Algebra 2 Monday, 9/22/14
advertisement

Algebra 2
Monday, 9/22/14
1. Warm-ups: pre-req skills needed for Chapter 2 (pg 57 #1-19 all)
2. Discussion/Notes/Guided Practice: 2.1 Relations and Functions
3. HW: A#2.1 pages 62-63 #13-22 all; and #24-42 evens -- due Tues
UPCOMING QUIZ and TEST DATES:
Wed 10/1: Quiz - Sections 2.1 - 2.4
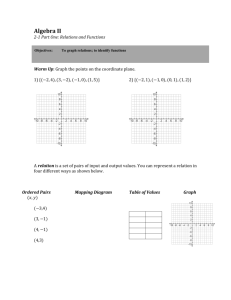
WARM-UPS: Complete page 57 #1-19 all
write your answers on this page
1. Identify the BIG Ideas for Chapter 2
5. Determine if a graph is discrete or continuous
2. Define key vocabulary terms for Section 2.1
3. Analyze and graph relations
4. Determine if a relation is a function
6. Understand and use the vertical line test to
determine if a graph is a function
7. Find functional values
Success Criteria: Q&A, Guided Practice Problems, HW
Learning target #1
Preview of Chapter 2
Linear Relations and Functions
Use your textbook and identify the five “BIG Ideas” for Chapter 2:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Preview of Chapter 2
Linear Relations and Functions
1. Analyze relations and functions
2. Identify, graph, and write linear equations
3. Find the slope of a line
4. Draw scatter plots and find prediction equations
5. Graph special functions, linear inequalities, and absolute value
inequalities
Learning target #2
Vocabulary for this section –
How many do you already know?
• Ordered pair:
• One-to-one function:
• Cartesian coordinate plane:
• Discrete function:
• Quandrant:
• Continuous function:
• Relation:
• Vertical line test:
• Domain:
• Independent variable:
• Range:
• Dependent variable:
• Function:
• Function notation:
• Mapping:
Learning target #2
• ________________: A pair of
coordinates, written in the form
(x, y), used to locate any point
on a coordinate plane.
• ________________________:
composed of the x-axis
(horizontal) and y-axis (vertical),
which meet at the origin (0, 0)
and divide the plane into four
quandrants.
Learning target #2
• Ordered Pair: A pair of
coordinates, written in the form
(x, y), used to locate any point
on a coordinate plane.
• Cartesian Coordinate Plane:
composed of the x-axis
(horizontal) and y-axis (vertical),
which meet at the origin (0, 0)
and divide the plane into four
quandrants.
Examples:
• ______________: is a set of
ordered pairs.
• ______________ (of a relation):
the set of all first coordinates (xcoordinates) from the ordered
pairs.
• _____________ (of a relation):
the set of all second coordinates
(y-coordinates) from the order
pairs.
Learning targets #2 & 3
Relation; Domain; Range
Learning targets #2 & 3
Examples:
• Relation: is a set of ordered pairs.
• Domain (of a relation): the set of
all first coordinates (x-coordinates)
from the ordered pairs.
• Range (of a relation): the set of all
second coordinates (y-coordinates)
from the order pairs.
• Relation:
{ (12, 28), (15, 30), (8, 20), (12, 20), (20, 50)}
• Domain:
{8, 12, 15, 20}
• Range:
{20, 28, 30, 50}
Function
Functions can be represented as 𝑓 𝑥 or 𝑔 𝑥 .
When speaking, we say “F of x” or “G of x”.
• A ___________ is a special type of
relation. Each element of the
domain is paired with exactly one
element of the range.
• A ______________ shows how the
members are paired. An example is
shown to the right.
• The example to the right is a
function; each element of the
domain is paired with exactly one
element of the domain. This is called
a one-to-one function.
Learning targets #2 & 4
Function
Functions can be represented as 𝑓 𝑥 or 𝑔 𝑥 .
When speaking, we say “F of x” or “G of x”.
• A ___________ is a special type of
relation. Each element of the
domain is paired with exactly one
element of the range.
• A ______________ shows how the
members are paired. An example is
shown to the right.
• The example to the right is a
function; each element of the
domain is paired with exactly one
element of the domain. This is called
a one-to-one function.
Learning targets #2 & 4
• Relation:
{(12, 28), (15, 30), (8, 20)}
Domain
Range
12
28
15
30
8
20
Example #1
Learning targets #1 - 4
• State the domain and range of the relation
{ −2, 2 , 1,4 , 3, 0 , −2, −4 , 0, 3 }. Draw a mapping. Is this
relation a function?
Guided Practice – Example #1
Learning targets #1 - 4
• State the domain and range of the relation
{ 7, 8 , 7, 5 , 7, 2 , 7, −1 }. Draw a mapping. Is this relation a
function?
Also…try #1, 2, 3, and 8 on page 62
Practice Function or not?
Domain
Range
Domain
Learning targets #2 & 4
Range
-3
1
-1
0
2
1
3
2
4
4
5
Domain
Range
-3
0
1
1
5
6
Relations: Discrete or Continuous?
Learning targets #2 & 5
Relations: Discrete or Continuous?
Discrete
Discrete graphs contain a set of
points not connected.
Learning targets #2 & 5
Continuous
Continuous graphs contain a smooth line
or curve.
Note: You can draw the graph of a continuous relation
Without lifting you pencil from the paper.
Vertical Line Test
Learning targets #2 & 6
Vertical Line Test
• If no vertical line intersects a
graph in more than one point,
the graph represents a function.
Learning targets #2 & 6
• If some vertical line intersects a
graph in two or more points, the
graph DOES NOT represent a
function.
Example #2
Learning targets #1 - 6
• The number if employees a company had in each year from 1999 to
2004 were 25, 28, 34, 31, 27, and 29. Graph this information and
determine whether it represents a function. Is the relation discrete
or continuous?
Example #3
• Graph the relation represented by
𝑦 = 𝑥 2 + 1.
• Find the domain and range.
• Determine if the relation is
discrete or continuous.
• Determine whether the relation is
a function.
Learning targets #1 - 6
Guided Practice – Examples #2&3
• Page 63 #4, 5, 6, 8, 9, and 10
Learning targets #1 - 6
Example #4
Learning target #7
• Given 𝑔 𝑥 = 0.5𝑥 2 − 5𝑥 + 3.5, find each value.
a. 𝑔(2.8)
b. 𝑔(4𝑎)
Guided Practice – Example #4
1. Find 𝑓 5 if 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 2 − 3𝑥
Learning target #7
2. Find ℎ(−2) if ℎ 𝑥 = 𝑥 3 + 1.
A#2.1
pages 62-63
#13-22 all;
and #24-42 evens
Due Tuesday!!!