heart have already been listened to by the therapeutist. Ann will be administered an injection by the doctor tomorrow. Wards are being cleaned and aired by the nurses now. With dyspnea, the faster breathing has lately been accompanied by the sensation of running out of air. Dandelion roots were used by me as a drug for better digestion. The lungs are being listened to by the doctor now. The paragraph on autoimmune reactions is being read by the students now. The pleura is moistened with a serous secretion. An inspiration had urgently been needed by the patient, before expiration was completed. The chest pain will have been reduced by keeping the chest wall still by 8 o’clock. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal by the diaphragm. The paragraph on the immune system wasn’t being read by the students when the teacher entered the class-room. These tablets were bought by my younger brother. Will the paragraph on eye diseases be read by the students next week? Wheezing has been caused by the narrowing of the airways. My sister is being examined by the ophthalmologist at the moment. Pulmonary function testing has been needed by the doctor to assess the benefits of treatment. The physician was waited for by his patients. The district doctor has already been sent for by us. The patient suffering from cataract was being examined by the ophthalmologist when the nurse entered the doctor’s consulting room. The debilitated is cared for well by the nurse. The patient’s lungs and heart have already been listened to by the therapeutist. Ann will be administered an injection by the doctor tomorrow. Wards are being cleaned and aired by the nurses now. The patch test to establish an allergen will be performed the next week by the dermatologist in charge. The patient had not been properly diagnosed which made treatment more difficult. Talcum powder was used to absorb moisture from the skin. The patients with allergies are usually treated by doctors with antihistamines. The patient with pharyngolaryngitis is being injected antibiotics now. The patient suffering from dyspnea has just been examined Each lung is enveloped in a double-folded membrane called pleura. Was the patient being injected antibiotics when the doctor entered the ward? Had the patient with chest pain been examined before the nurse entered the ward? Nasal cavities are lined with cilia to help filter out foreign bodies. That patient with laryngitis wasn’t being injected antibiotics at 7 o’clock yesterday. That patient suffering from cough won’t have been examined by 9 o’clock. Air passageways can be obstructed by enlarged adenoids. Coughing episodes have recently been accompanied by chest pain. This famous pulmonologist was being spoken about at the meeting yesterday. The entrance to the larynx is covered by epiglottis. The amount of exercise that can be performed has been limited by his shortness of breath. The patient is being looked at with great surprise. The patient suffering from dermatitis is being examined by the dermatologist now. Antibiotics are used by patients with preexisting lung diseases. Small amounts of white sputum have just been coughed up by the patient suffering from bronchitis. The debilitated is cared for well by the nurse. The district doctor has already been sent for by us. The patient suffering from cataract was being examined by the ophthalmologist when the nurse entered the doctor’s consulting room. Pulmonary function testing has been needed by the doctor to assess the benefits of treatment. The physician was waited for. The patient suffering from glaucoma is being examined by the ophthalmologist at the moment. Wheezing has been caused by the narrowing of the airways. This nurse is often laughed at. Will the paragraph on eye diseases be read by the students next week? The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominal by the diaphragm. The chest pain will have been reduced by keeping the chest wall still by 2 o’clock. The paragraph on the immune system wasn’t being read by the students when the teacher entered the class-room. The pleura is moistened with a serous secretion. An inspiration had urgently been needed by the patient, before expiration was completed. The paragraph on autoimmune reactions is being read by the students now. The smallest of the bronchial branches are called bronchioles. With dyspnea, the faster breathing has lately been accompanied by the sensation of running out of air. The lungs are being listened to by the doctor now. Трансформуйте наступні речення у пасивний стан: The nurse checked the blood pressure of the patient before the operation. They were carrying the injured person to the hospital. The patient has lost teeth because of severe gum disease. Some individuals or animals produce antibodies against infectious agents. The teacher will have told the students about strategies for preventing the transmission of HIV by the next week. The doctor and the patient were carrying out their experiments to identify an allergen at 4 o’clock yesterday. The students usually study symptoms of different diseases at the lessons. Protestor Smirnov delivers lectures in Chemistry every morning. I have learnt most information about the endodontic treatment from this book. The denturist will have made a new denture by the next week. The teacher hasn’t explained us the etiology of the respiratory tract diseases yet. The doctor is performing the spinal puncture during the operation now. The new virus particles destroy lymphocytes. The students have already studied the organs of the respiratory system. He was learning internal and external respiration from 3 till 4 yesterday. We use the term “atopic disease” to describe a group of often inherited Ig Emediated diseases. Look! The dentist is pulling the patient`s tooth with forceps. Then the stomatologist gave my sister anesthesia. Before he went to bed he had brushed his dentures. Doctor Petrenko was examining the patients the whole morning yesterday. The students haven’t filled in the case history yet. Bony cage protects lungs and other organs in the chest. Root canal treatment provides desirable curing effect. The dentist has just performed the process of cleansing patient’s teeth . Last week the dentist