American Literature Timeline: 11th Grade Overview
advertisement

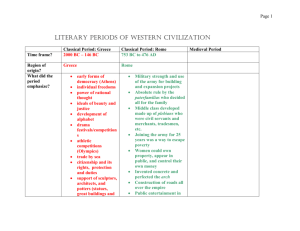
American Literature Timeline 11th Grade American Literature Native American (30,000 B.C. – 1730 A.D.) • Historical Events • 30,000 B.C. – 1492 A.D. – settlement of American Indians into various tribes on the American continents (Indians traveled to this continent by crossing the Bering Strait) • 1492 – Columbus discovers America landing in the Bahamas • 1521 – Cortez conquers Aztecs in Mexico Native American • Characteristics of Native American Culture: • Ancestors arrived more than 10,000 years ago. • Each of the 700 tribes spoke their own language and had their own folklore and mythology. • Focus on the common origin of all things • Tribal traditions and rituals • Respect for all nature Native American • Types of Literature • Mostly oral • Some written • Ceremonial songs and prayers • Historical narratives • poems Native American • Writers and their works: • Walam Olum • Navajo Origin Legend • Spring Song Puritans (1607-1702) • Historical Events: • 1620 – Pilgrims landed at Plymouth Rock • 1629 – Puritans come to New England • 1692-The Salem Witch Trials take place. Nineteen people are killed. Puritans • Characteristics of Puritan Culture: • The Puritans left England because they wanted to purify the Church of England. • They believed that the Bible was God’s instruction to man and therefore a guide for writing and establishing government. • Puritans believed in predestination—the belief that God has already determined who is saved (the elect) and who is not (the unregenerate). • Puritans lived very simple lives. • They believed that anything done for entertainment, such as gambling, excessive drinking, dancing, and singing, was sinful. • They highly valued art, literature, and education. Puritans • Types of Literature: • Sermons • Diaries • Journals • Narratives • Poetry ***Fiction and drama were forbidden!!! FICTION Puritans • Writers and their works: • Jonathan Edwards – “Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God” (sermon) • Anne Bradstreet – “Upon the Burning of Our House” (poem) • Cotton Mather Colonial (1750-1800) “The Age of Reason”/The Enlightenment” • Historical Events: • 1765 – Colonists resist new Stamp Act passed by the British • 1770- The British kill colonists in the Boston Massacre • 1776 – Americans declare independence and Thomas Jefferson writes the Declaration of Independence • 1775-1783 – Revolutionary War; Americans defeat the British • 1789 –George Washington becomes the first president of the United States Colonial (1750 – 1800) – “The Age of Reason”/ “The Enlightenment” • Characteristics of Colonial Culture: • Also known as the Age of Reason or the Enlightenment • People believed that the universe was an orderly place that could be understood by using reason. • Believed that reason could result in advances in science, a better government, and an ideal society. Colonial (1750-1800) “The Age of Reason” / “The Enlightenment” • Types of Literature: • Mostly political writings • Broadsides (posters that let people know what was going on) • Persuasive and argumentative writings • Almanacs (Benjamin Franklin), speeches, essays, pamphlets (essays), and poetry Colonial (1750-1800) – “The Age of Reason”/ “The Enlightenment” • Writers and their works: • Benjamin Franklin – “Poor Richard’s Almanac” • Patrick Henry- “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” • Thomas Paine- “Common Sense” • Phillis Wheatley – “On Being Brought from Africa to America” (poem) • Thomas Jefferson – Declaration of Independence American Romanticism (1800-1840) • Historical Events • 1803 – expansion of U.S. through the Louisiana Purchase • 1812 – 1814 – War of 1812 against the British • 1830-Passage of the Indian Removal Act • 1848-First Women’s rights convention in Seneca Falls, NY • 1850-The Fugitive Slave Act promises punishment to anyone helping an escaped slave. American Romanticism: • Characteristics of Romanticism: • Valued feeling and intuition over reason • Placed faith in inner experience and the power of the imagination • Shunned the artificiality of civilization and sought unspoiled nature • Preferred youthful innocence to educated sophistication • Stood for individual freedom and the worth of the individual • Saw nature’s beauty as a path to spiritual and moral development American Romanticism • Characteristics Continued: • Looked to the wisdom of the past and distrusted progress • Found beauty and truth in exotic locations, the supernatural realm, and the inner world of the imagination • Saw poetry as the highest form of expression • Found inspiration in myth, legend, and folklore American Romanticism • Characteristics of the Romantic Hero: • Is young or possesses youthful qualities • Is innocent and pure of purpose • Has a sense of honor based not on society’s rules but on higher principles • Has a knowledge of people and life based on deep, intuitive understanding, not on formal learning (noble savage) • Loves nature and avoids town life • Searches for higher truth in the natural world American Romanticism: • Types of Literature: • Poetry- The Romantics believed poetry to be the highest form of art; the ideal form of expression • Novels • Short stories • Sketches • Folklore American Romantic Writers and Their Works • William Cullen Bryant – “Thanatopsis” • Henry Wadsworth Longfellow – “The Tide Rises, the Tide Falls” • Washington Irving – “The Devil and Tom Walker” • The Fireside Poets – a group of poets whose poems Americans read in the evening “by the fireside” • James Fenimore CooperThe Last of the Mohicans Transcendentalism (1840 – 1860) • Historical Events: • Occurred during the same time period as Romanticism and Dark Romanticism • 1852 – The anti-slavery novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe is published Transcendentalism • Characteristics: • Arose in the New England area • There are kinds of knowledge that “transcend” or “rise above” reason and experience • People should have faith in their “inner