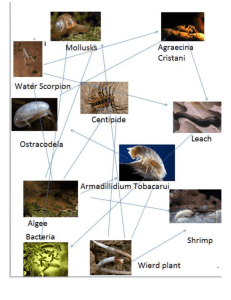
Food Web
advertisement

Food Chain Who can tell me what a food chain is? What is a food chain? Shows how each living thing gets its food. Some animals eat plants and some animals eat other animals. For example, a simple food chain links the trees & shrubs, the giraffes (that eat trees & shrubs), and the lions (that eat the giraffes). Each link in this chain is food for the next link. Food Chain vs. Food Web Who can tell me what the difference between a food change and a food web is? Chains vs. Webs A food web is several food chains put together that show many different organisms and their source of food/energy. Chains vs. Webs What is the source of energy for all food webs? Producers Plants are called producers because they are able to use light energy from the Sun to produce food (sugar) from carbon dioxide and water. Autotroph: Organism that produces its own food (plants) Consumers Animals cannot make their own food so they must eat plants and/or other animals. They are called consumers. Consumers There are three groups of consumers. Animals that eat ONLY PLANTS are called herbivores (or primary consumers). carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers carnivores that eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers e.g., killer whales in an ocean food web ... phytoplankton → small fishes → seals → killer whales Animals that eat OTHER ANIMALS are called carnivores. Heterotroph: Organism that must consume (or eat) its food (animals). Decomposers Then there are decomposers (bacteria and fungi) which feed on decaying matter. Using the simple food chain below to describe how energy comes from the sun to the plants and the plants pass the energy to the organisms that eat the plants and the process continues. Sun trees giraffes lions The sun provides energy to the tree, the tree provides energy to the giraffe, and the giraffe provides energy to the lion. This is the flow of energy. Arrange the following into a food web. (Include arrows and group them by producers, consumers and decomposers) Ultimate energy source! Producers: get energy from the sun Consumers: get energy from producers Decomposers: Breakdown dead materials – include fungus and bacteria Trophic Level step in a food chain or food web. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Carnivore organism that obtains energy by eating animals. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Herbivore organism that obtains energy by eating only plants. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Omnivore organism that obtains energy by eating both plants and animals. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Energy Pyramid diagram used to show how energy is distributed in food chains of food webs. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Producer organism that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce food from inorganic compounds; also called an autotroph. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Consumer organism that relies on other organisms for its energy and food supply; also called a heterotroph. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Decomposer organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Food Chain series of steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: Food Web network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem. Understanding Level: 1 2 3 4 Define (in your own words): __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Draw: In this food chain, the spiders are – A B C D producers primary consumers competitors secondary consumers Wolves and hawks are at the same trophic level because they – A B C D both live on land are both large mammals both eat primary consumers have similar hunting patterns Which organisms in this food web can be described as both primary and secondary consumers? A B C D Hawks Weasels Raccoons Mice Energy used by producers in a grassland food web is provided by —– A B C D sunlight photosynthesis oxygen carbon dioxide In this diagram of a marine food web, which term describes the sea turtle? A B C D Aquatic herbivores Autotrophic producers Third-level consumers Primary decomposers The diagram represents different levels of a marine food pyramid. Between which two levels is the greatest amount of energy transferred? A B C D R and Q S and R T and S U and T According to this food web, which of the following are omnivores? A B C D Snakes Rabbits Mice Grasshoppers The diagram shows a standard pyramid of numbers that indicates the number of individual organisms in a community. Which of the following situations would form a pyramid showing more consumers than producers? A B C D A small plot with 500 corn plants and 100 grasshoppers One pond with 300 producers and one snake An 11,000 m3 lake with 75 fish and one alligator One giant oak tree with 10,000 insects and 10 lizards The diagram above is intended to show relationships in an ecosystem. What do the arrows represent? A B C D The direction of population migration Differences in dietary habits Progressively smaller organisms The direction of energy flow Insecticides help humans compete with insects for a resource. Which resource is most likely to be preserved for humans through the use of insecticides? A B C D sunlight water food air In this food pyramid, which level contains the greatest amount of energy? A B C D Tertiary consumers Secondary consumers Primary consumers Producers Viruses differ from bacteria in that all viruses – A B C D cause insect-borne diseases can be destroyed by antibiotics have rigid cell walls must be reproduced in living cells