placed veneers on the patient’s stained teeth. The doctor was examining this patient at 10 o’clock yesterday. This student had studied sense organs by 7 o’clock last night. Nurses keep medical instruments sterile. The doctor was investigating the etiology of this disease during the whole day on Friday. They had translated the text by 7 o’clock yesterday. Veneers provide desirable aesthetic effect. A dentist will perform the process of cleansing patient’s teeth next week. At last the dentist has placed crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. The students are reading the article about nervous system disorders now. Taras had investigated the symptoms of meningitis and encephalitis by 6 o’clock yesterday. Local anesthetics provide a patient with pain-free experience. A dentist will perform the process of cleansing patient’s teeth next time. Last week the dentist placed crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. Doctors make their morning rounds every day. The skin performs the function of an important blood depot. Dr. Petrenko was delivering his lecture on Anatomy at this time on Tuesday. We did not discuss questions concerning maintence of veneers at our meeting yesterday. Has teeth whitening provided a white smile for you discoloured teeth? I am reading a very interesting article on advantages of dental implants now. The students haven’t finished their research work yet. The patient needs a dental crown to protect a severely worn down tooth. At 3 p.m. the teacher was checking the students’ test-papers on professional dental cleanings. The dentist will perform the procedure of teeth whitening next week. At last the dentist has placed crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. Local anesthetics provide a patient with pain-free experience. Next week the dentist will place crowns on the patient’s shaped teeth. Root canal treatment provides desirable curing effect. The dentist has just performed the process of cleansing patient’s teeth. We are learning about the cases of dental implants failure. Tooth whitening hasn’t made dark teeth look whiter. Dentists place veneers mainly on front teeth. Will they be making veneers in the dental laboratory at this time tomorrow? After that the dentist recommended the patient the proper diet. My brother was cleansing the patient’s teeth at that time. The patient disinfects his retainer once a week. The professor will deliver a lecture on teeth whitening next Monday. The surgeon was still performing the operation at 7 p.m. The denturist has already instructed the patient how to take care of partial dentures. The dentist advised the patient to keep the dentures in place over night until the adjustment period is over. This endodontist is performing root treatment now. Researchers are investigating potential new materials for dental restorations. Will they make veneers in the dental laboratory tomorrow? The surgeons were performing the operation at this time on Monday. The dentist has just written out the prescription. The dentist will restore the tooth tomorrow. The nurse was sterilizing dental instruments when I came in. I am reading a very interesting article on advantages of dental implants now. The nurse checked the blood pressure of the patient before the operation. Will teeth whitening provide a white smile for your discoloured teeth? We sent for the doctor. I am reading a very interesting article on pulmonary disorders now. Pleural effusion has just produced pleuritic pain. People can’t avoid some allergens. Foreign particles lodged in the airway will have caused wheezing by the evening. The nurse is injecting corticosteroids under the skin to control the severe patient’s itching. Will they do this test for identifying particular allergens tomorrow? The doctor has detected wheezing by listening with a stethoscope as the person breathes. The nurse was injecting antibiotics to the patient with pneumonia at 2 o’clock yesterday. The physician is examining the patient suffering from laryngitis now. The teacher hasn’t announced the results of the examination in Anatomy yet. The dentist will fill the patient’s tooth tomorrow. The surgeons are still operating on the patient with appendicitis. The doctor has just advised him to take analgesics to relieve headache. The nurse will give the patient intra-venous injection in a quarter of an hour. They were discussing her report on eye diseases from 10 till 11 o’clock yesterday. The doctor has filled in this patient’s case history this week. The scientists use radioallergosorbent test for measuring the quantity of specific antigens IgE in the serum. The nurse is still airing the ward. The doctor had prepared the operation room before the ambulance brought the victims to the hospital. Allergic reaction to ragweed pollen injured the normal tissues in this patient. The skin performs the function of an important blood depot. Dr. Petrenko was delivering his lecture on Anatomy at this time on Tuesday. The students haven’t finished their research work yet. Pleural effusion has just produced pleuritic pain. We sent for the doctor. I am reading a very interesting article on pulmonary disorders now. Foreign particles lodged in the airway will have caused wheezing by the evening. The nurse is injecting corticosteroids under the skin to control the severe patient’s itching. People can’t avoid some allergens. The doctor has detected wheezing by listening with a stethoscope as the person breathes. The nurse was injecting antibiotics to the patient with pharyngolaryngitis at 2 o’clock yesterday. Will they do this test for identifying particular allergens tomorrow? The dentist will fill the patient’s tooth tomorrow. The teacher hasn’t announced the results of the examination in Anatomy yet. The physician is examining the patient suffering from laryngitis now. The doctor has just advised him to take analgesics to relieve headache. The surgeons are still operating on the patient with appendicitis. The nurse will give the patient intra-venous injection in a quarter of an hour. The doctor has filled in this patient’s case history this week. They were discussing her report on eye diseases from 10 till 11 o’clock yesterday. The scientists use radioallergosorbent test for