Rational_exponents - World of Teaching
advertisement

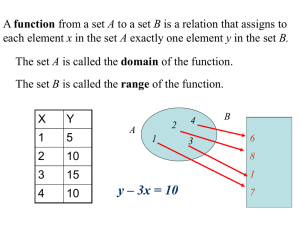
How Do We Use Rational Exponents? • Do Now: Perform the indicated operation and simplify 1. 2. 1 nth Roots nth Roots An nth root of number a is a number whose nth power is a. n a a number whose nth power is a If the index n is even, then the radicand a must be nonnegative. 4 16 2, but 4 16 is not a real number 5 32 2 2 age 393 Square Root of x2 x x 2 3 Radicals 4 Rational Exponents 5 Exponent 1/n When n Is Even 6 When n Is Even 1 2 100 100 10 1 4 625 625 5 4 1 6 64 64 2 4 6 1 2 4 is not yet defined 7 Exponent 1/n When n Is Odd 8 Exponent 1/n When n Is Odd 1 3 27 27 3 3 27 1 3 27 3 3 1 5 1 1 1 5 32 2 32 9 nth Root of Zero 0 0 n 10 Rational Exponents 11 Evaluating in Either Order 8 8 2 4 2 3 2 3 8 64 4 2 3 2 or 8 3 2 3 12 Negative Rational Exponents 13 Evaluating a-m/n 8 2 3 1 8 2 3 1 8 3 2 1 1 2 2 4 14 Rules for Rational Exponents 15 7 Simplifying y 1 6 6 6 y y 6 a b ab 1 2 1 3 16 Simplifying y 1 6 6 6 y y 6 1 1 a b ab a b a b 1 2 1 3 1 2 a 1 3 1 1 1 1 3 2 b 3 2 a b 2 3 17 Simplifying y 1 6 6 6 y y 6 a b ab a b 1 2 1 3 9 x y 8 3 2 1 10 12 2 z 2 3 18 Multiplying Radicals – Different Indices 1 4 1 2 4 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 3 1 1 4 2 3 4 2 2 8 4 3 4 19 Multiplying Radicals Different Indices 4 3 1 4 1 2 1 3 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 4 2 3 4 2 2 8 4 3 4 2 3 2 3 20 Different Indices 4 3 1 4 1 2 1 1 4 2 1 3 1 2 2 6 2 2 2 2 2 3 4 2 2 8 4 3 4 3 6 2 3 2 3 2 3 21 Different Indices 4 3 1 4 1 2 1 1 4 2 1 3 1 2 2 6 2 2 2 2 2 3 4 2 2 8 3 6 3 4 4 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 6 2 6 3 22 Different Indices 4 3 1 4 1 2 1 1 4 2 1 3 1 2 2 6 2 2 2 2 2 3 4 2 2 4 8 3 6 3 4 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 108 6 2 6 3 6 23 Rational Exponents Eliminate the root, then the power 2 3 a 2 24 Eliminate the Root, Then the Power 2 3 a 2 3 a 23 2 a 8 2 3 a 8 2 a 2 2 CHECK 25 Negative Exponents r 1 2 3 1 26 Negative Exponents Eliminate the root, then the power r 1 2 3 1 3 r 1 13 2 3 r 1 1 2 r 1 2 r 1 1 r2 CHECK 1 r 0 27 Negative Exponents Eliminate the root, then the power 2t 3 2 3 1 28 No Solution Eliminate the root, then the power 2t 3 2 3 1 3 2t 3 13 2 3 2t 3 1 2 2t 3 2 1 29 No Solution Eliminate the root, then the power 2t 3 2 3 1 3 2t 3 13 2 3 2t 3 1 2 2t 3 2 1 No real solution 30 Strategy for Solving Equations with Exponents and Radicals 31 This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching. 32