AA - Study Guide - Imperialism, Progressive Era, and WWI
advertisement

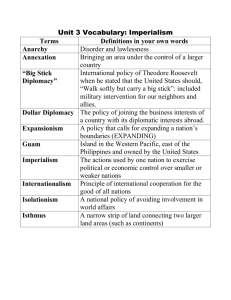
Study Guide – Age of Imperialism, Progressive Era, and WWI Chapter 7 - What is Imperialism? - What were the causes of American / “Western” imperialism? (* Anglo-Saxonism * Ethnocentrism * Military bases and Overseas markets * Jingoism) - How did U.S. Naval Officer Alfred Mahan’s ideas affect U.S. imperialism and militarism as well as the actions of other major world powers around the world? - What is yellow journalism? - Causes of the Spanish-American War - How did the United States achieve victory in the Spanish-American War? - Consequences of the Spanish-American War - Annexing the Philippines - Changes in U.S. foreign policy, from “Monroe Doctrine” to “Roosevelt Corollary” and “dollar diplomacy” - “Open Door Policy” regarding China - How did the U.S. build the Panama Canal, including its diplomatic dealings with first Columbia and then the new nation of Panama? Chapter 8 - Describe the conditions of cities and in the country and why the Progressive reformers wanted change. - Triangle Shirtwaist Fire – what reforms did this motivate? - What were reforms in child labor laws and workers’ compensation during this era? - 16th, 17th, 18th, and 19th Amendments * (Prohibition, women’s suffrage, direct election of Senators, and income tax) - Know the following terms: Muckrakers, referendum, recall, direct primary, and initiative - How did Theodore Roosevelt change the presidency? - How did President Theodore Roosevelt handle the Coal Strike of 1902? - What were President Theodore Roosevelt’s actions in Northern Securities vs. the United States? - What were President Theodore Roosevelt’s actions regarding western land reserves and conservation? - Consumer protections: Meat Inspection and Pure Food and Drug Acts - What was the significance of the following: Federal Reserve Act, Federal Trade Commission, and Clayton Antitrust Act? Chapter 9 - What were the causes of World War One? - Specifically, how did “the crisis in the Balkans” and nationalism, the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the quest for “balance of power” with the alliance system in Europe cause World War One? - Know the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance - Schlieffen Plan - What does “consent of the governed” and “national self determination” mean? - Know the major events relating to the U.S. becoming involved in World War One, including the sinking of the Lusitania and the Sussex, the Sussex Pledge, Germany resuming unrestricted submarine warfare, the first Russian Revolution, and the Zimmerman Telegram. - Know how the War Industries Board, the National War Labor Board, the Committee on Public Information, and the Selective Service Act of 1917 effected the United States preparation for World War One. - How did the Espionage Act of 1917 and the Sedition Act of 1918 limit free speech and a citizen’s ability to oppose the U.S. war effort? - Importance of artillery fire, the machine gun, and trench warfare upon WWI - First Battle of Marne, First Battle of Ypres, and Battle of Saint Mihiel - German Spring Offensive, 1918 - Allied Powers “Hundred Days Offensive” - Effects of “Spanish Influenza” - Wilson’s 14 Points, including “national self determination” and League of Nations - Treaty of Versailles and consequences of WWI, including … - War reparations and “war guilt clause” and - Four empires come to an end