measuring the quantity of specific antigens IgE in the serum. The doctor had prepared the operation room before the ambulance brought the victims to the hospital. The nurse is still airing the ward. Allergic reaction to ragweed pollen injured the normal tissues in this patient. Dr. Petrenko was delivering his lecture on Anatomy at this time on Tuesday. The skin performs the function of an important blood depot. The students haven’t finished their research work yet. The skin performs the function of an important blood depot. Dr. Petrenko was delivering his lecture on Anatomy at this time on Tuesday. The students haven’t finished their research work yet. I have inhaled some particle but I have already coughed it out. Some kind of suffocation was interrupting this patient’s breathing from 1105 to 1112 a.m. yesterday. I’ll identify the allergen through careful detective work. I identified the allergen through careful detective work. Some kind of suffocation was interrupting this patient’s breathing from 11 05 to 1112 a.m. yesterday. I have inhaled some particle but I have already coughed it out. We do not discuss questions concerning allergy treatment at our meetings. We are studying anatomy and physiology of respiration at the moment. Cold air will have influenced his cough before he enters the house. Somebody built this hospital in 1963. The surgeons were performing pharyngotomy at this time on Monday. The cough had brought up sputum before I took medicines. He will inject dilute solution made from extract of insect venom next week. At present the workers are fixing the pulmonary department of the regional hospital. Clear, white, and watery sputum has indicated the presence of a virus. We use antihistamines for treating allergies. The professor was showing us the film about lung cancer caused by cigarette smoking during the whole lesson on Friday. Dyspnea will have limited the amount of the performed physical exercises before he even thinks of it. We sent for the doctor. I am reading a very interesting article on pulmonary disorders now. Pleural effusion has just produced pleuritic pain. People can’t avoid some allergens. Foreign particles lodged in the airway will have caused wheezing by the evening. The nurse is injecting corticosteroids under the skin to control the severe patient’s itching. Will they do this test for identifying particular allergens tomorrow? The doctor has detected wheezing by listening with a stethoscope as the person breathes. The nurse was injecting antibiotics to the patient with pharyngolaryngitis at 2 o’clock yesterday. The physician is examining the patient suffering from laryngitis now. The teacher hasn’t announced the results of the examination in Anatomy yet. The dentist will fill the patient’s tooth tomorrow. The surgeons are still operating on the patient with appendicitis. The doctor has just advised him to take analgesics to relieve headache. The nurse will give the patient’s intra-venous injection in a quarter of an hour. They were discussing her report on eye diseases the from 10 till 11 o’clock yesterday. The doctor has filled in this patient’s case history this week. The scientists use radioallergosorbent test for measuring the quantity of specific antigens IgE in the serum. The nurse is still airing the ward. The doctor had prepared the operation room before the ambulance brought the victims to the hospital. Allergic reaction to ragweed pollen injured the normal tissues in this patient. Передайте наступні речення непрямою мовою: “There will be a scientific TV program on the types of dental restorations tonight”, our teacher said to us. The doctor asked, “Do you smoke or drink any alcohol?” “Don't disturb him. He is working at his report on amalgams and composite resin”, my mum said to me. She said, “Ann has been preparing for her report for two hours already.” “Don’t take these medications today”, the doctor ordered. Then she said, “I went going to see my dentist. I wanted to get a dental checkup”. “I will keep the dentures in place overnight until the adjustment period is over”, said the patient. The doctor asked , “What side effects of this medicine have you had recently?” The student said, “I can't answer your question now, I don't remember everything about direct and indirect restorations. ” The doctor asked , “Are you taking any medicines at the moment?” The nurse said, “Don't worry. The dentist will be here to give you a hand.” She said, “Barbara has been a nurse for 20 years in this dental clinic and she is still working here” The nurse said, “Now, the doctor is doing everything possible to save your son”. The patient asked, “Shall I be discharged from the hospital tomorrow?” Mary said: “I’ll call the first aid station”. The doctor asked his assistant, “When did the lymph nodes in this patient swell?” The pediatrician said to the child, “Don’t be afraid and don’t cry”. The professor said to the students: “Many people experience serious long-term complications often resulting in autoimmune reactions”. The patient’s parents asked, “Will our son feel better soon after taking these drugs?” Sane said, “I’ve already talked to the doctor”. She asked, “How long do the active symptoms of this disease persist?” The doctor said, “Don’t enter the operating room!” The nurse said to the doctor, “I haven’t filled in the case history of this patient yet”. The doctor asked,” Did you have any allergic reactions before?”. The nurse said to the dentist, ”I gave that patient some sedative drugs last night”. The doctor said, ”Don’t use fluoride toothpaste for your teeth so often”. The dentist asked the patient,” When will you come to my office next time?” Tony asked the nurse, “Do you consider the pulse of the patient to be accelerated?” The patient said, “She didn’t expect to have complications after influenza”. Sam asked the nurse, “When will you give me an injection?” The doctor asked,” Do you feel numbness in this area?”