ECONOMIC RESOURCES Human Resources
advertisement

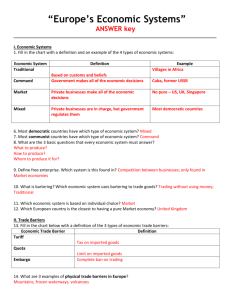
Unit 1 • Needs are essential • Everyone Needs – food & water – Clean air – Shelter • In today's society other needs include: – Good education – Employment – Safety • Wants add to the quality of life • Most products purchased do more than meet your needs, they make your life easier and more comfortable. • Our country, economic status, lifestyle, and jobs determine whether something is a need or a want. • Goods satisfy your wants and needs for material things that you can see or touch. • Services also satisfy wants and needs but must be provided to you at the time you want to consume them. • Consumers decided which products and services to purchase and where to purchase them. • Businesses decide what products and services to produce. • ________ is the motivation of business • Having unlimited wants and needs but limited resources is known as the basic economic problem. • The basic economic problem results from scarcity. • The means by which goods and services are produced are known as economic resources. • Economic resources are also known as factors of production. • There are 3 kinds of economic resources: – Natural Resources – Human Resources – Capital Resources • Natural Resources – Raw material supplied by nature. • • • • • • Water Air Lumber Minerals Oil Animals • Human Resources – The people who produce goods and services • • • • Owners, managers, employees of a business Factory Workers Farmers Entrepreneurs • Capital Resources – Products and money used in the production of goods and services • • • • • Buildings Equipment Machinery Supplies Money • All nations of the world face the basic economic problem. Each country must decide how the available resources will be used to meet the wants and needs of its people. • All economies must answer 3 economic questions: 1. What goods and services will be produced? 2. How will the goods and services be produced? 3. Which needs and wants will be satisfied with the good and services produced? • The decision making process helps consumers and businesses to carefully calculate the opportunity cost of decisions before actually making the decisions as well as helping select the most satisfying alternatives from a set of choices. 1. Define the Problem 2. Identify the Choices 3. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each choice 4. Make a decision 5. Act on your decision 6. Review your decision • A nations plan for answering the 3 economic questions is called its economic system • The main types of economic systems in the world today are – Market Economy – Command Economy – Traditional Economy – Mixed Economy • An economy in which resources are owned and controlled by the government. • North Korea , Cuba • Communism is a command economy • An economy in which the resources are owned and controlled by the people of the country • America, Germany, Canada, Hong Kong • An economy in which goods and services are produced the way they have always been produced. • Amish, Inclusive Native American communities • Less developed countries which do not participate in global trading generally have a traditional economy. • An economy that combines elements of different economies • Most economies are truly mixed economies • Another name for the economic system in the United States is capitalism which refers to the private ownership of resources by individuals rather than by government. • 4 principles U.S. economic system is based on are: 1. 2. 3. 4. Right to own private property Freedom of choice Right to make a profit Freedom of competition • Understanding demand tells a business what type and what quantity of products and services to supply. • Prices are affected by the relationship between supply and demand. • When demand is high the price will tend to go up. • If there is a large supply price will tend to remain low. • Economic activities move in cycles. • The movement of the economy from one condition to another and back again is called a business cycle which reflects the recurring ups and downs of GDP. • The 4 phases of the business cycle: 1. Prosperity • Most people are working, production and demand are high, wages are good, GDP is growing 2. Recession • Demand decreases, unemployment rises, GDP growth slows for 2 or more quarters 3. Depression • High unemployment, weak sales, business failures, GDP falls rapidly 4. Recovery • Unemployment decreases, demand increases, GDP slowly begins to rise.