Cell Architecture
advertisement

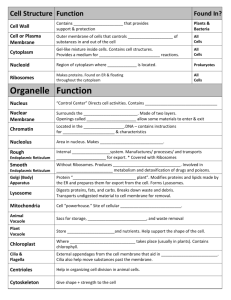
Cell Architecture CELL THEORY • Mathias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann • Prokaryotic cell • Eukaryotic cell – plant cell and animal cell • Figure 9-1 Animal cell substructures Single and Double Membrane Substructures • Single Membrane Structures – Plasma Membrane – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Apparatus – Lysosome – Peroxisome – Endosome • Double membrane structures – Nucleus and Mitochondria Plant Cell Substructures Single and Double Membrane Substructures • Single Membrane Structures – Plasma Membrane – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Apparatus – Lysosome – Peroxisome – Endosome • Double membrane structures – Nucleus and Chloroplast Plasma Membrane Chapter10 Fig.10-1 EM OF A THIN ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE How do endosomes work? Lysosomes • Internal compartment is very different form the cytosol –more acidic pH • Degrades substances that are obsolete • Phagocytosis and Endocytosis • All lysosmal enzymes are acid hydrolases • Tays Sach’s disease – defect in enzyme catalyzing a step in the lysosomal breakdown of gangliosides. Autophagy Plant Vacuoles • Similar to lysosomes – degradative enzymes • Concentration of solutes is larger inside the vacuole than outside • Stores small molecules and is permeable to water • Elongation of the plant is related to water uptake by the vacuole EM OF A PLANT CELL Peroxisomes • 0.2-1.0 micrometer in diameter • Oxidases • Catalase 2H₂O₂ -----> 2H₂O + O₂ • Main site of fatty acid peroxidation • Various toxic molecules that enter the body are degraded here Mitochondrial vs. Peroxisomal Oxidation Fig. 12-12 Endoplasmic Reticulum • Smooth ER: – Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Lipids – Metabolism of Carbohydrates – Detoxify Drugs and Poisons • Rough ER: – Synthesis of Secretory Proteins, Membrane and Organelle Proteins ROUGH ER IS MADE OF RIBOSOMES RIBOSOMES • Composed of rRNA and protein • Site of protein synthesis • Proteins are marked for different organelles or for secretion • Ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus • Free Ribosomes PROTEIN MODIFICATION IN THE ER SECRETED PROTIENS – GLYCOSYLATION – DISULFIDE BOND FORMATION HORMONE SECRETING CELL FROM RAT PITUITARY Golgi Apparatus Golgi - Function • Flattened membrane vesicles or sacs • Cis, medial and trans -Golgi • Proteins targeted for different points in the cell are modified differently • Secretory proteins • Plasma membrane proteins • Membrane or soluble proteins to other organelles HOW SECRETORY PROTEINS ARE TRANSPORTED? ORGANELLES WITH DOUBLE MEMBRANES • MITOCHONDRIA – Power house of the cell – Site of cellular respiration – Organic molecules are used fro ATP synthesis NUCLEUS contains chromosomes, DNA and RNA CHLOROPLAST Site of Photosynthesis EM OF A MITOCHONDRION STRUCTURE OF A MITOCHONDRION OUTER MEMBRANE AND INNER MEMBRANE • OUTER MEMBRANE – 50% lipid and 50% protein – Porin proteins (MW of 10,000) INNER MEMBRANE - CRISTAE POWER HOUSE OF THE CELL Nucleus • Inner membrane and outer membrane • Outer membrane is continuous with rough ER • The intermembrane space is continuous with the lumen of the ER • Nuclear pores and nucleoporins • Heterochromatin • Ribosomal RNA assembly HETEROCHROMATIN CHLOROPLAST • • • • • • Double membraned organelle Length is 10µm and thickness of 0.5-2 µm Sacs - Thylakoids Stacks are grana Matrix space called Stroma Photosynthesis MITOCHONDRIA AND CHLOROPLAST • • • • ATP production Move around in the cell Contain their own DNA Some of their proteins are encoded in the nucleus EM OF A PLANT CHLOROPLAST