. The nurse said to the dentist, ”I have given that patient some sedative drugs”. The doctor said, ”Brush and floss your teeth more carefully”. The dentist asked the patient,” When did you have your tooth extracted?” The traumatologist asked her, “Pull up the sleeve so that I can look at the wound”. The teacher explained us, “A person with HIV can remain well for over a decade”. She asked, “Is the immune system of premature infants fully developed?” Olga’s relatives were told, “Olga’s condition has improved greatly since last week”. The doctor said, ”You will feel numbness in a minute”. The nurse asked the dentist, ”Why have you administered antibiotics”. The doctor said, ”Don’t move”. The dentist asked the patient, ”Do you have any allergic reactions?” The student asked, “When will neurologic examination be performed?” The doctor said to me, “Don’t take off the plaster cast for a week”. She said, “Antituberculosis vaccination is administered to all the babies in maternity homes”. The patient said, “My dentures have been ill fitting for quite some time” He said, “Two days ago we watched the endodontist removing the pulp”. “If I feel better, I shall attend the lecture in Anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. The lecturer said, “Learn the procedure of simple tooth extraction in detail”. The student asked, “Are innate and learned immunity independent of each other?” The teacher said, “We’ll study the diseases of the nervous system next week”. The patient asked the doctor, “What drugs are usually taken to reduce fever?” The doctor said to him, “Don’t forget to have your chest examined once a year”. Describing his general state the patient said: “I suffered from severe headaches, cough, and had trouble sleeping”. The denturist said, “Yesterday I fabricated maxillary denture for your grandfather”. “Do you prefer composite resin or ceramic filling for your front tooth?” the dentist asked his patient. The lecturer said: “You’ll have to know in detail three types of neurons”. The nurse asked the doctor, “Why has the blood pressure fallen?” He asked, “Are they performing magnetic resonance imaging now?” The doctor asked, ”Do you feel numbness in this area?”. The nurse said to the dentist, ”I have given this patient some sedative drugs”. The lecturer said, “Learn the structure of the nervous system in detail”. “Have you already interviewed the patient to obtain his medical history?” the professor asked the student. The doctor said to the patient, ”You will feel numbness in a minute”. The dentist asked the patient, ”Have you ever had any allergic reactions?” “Don’t speak loud, the patient is sleeping after the medical procedure”, the doctor said to him. The doctor said, ”Don’t use fluoride toothpaste for your teeth so often”. The dentist asked the patient, ”When will you come to my office next time?” “What was muscle atrophy caused by?” asked the nurse. I said to the doctor, “This patient suffers from severe headaches”. The teacher said, “In a week we are having practice in the polyclinic”. He asked, “When will you perform tooth extraction?” “If I feel better, I’ll attend the lecture in anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. The student said to the lecturer, “I have got most information about the structure of the CNS from this book”. The dentist asked, “Do you feel numbness?” My sister said to me: “Don’t speak loud, mother is sleeping after the procedure of tooth extraction”. The teacher said, “We are having a test on the structure of the nervous system in a week”. He asked, “Did you order special tests to confirm the diagnosis?” The patient asked the doctor, “When will you perform the spinal tap?” The laryngologist said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. “Write three sentences in passive voice”, our teacher said to us. The doctor asked, “Did you take any drugs yesterday?” “My sister will become an orthodontist”, he said. Then she said, “Brush your teeth thoroughly but not too vigorously”. The patient complained, “I have been suffering from severe halitosis for over a year”. The maxillofacial surgeon said to me, “Make a panoramic X-ray tomorrow”. The mother said to her son, “The dentist has prescribed you this toothpowder to maintain oral hygiene”. “When will you like to have your appointment?” the dentist asked Tom. The nurse said to us. “There is no dentist here, in the office. He has just left. He’ll come back tomorrow”. The lecturer said, “Learn the procedure of ultrasonic teeth cleaning in detail.” The patient said,” My dentures have been ill-fitting for quite some time”. ”The dentist had left the office before I came”, the nurse said to us. He said, “We have already watched the endodontist removing the pulp.” The professor asked, “Did you like your practice at the dental clinic?” “If I feel better, I shall attend the lecture in Anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. The doctor asked, “Do you smoke or drink any alcohol?” The patient said, “My dentures have been ill-fitting for quite some time. What shall I do?” He said, “Two days ago we watched the endodontist removing the pulp”. The doctor said, “I was examining the patient”. Describing his general state the patient said: “I suffered from severe headaches, cough, and had trouble sleeping”. He asked: “Why have you ordered computed tomography?” The student asked: “Do you know that interneurons are found only in the CNS where they connect neuron to neuron?” The patient in ward 4 said, “Don’t open the window, please”. The doctor said: “I have been examining patients since morning”. The patient complained: “I suffer from severe headaches beginning in the morning or early afternoon and worsening during the day”. He asked: “Who is performing electroencephalography?” My mother who suffers from migraine headaches asked the doctor: “Must I take drugs every day to prevent migraine attacks from recurring?” The pediatrician said to the child, “Don’t cry and sit calm, please”. The teacher asked, “When and why did lymph nodes swell in this patient?” The immunologist asked the patient, “Do you feel better after taking the drugs?” The physician said to the patient, “Strip to the waist, please!” The professor said to us, “I’ll discharge your father from the hospital in two days”. He said, “I suffered from this neurological disorders last year”. The doctor said: “I shall examine patients”. Respiratory therapist said: “I have already removed secretions from the airways”. Ann asked: “When will my mother be hospitalized?” Lily asked me, “Had you learned the general structure of