light” • Strong belief in the importance of the individual and self-reliance • Looked to nature for inspiration and guidance • All people are connected by the “Oversoul” – a spiritual force connecting nature and humans • Optimistic view of life Trancendentalism • Types of Literature: • Essays • Novels • Short stories • Poetry Transcendentalist Writers and Their Works • Henry David Thoreau – Walden, “Civil Disobedience” • Ralph Waldo Emerson – “Nature,” “Self-Reliance” Dark Romanticism/AntiTranscendentalism (1840 – 1860) • Historical Events: • Occurred during the same period as Romanticism and Transcendentalism Dark Romanticism/AntiTranscendentalism • Characteristics of Dark Romanticism: • Shared some of the same beliefs as Romanticism • Pessimistic viewpoint - literature often focuses on death and tragedy • Truth and happiness are not always found in life • Human nature is a mix of good and evil • Focus on the darker side of human nature • A belief in the supernatural with a focus on the dark, evil side of the supernatural • Also known as “Anti-Transcendentalism” Dark Romanticism/AntiTranscendentalism • Types of Literature: • Essays • Novels • Short stories • Poetry Dark Romantic Writers and Their Works: • Edgar Allan Poe – “The Raven,” “The Pit and the Pendulum” • Nathaniel Hawthorne – The Scarlet Letter, “The Minisiter’s Black Veil” • Herman Melville – Moby Dick Realism and Naturalism (1855-1900) • Historical Events: • 1861-1865 – Civil War • (not much was written during this time because the war was too painful to write about; much literature about the war came many years AFTER the war was over) • 1863-The Emancipation Proclamation, freeing the slaves, is issued by Abraham Lincoln • 1865-The Thirteenth Amendment outlaws slavery • 1876-Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone • 1881-The Red Cross is organized by Clara Barton • 1898-The Spanish-American War breaks out Characteristics of Realism • Civil War literature was very political in nature • Expression of life as it is actually lived • Used clear, direct language to present ordinary everyday events. • Subjects of literature often consist of factories, slums, workers, bosses, criminals, and social outcasts • Regionalism, or local color, focuses on the unique character of various regions and depicts their dialect, customs, and characters • Sometimes contains humor and social commentary • Began because of the Civil War; the war opened the population’s eyes to the realities of life and death Characteristics of Naturalism • Extreme form of realism • Human beings have no control over their fates. • People were victims of their surroundings, drives, and desires. • Influence of scientific method. A writer carefully gathers facts about human experience and then draws conclusions • Nature is powerful and shows no mercy Types of literature: • Short stories • Novels • Poetry (only a couple written during the Civil War by a poet named Walt Whitman) • Travel books • Songs • Spirituals • Diaries and journals (almost the only literature written during the Civil War) Writers and Their Works: • Mark Twain (Realism)Adventures of Tom Sawyer, Adventures of Huckleberry Finn (considered first and finest “American” novel), “The Jumping Frog of Calaveras County” • Stephen Crane – The Red Badge of Courage (one of the most famous novels about the Civil War; written many years after the war) • Jack London (Naturalism) – Call of the Wild, “To Build a Fire” • Kate Chopin-The Awakening Modernism (1900-Present) • Historical Events: • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1914-1918—World War I 1929 – Stock Market Crash 1930-1940 – Great Depression 1941-1945 – U.S. involvement in World War II 1945-America drops the atomic bomb on Japanese cities 1954 – Prayer in public schools becomes illegal 1961- Alan Shepard is the first American in space 1964-The Beatles debut in America on the Ed Sullivan Show 1968 – Martin Luther King, civil rights leader, is assassinated 1973 – U.S. troops withdraw from Vietnam 1986- Space shuttle Challenger explode on take-off 1989-The Berlin Wall is torn down in Germany 2001- Terrorist attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon Characteristics of Modernism: • Growth in America’s industrial power, military strength, and influence in world affairs • Modernism lasted from around the beginning of the 20th century until the end of World War II. • Writers rejected the literary rules of the 19th century and opposed conventional morality, taste, traditions, and economic values • Writers looked for new and varied modes of expression • Stream of consciousness writing developed • Stories had no clear resolution at the end • Readers struggle to find meaning in texts because life itself is a struggle. Characteristics of Modernism (continued) • The Harlem Renaissance of the 1920s was the first significant artistic movement of African-Americans. Harlem, NY was where many of these artists lived, worked, and performed. • In Postmodern writing, characters struggle to make sense of the ever-changing world in which they live. • Postmodern literature tends to have a pessimistic tone. • The “American Dream,” the hope for happiness from a home, money, and good job, suffered a loss during this time due to war and the Great Depression. Types of Literature: • Short stories • Poetry • Dramas • Novels • Essays • Songs • Speeches Writers and Their Works: • F. Scott Fitzgerald – The Great Gatsby (great novel about the American Dream) • William Faulkner – The Sound and the Fury, “A Rose for Emily” • Ernest Hemingway – The Old Man and the Sea • Zora Neale Hurston-A Raisin in the Sun Writers and their Works (continued): • Claude McKay- If We Must Die • Alice Walker – The Color Purple • T. S. Elliot – “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock” • Langston Hughes – “The Negro Speaks of Rivers,” “A Dream Deferred” Writers and Their Works (continued): • John Steinbeck-The Grapes of Wrath • Sylvia Plath – The Bell Jar • Tennessee Williams – Cat on a Hot Tin Roof • Arthur Miller – The Crucible