P A R T
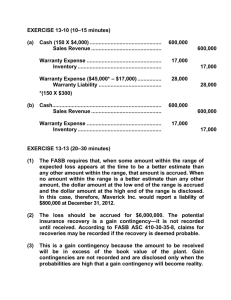
4
Sales
Formation & Terms
Product Liability
Performance of Sales Contracts
Remedies for Breach of Sales
Contracts
McGraw-Hill/Irwin Business Law, 13/e
© 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
C H A P T E R
20
Product Liability
“A manufacturer is not
through with his
customer when a sale is
completed. He has then
only started with his
customer.”
Henry Ford, founder of Ford Motor
Company, in My Life and Work
(cowritten with Samuel Crowther,
1922)
Learning Objectives
Evolution
of product liability law
Theories of product liability recovery:
Express warranty, implied warranties,
negligence, strict liability
Other theories of recovery
Time limitations, disclaimers, defenses
Damages
20 - 4
Express Warranty
Express warranty created in three ways:
20 - 5
If affirmation of fact or promise about goods
becomes part of the basis of the bargain
A description of the goods that becomes part
of the bargain warrants that goods will
conform to description
A sample or model of goods warrants that
goods will conform to sample
Implied Warranties
Implied warranties are created by operation
of law rather than seller’s express statements
Warranty of merchantability [UCC 2-314(1)]
See Crowe v. CarMax Auto Superstores, Inc. and
Hong v. Marriott Corp.
Warranty of fitness for a particular purpose
[UCC section 2–315]
See Bako v. Crystal Cabinet Works, Inc.
20 - 6
Negligence Theory
Product liability suits based on negligence
allege that seller or manufacturer breached a
duty to plaintiff by failing to eliminate a
reasonably foreseeable risk of harm:
(1) negligent manufacture of the goods (including
improper materials and packaging)
(2) negligent inspection
(3) negligent failure to provide adequate warnings
(4) negligent design
20 - 7
Strict Liability Theory
American Law Institute published section
402A of Restatement (Third) of Torts (1998)
20 - 8
Seller or distributor of a defective product is
subject to liability for harm to persons or
property caused by the defect
Three kinds of product defects:
manufacturing defects, inadequate warnings
or instructions, design defects
Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act
Federal Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act applies
to sales of consumer products > $10 per item:
20 - 9
If written warranty, it must be full or limited
Full warranty promises to (1) remedy any
defects in the product and (2) replace product
or refund purchase price if, after reasonable
number of attempts, it cannot be repaired
Seller who gives a limited warranty is bound to
whatever promises it actually makes
Damages
Consequential damages: Physical, economic, or
emotional damages directly or indirectly related
to the event causing harm
Basis-of-the-bargain damages: Value of goods
as promised under the contract minus value
of goods as received
Punitive damages: To punish defendants for
or deter others from knowing and
outrageous conduct
20 - 10
Disclaimers
Product liability disclaimer:
Seller attempts to eliminate risk
of liability by clause in contract
Example: Car sold “as is”
Remedy limitation: attempt to
bar recovery of certain damages
Example: “30 day warranty”
See Trinity Industries, Inc. v.
McKinnon Bridge Co.
20 - 11
Test Your Knowledge
True=A, False = B
Implied warranties are created by seller’s
conduct rather than express statements
Merchantability, essentially, is that goods
must be fit for the ordinary purposes for
which such goods are used
A disclaimer is a clause in the sales contract
in which seller attempts to eliminate liability
seller might otherwise have under law
20 - 12
Test Your Knowledge
True=A, False = B
Under foreign–natural test, defendant is liable
if object or substance is “foreign” to product,
but not liable if it is “natural” to the product
Under the Restatement of Torts (Third), three
kinds of product defects exist: manufacturing
defects, inadequate warnings, design defects
The Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act requires
every written warranty to be a full warranty
20 - 13
Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice
Express warranty may be created by _______
that becomes part of the basis of the bargain
for the agreement:
(a) a statement of fact or promise about goods
(b) a description of the goods indicating goods
will conform to the description
(c) a sample or model of goods to be sold
indicating goods will conform to the sample
(d) all of the above
(e) both A and B, but not C
20 - 14
Test Your Knowledge
Multiple Choice
Drew was injured when his car rolled over
after the tires delaminated and caused him to
lose control. Drew could sue, claiming:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
20 - 15
negligence (design or manufacture)
strict liability
breach of warranty
all of the above
Thought Questions
What is your opinion
of product liability
lawsuits? If you were
injured because of a
defect in a product,
would you file a
lawsuit against the
manufacturer?
20 - 16