the nervous system before I came?” The teacher said to the students, “Be attentive, please”. The immunologist asked the patient, “Does anybody in your family suffer from congenital immunodeficiency?” The physician admitted, “This patient’s general condition is extremely grave now”. The pediatrician said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. Oleg promised, “Next week I’ll deliver an interesting report dealing with the mysterious brain functions”. The teacher asked the student, “What components of the immune system do you know?” The teacher asked the student, “What classes of antibodies do you know?” The neurologist said to us, “The examination, performed 3 days ago, revealed lower limb paralysis”. The doctor said to the parents, “I’ll test your child’s reflexes in some minutes”. The intern asked the doctor, “Can people who have been repeatedly exposed to HIV infection over years remain uninfected?” The neurologist said to the man, “Touch your nose with a forefinger and then touch my finger”. The lecturer said to us, “You’ll begin studying physiology of the nervous system next week”. I said to my friend, “Here, at the district hospital, it is very interesting to watch otolaryngologists perform physical examinations”. The teacher asked the student, “What main types of immunity do you know?” The patient asked the doctor, “Is avoiding an allergen better than allergic reaction treatment?” The ophthalmologist said to the woman, “Close your left eye and look at the table with your right one”. The student said to the lecturer, “I have got most information about the structure of the CNS from this book”. The teacher said, “We are having a test on the structure of the nervous system in a week”. He asked, “Did you order special tests to confirm the diagnosis?” The patient asked the doctor, “When will you perform the spinal tap?” The laryngologist said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. Describing his general state the patient said: “I suffered from severe headaches, cough, and had trouble sleeping”. The student asked: “Do you know that interneurons are found only in the CNS where they connect neuron to neuron?” He asked: “Why have you ordered computed tomography?” The patient in ward 4 said, “Don’t open the window, please”. The doctor said, “I was examining the patient”. The patient complained: “I suffer from severe headaches beginning in the morning or early afternoon and worsening during the day”. My mother who suffers from migraine headaches asked the doctor: “Must I take drugs every day to prevent migraine attacks from recurring?” The doctor said: “I have been examining patients since morning”. He asked: “Who is performing electroencephalography?” The pediatrician said to the child, “Don’t cry and sit calm, please”. Respiratory therapist said: “I have already removed secretions from the airways”. The doctor said: “I shall examine patients”. Lily asked me, “Had you learned the general structure of the nervous system before I came?” Ann asked: “When will my mother be hospitalized?” The teacher said to the students, “Be attentive, please”. The physician said to the patient, “Strip to the waist, please!” The professor said to us, “I’ll discharge your father from the hospital in two days”. The teacher asked, “When and why did lymph nodes swell in this patient?” He said, “I suffered from this neurological disorders last year”. The immunologist asked the patient, “Do you feel better after taking the drugs?” The physician admitted, “This patient’s general condition is extremely grave now”. The pediatrician said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. The immunologist asked the patient, “Does anybody in your family suffer from congenital immunodeficiency?” Oleg promised, “Next week I’ll deliver an interesting report dealing with the mysterious brain functions”. The teacher asked the student, “What components of the immune system do you know?” The intern asked the doctor, “Can people who have been repeatedly exposed to HIV infection over years remain uninfected?” The lecturer said to us, “You’ll begin studying physiology of the nervous system next week”. The teacher asked the student, “What classes of antibodies do you know?” I said to my friend, “Here, at the district hospital, it is very interesting to watch otolaryngologists perform physical examinations”. The neurologist said to the man, “Touch your nose with a forefinger and then touch my finger”. The neurologist said to us, “The examination, performed 3 days ago, revealed lower limb paralysis”. The patient asked the doctor, “Is avoiding an allergen better than allergic reaction treatment?” The doctor said to the parents, “I’ll test your child’s reflexes in some minutes”. The teacher asked the student, “What main types of immunity do you know?” The ophthalmologist said to the woman, “Close your left eye and look at the table with your right one”. The student said to the lecturer, “I have got most information about the structure of the CNS from this book”. The patient asked the doctor, “When will you perform the spinal tap?” He asked, “Did you order special tests to confirm the diagnosis?” The laryngologist said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. The teacher said, “We are having a test on the structure of the nervous system in a week”. The doctor said, “I am examining the patient”. “In a year we shall have practice in the neurological department”, said our professor to us. He asked: “When will you perform the spinal tap?” “Have you suffered from this disease since childhood?” the doctor asked his patient. The physician said to the patient: “Breathe deeply”. The student said to the lecturer, “I have got most information about the structure of the CNS from this book”. The teacher said, “We are having a test on the structure of the nervous system in a week”. He asked, “Did you order special tests to confirm the diagnosis?” The patient asked the doctor, “When will you perform the spinal tap?” The laryngologist said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. The doctor said: “I’ll examine all these patients tomorrow”. The neurologist asked: “Do you feel membranes, tinglish, or pain?” “Where and how often have your symptoms recently occurred?”, asked the