Energy Pyramids & Food Webs
advertisement

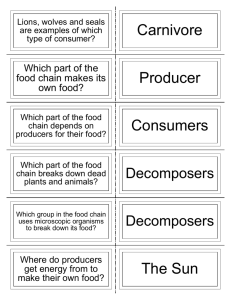
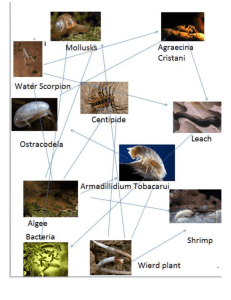
Warmup Write about the ecological stage pictured below, and what is going to succeed it. Use words like primary, secondary, climax, pioneer, and opportunist if you can. JANUARY 27TH, 2010 Ecological Roles Producer Consumer Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Decomposer Scavenger Producers Producers catch sunlight and convert it to sugar using chloroplasts. 6H20 + 6CO2 + sunlight C6H12O6 + 6O2 Only extremophylic ecosystems can exist without true producers to support them. Producers are the most numerous by both number and mass (how many and how much). Common ones include algae, cyanobacteria (pictured below), grasses, bushes, trees, seaweed, and kelp. Consumers Consumers can be grouped into three different categories: Herbivores eat only producers. Carnivores eat only other consumers. Omnivores eat both consumers and producers. All consumers use sugar to release energy. Some do so mainly using oxygen (respiration or aerobic metabolism). Others do so without oxygen (fermentation or anaerobic metabolism). Decomposers Decomposers are like consumers in that they use stored energy from other organisms. They differ in that they break down and recycle organic material in the process. Without decomposers, we would be buried under miles of wood, leaves, and dead bodies. Decomposers include scavengers, bacteria, fungi, and protists (a category of single-celled organisms) and can also include things like earthworms, termites, and ants. Two ingredients decomposers recycle include Carbon and Nitrogen. Energy Loss Producers use some energy they capture to grow, repair and reproduce cells, and live. They also waste some energy. Consumers only digest a fraction of the energy stored in their food. They then use some of that energy to stay warm, grow, repair and reproduce cells, and move. They also waste some energy. At each level, there is successively less energy available because of all the use, loss, and waste. Energy Pyramid Practice Organize the following list of organisms into producers, different types of consumers, and decomposers. Then use your categories to create and energy pyramid. The pyramid can be as many levels tall as needed. cattail, sawgrass, water lily, pickerel weed, spike rush, bullrush, fish, crabs, shrimp, tadpoles, insect larvae, frogs, birds, insects, cougar, deer, snails, earthworms, bacteria http://www.enchantedlearning.com/biomes/marsh/freshwaterprintout.shtml Practice Use the food web to create an energy pyramid. Identify the top carnivore. Practice Identify each of these as a producer, certain type of consumer, or decomposer. Map out the possible relationship of each organism to each other organism. Algae Krill Plankton Whale (Hint: Whales eat Krill. Krill eats plankton. Plankton eats Algae) Food Web Example Food Web Example Practice Create a food web for the list of species below. Cattail, sawgrass, water lily, pickerel weed, spike rush, bullrush, fish, crabs, shrimp, tadpoles, insect larvae, frogs, birds, insects, cougar, deer, snails, earthworms, bacteria.