physician. The doctor said to his assistant: “Insert the needle into the spinal canal, please”. The doctor said: “I examine patients every day”. The lecturer said: “You’ll have to know in detail three types of neurons”. He asked: “Have you ordered special tests to confirm the diagnosis?” The doctor said to his assistant: “Insert the needle into the spinal canal, please”. The nurse asked the doctor: “Why has the blood pressure fallen?” The doctor said: “I examined patients every day”. “If I feel better, I will attend the lecture in anatomy tomorrow”, said Helen to me. He asked: “What diagnosis did you make?” The doctor said to the patient: “Don’t move”. “Have you already interviewed the patient to obtain his medical history?” the professor asked the student. The doctor said: “I have examined patients”. The teacher said: “We are having a test on the structure of the nervous system in a week”. He asked: “Are they performing magnetic resonance imaging tomorrow?” The lecturer said: “Learn the structure of the nervous system in detail”. “Where and how often do your symptoms occur?” asked the physician. The doctor said: “I have examined patients”. Examining the patient the doctor said: “The CNS is within normal limits now”. “Don’t speak loud, the patient is sleeping after the medical procedure”, the doctor said to him. The neurologist asked: “Do you feel numbness, tingling, or pain?” “What was muscle atrophy caused by?” asked the nurse. The teacher asked the student, “What main types of immunity do you know?” The patient asked the doctor, “Is avoiding an allergen better than allergic reaction treatment?” The ophthalmologist said to the woman, “Close your left eye and look at the table with your right one”. The neurologist said to us, “The examination, performed 3 days ago, revealed lower limb paralysis”. The doctor said to the parents, “I’ll test your child’s reflexes in some minutes”. The teacher asked the student, “What components of the immune system do you know?” The immunologist asked the patient, “Does anybody in your family suffer from congenital immunodeficiency?” The pediatrician said to the child, “Open your mouth, please”. The physician admitted, “This patient’s general condition is extremely grave now”. Oleg promised, “Next week I’ll deliver an interesting report dealing with the mysterious and remarkable brain functions”. The teacher asked the student, “What classes of antibodies do you know?” The intern asked the doctor, “Can people who have been repeatedly exposed to HIV infection over years remain uninfected?” The neurologist said to the man, “Touch your nose with a forefinger and then touch my finger”. The lecturer said to us, “You’ll begin studying physiology of the nervous system next week”. I said to my friend, “Here, at the district hospital, it is very interesting to watch otolaryngologists perform physical examinations”. The teacher asked, “When and why did lymph nodes swell in this patient?” The immunologist asked the patient, “Do you feel better after taking the drugs?” The physician said to the patient, “Strip to the waist, please!” The professor said to us, “I’ll discharge your father from the hospital in two days”. He said, “I was treated for my neurological disorders last year”. The doctor said: “I shall examine patients”. Respiratory therapist said: “I have already removed secretions from the airways”. Ana asked: “When will my mother be hospitalized?” Lily asked me, “Had you learned the general structure of the nervous system before I came?” The teacher said to the students, “Be attentive, please”. The doctor said: “I have been examining patients since morning”. The patient complains: “I suffer from severe headaches beginning in the morning or early afternoon and worsening during the day”. He asked: “Who is performing electroencephalography?” My mother who suffers from migraine headaches asked the doctor: “Must I take drugs every day to prevent migraine attacks from recurring?” The pediatrician said to the child, “Don’t cry and sit calm, please”. The doctor said, “I was examining the patient”. Describing his general state the patient said: “I suffered from severe headaches, cough, and had trouble sleeping”. He asked: “Why have you ordered computed tomography?” The student asked: “Do you know that interneurons are found only in the CNS where they connect neuron to neuron?” The patient in ward 4 said, “Don’t open the window, please”. Перекладіть наступні речення англійською мовою: Відомо, що природний тип імунітету успадковується людиною. Вчора в цей час студенти обговорювали текст про різні типи алергічних реакцій. Ми щойно прочитали цікаву статтю про захворювання верхніх дихальних шляхів. Окуліст сказав, що він заповнив історію хвороби цього пацієнта минулого разу. Пацієнта з третьої палати було уже прооперовано, коли зайшов професор. Терапевт сказав, що кров’яний тиск цього пацієнта вже виміряно. Всі імпульси передаються від одного нейрона до іншого через нервові волокна. Незабаром лікар введе йому вакцину, щоб викликати активний імунітет. Коли ми зайшли в палату, нашого товариша якраз оглядав окуліст. Ми знали, що вона працювала у лабораторії вчора весь день. Його головний біль був викликаний високим кров’яним тиском. Ти добре розмовляєш англійською? – Так. Я вивчаю англійську мову протягом 7 років. Переливання крові буде зроблено досвідченим лікарем до 2 годин. Медсестра сказала, що температуру цього пацієнта вже виміряно. Викладач з анатомії каже, що активність тіла контролюється нервовою системою. Він знає, що лекція з анатомії буде дуже цікавою. Цю лекцію буде прочитано професором з Лондона. Операцію було відмінено хірургом, оскільки пацієнт почувався дуже погано. Коли черговий лікар зайшов у палату, медсестра вимірювала мені температуру. Тебе коли-небудь оглядав окуліст? – Ні. У мене ніколи не було проблем із зором. Ця стаття про органи відчуття зараз обговорюється студентами на практичному занятті. Хірург сказав, що використав цей інструмент наприкінці операції, яку було виконано в середу. Пацієнта, що хворіє пневмонією, оглянуть через 2 години. Цей професор піде на конференцію? – Так, його запросили. Зараз важко говорити про стан цього пацієнта. Його ще не прооперували. На кафедрі біології проводиться більше сотні експериментів щороку. Він сказав, що викликав дільничного лікаря 15 хвилин тому. Коли ми зайшли у палату, Олег якраз приймав ліки від головного болю. Завтра протягом цілої пари професор розповідатиме нам, які захворювання може викликати куріння. Коли я зайшов до кабінету лікаря, історія хвороби вже була заповнена педіатром. У даний момент голку вводять у спинний канал, щоб отримати зразок мозкової рідини. Статтю про профілактику захворювань головного мозку буде написано цим студентом завтра. Коли медсестра зайшла у палату, живіт пацієнта пальпувався хірургом. Професор розповідатиме про причини захворювання СНІДом завтра на другій парі. Лікар щойно описав усі симптоми пацієнта, який хворіє на менінгіт. Ми знаємо, що головний мозок людини може бути ушкоджений злоякісною пухлиною. Стоматолог сказав, що хворий зуб цієї жінки уже вилікувано. Відомо, що близько 90% інформації сприймається людиною через очі. Операцію закінчать до того часу, як прийдуть студенти. Я знаю цього чоловіка. Він ніколи не хворів на дерматит. Коли медсестра зайшла у палату, терапевт якраз оглядав пацієнта. З якого часу ви працюєте в цьому диспансері? – Я працюю тут з 2001 року. Вони готуватимуть ці ліки проти алергії 45 хв., перш ніж усе буде зроблено. Підлогу в палатах буде вимито до повернення пацієнтів із інгаляційної. Пневмонія спричиняється різними мікроорганізмами. Консультуючий лікар сказав зробити завтра церебральну ангіографію для того, щоб визначити патологію кровоносних судин головного мозку. Цей імунолог розмірковує над діагнозом того маленького хлопчика впродовж дня. Алерголог виписував рецепти впродовж п’яти хвилин до того, як я прийшов. Коли постраждалих привезли до лікарні, операційну вже було підготовлено. Вітряна віспа спричинила пневмонію у цього пацієнта. Лікар повинен був передбачити те, що цей препарат викличе небажані побічні явища. Хто з ваших колег робить операцію вже п’яту годину поспіль? Ми шукали аптеку майже 20 хвилин перш ніж знайшли її. Тебе вже питали про самопочуття після прийняття відхаркуючих препаратів? Діагноз пневмонії буде напевне підтверджено рентгенологічним дослідженням Студент був дуже радий, що його відправили на міжнародну студентську конференцію. Міжнародний семінар імунологів уже завершився. Він тривав майже тиждень. Я читала медичну енциклопедію протягом кількох хвилин перш ніж знайшла потрібну інформацію стосовно алергічного риніту. Діагноз було встановлено ще до того, як прозвучали такі симптоми, як синюшність, утруднене дихання, загрудинний біль і “барабанні палички”. У той час, коли вислуховувалися легені, було почуто явні хрипи, що вказувало на пневмонію. Цього хворого госпіталізували для того, щоб провести ефективну терапію. Здається, що він не слухає те, що професор розповідає про сенсорну систему. До початку наступного тижня ваш кашель буде вилікувано. Мій син не чекатиме й 5 хвилин поки прийде лікар. Інколи пневмонію може бути спричинено грибком. Бабуся всюди шукає свої ліки від зобу. Вона шукає їх уже півгодини. Він працює імунологом у терапевтичному відділенні обласної лікарні вже десять років. Науковці працювали над цією проблемою три роки до того, як вони поїхали на всесвітню наукову конференцію, присвячену алергічним реакціям. Палату все ще провітрюють. Зразки харкотиння і крові було вивчено ще до кінця робочого дня. Пацієнт був задоволений тим, що його так ретельно обстежили вчора. Коли викладач увійшов до класу, студенти обговорювали вчорашню телепередачу про ставлення громадськості до ВІЛ-інфікованих людей. Вони обговорювали її уже десять хвилин. Я вже півроку шукаю причину своєї алергії і ніяк не можу знайти. О сьомій вечора операцію ще робили. Цим видом пневмонії інфікуються переважно у лікарнях і готелях через вентиляційні системи. Стан пацієнта був надто важким, щоб транспортувати його в іншу лікарню. Цей професор піде на конференцію? – Так, його запросили. Зараз важко говорити про стан цього пацієнта. Його ще не прооперували. На кафедрі біології проводиться більше сотні експериментів щороку. Він сказав, що викликав дільничного лікаря 15 хвилин тому. Коли ми зайшли у палату, Олег якраз приймав ліки від головного болю. Підлогу в палатах буде вимито до повернення пацієнтів із інгаляційної. Пневмонія спричиняється різними мікроорганізмами. З якого часу ви працюєте в цьому диспансері? – Я працюю тут з 2001 року. Консультуючий лікар сказав зробити завтра церебральну ангіографію для того, щоб визначити патологію кровоносних судин головного мозку. Вони готуватимуть ці ліки проти алергії 45 хв., перш ніж усе буде зроблено. Коли постраждалих привезли до лікарні, операційну вже було підготовлено. Алерголог виписував рецепти впродовж п’яти хвилин до того, як я прийшов. Вітряна віспа спричинила пневмонію у цього пацієнта. Цей імунолог розмірковує над діагнозом того маленького хлопчика впродовж дня. Лікар повинен був передбачити те, що цей препарат викличе небажані побічні явища. Хто з ваших колег робить операцію вже п’яту годину поспіль? Ми шукали аптеку майже 20 хвилин перш ніж знайшли її. Тебе вже питали про самопочуття після прийняття відхаркуючих препаратів? Діагноз пневмонії буде напевне підтверджено рентгенологічним дослідженням Студент був дуже радий, що його відправили на міжнародну студентську конференцію. Діагноз було встановлено ще до того, як прозвучали такі симптоми, як синюшність, утруднене дихання, загрудинний біль і “барабанні палички”. Міжнародний семінар імунологів уже завершився. Він тривав майже тиждень. У той час, коли вислуховувалися легені, було почуто явні хрипи, що вказувало на пневмонію. Цього хворого госпіталізували для того, щоб провести ефективну терапію. Я читала медичну енциклопедію протягом кількох хвилин перш ніж знайшла потрібну інформацію стосовно алергічного риніту. Мій син не чекатиме й 5 хвилин поки прийде лікар. Інколи пневмонію може бути спричинено грибком. Здається, що він не слухає те, що професор розповідає про сенсорну систему. До початку наступного тижня ваш кашель буде вилікувано. Бабуся всюди шукає свої ліки від зобу. Вона шукає їх уже півгодини. Палату все ще провітрюють. Науковці працювали над цією проблемою три роки до того, як вони поїхали на всесвітню наукову конференцію, присвячену алергічним реакціям. Зразки харкотиння і крові було вивчено ще до кінця робочого дня. Пацієнт був задоволений тим, що його так ретельно обстежили вчора. Він працює імунологом у терапевтичному відділенні обласної лікарні вже десять років. Я вже півроку шукаю причину своєї алергії і ніяк не можу знайти. О сьомій вечора операцію ще робили. Коли викладач увійшов до класу, студенти обговорювали вчорашню телепередачу про ставлення громадськості до ВІЛ-інфікованих людей. Вони обговорювали її уже десять хвилин. Стан пацієнта був надто важким, щоб транспортувати його в іншу лікарню. Цим видом пневмонії інфікуються переважно у лікарнях і готелях через вентиляційні системи. Цей професор піде на конференцію? – Так, його запросили. Він сказав, що викликав дільничного лікаря 15 хвилин тому. Коли ми зайшли у палату, Олег якраз приймав ліки від головного болю. Зараз важко говорити про стан цього пацієнта. Його ще не прооперували. На кафедрі біології проводиться більше сотні експериментів щороку. Цей професор піде на конференцію? – Так, його запросили. Зараз важко говорити про стан цього пацієнта. Його ще не прооперували. На кафедрі біології проводиться більше сотні експериментів щороку. Він сказав, що викликав дільничного лікаря 15 хвилин тому. Коли ми зайшли у палату, Олег якраз приймав ліки від головного болю. Чому ти така схвильована? – Цілий день я намагаюсь додзвонитись до своїх батьків, але ніхто не відповідає. Екстракти з пилкових алергенів застосовують для проведення шкірних тестів на чутливість до рослинного пилку, а також в імунотерапії при пилковій алергії. Мого брата все ще оперують. Що зможе примусити його піти на консультацію до невропатолога? Лікуючий невропатолог вважав, що цей препарат сприятиме запобіганню нападів мігрені. Я переглядаю статті стосовно імунної реакції організму людини на такі захворювання, як вітряна віспа, кір та поліомієліт з шостої ранку. Він жив зі своєю дружиною понад 5 років, коли дізнався, що вона ВІЛінфікована. Зараз обговорюють фізіологію дихання. Мене вже попередили про небезпеку кровохаркання. Пневмонія почалася після того, як патогенний мікроорганізм вдихнули в легені. Він мріє стати лікарем з дитинства. Він вживав наркотики впродовж багатьох років, тому й не дивно, що він заразився ВІЛ-інфекцією. Ці ліки мені призначено лікарем. Студентам ще не оголосили результатів іспиту з анатомії. У цей момент дуже уважно слухають скарги пацієнта для того, щоб поставити правильний діагноз на основі симптомів. Скільки часу ви вивчаєте англійську мову? – Я вивчаю її вже три роки. Мати годувала дитину грудним молоком уже кілька днів, коли результати високочутливого тесту Р24 виявили у неї вірус імунодефіциту. Йому наказали не рухатись. Йому щойно порадили нову мікстуру від кашлю. У людини, яку було інфіковано пневмококом, розвивається частковий імунітет до цього типу вірусу. Вони вже півтори години обговорюють питання природи набутого імунітету. Коли Марія закінчила медичний інститут, її сестра уже три роки працювала лікарем у інфекційній лікарні. Лікар сказав, що аналіз мокротиння уже зроблено. При запаленні легень уражаються як альвеоли, так і тканини навколо них. Невропатолог сказав, що наступного тижня призначить цьому хворому з геміплегією комп’ютерну томографію. Цей пацієнт гуляє у дворі лікарні вже дві години? Його батьки продали квартиру, в якій прожили 20 років. Їм потрібні гроші на лікування ВІЛ-інфікованого сина. Ці записи в історії хвороби було зроблено на цьому тижні. Якщо не прийняти жодних застережних заходів, інфекцію буде принесено до легень кров’яним руслом. Лікар сказав студентам-практикантам, що, якщо кровоносні судини, що контролюють м’язи руху лівої ноги, заблокуються, то ногу спаралізує. З якого часу ви працюєте в цьому диспансері? – Я працюю тут з 2001 року. Вони готуватимуть ці ліки проти алергії 45 хв., перш ніж усе буде зроблено. Підлогу в палатах буде вимито до повернення пацієнтів із інгаляційної. Пневмонія спричиняється різними мікроорганізмами. Консультуючий лікар сказав зробити завтра церебральну ангіографію для того, щоб визначити патологію кровоносних судин головного мозку. Цей імунолог розмірковує над діагнозом того маленького хлопчика впродовж дня. Алерголог виписував рецепти впродовж п’яти хвилин до того, як я прийшов. Коли постраждалих привезли до лікарні, операційну вже було підготовлено. Вітряна віспа спричинила пневмонію у цього пацієнта. Лікар повинен був передбачити те, що цей препарат викличе небажані побічні явища. Хто з ваших колег робить операцію вже п’яту годину поспіль? Ми шукали аптеку майже 20 хвилин перш ніж знайшли її. Тебе вже питали про самопочуття після прийняття відхаркуючих препаратів? Діагноз пневмонії буде напевне підтверджено рентгенологічним дослідженням Студент був дуже радий, що його відправили на міжнародну студентську конференцію. Міжнародний семінар імунологів завершився. Він тривав майже тиждень. Я читала медичну енциклопедію протягом кількох хвилин перш ніж знайшла потрібну інформацію стосовно алергічного риніту. Діагноз було встановлено ще до того, як прозвучали такі симптоми, як синюшність, утруднене дихання, загрудинний біль і “барабанні палички”. У той час, коли вислуховувалися легені, було почуто явні хрипи, що вказувало на пневмонію. Цього хворого госпіталізували для того, щоб провести ефективну терапію. Бабуся всюди шукає свої ліки від зобу. Вона шукає їх уже півгодини. Мій син не чекатиме й 5 хвилин поки прийде лікар. До початку наступного тижня ваш кашель буде вилікувано. Інколи пневмонію може бути спричинено грибком. Здається, що він не слухає те, що професор розповідає про сенсорну систему. Він працює імунологом у терапевтичному відділенні обласної лікарні вже десять років. Науковці працювали над цією проблемою три роки до того, як вони поїхали на всесвітню наукову конференцію, присвячену алергічним реакціям. Палату все ще провітрюють. Зразки харкотиння і крові було вивчено ще до кінця робочого дня. Пацієнт був задоволений тим, що його так ретельно обстежили вчора. Коли викладач увійшов до класу, студенти обговорювали вчорашню телепередачу про ставлення громадськості до ВІЛ-інфікованих людей. Вони обговорювали її уже десять хвилин. Я вже півроку шукаю причину своєї алергії і ніяк не можу знайти. О сьомій вечора операцію ще робили. Цим видом пневмонії інфікуються переважно у лікарнях і готелях через вентиляційні системи. Стан пацієнта був надто важким, щоб транспортувати його в іншу лікарню.