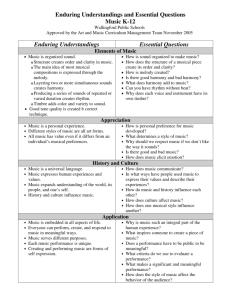
Elements of Music: Melody, Rhythm, Harmony, Form, Texture

The Elements of Music
1) Melody
2) Rhythm
3) Harmony
4) Texture
5) Form
6) Tempo and Dynamics
1) Melody: Musical Line
• The Nature of Melody
– Melody is a succession of single tones perceived by the mind as a unity
– Most memorable part of a song
– Range: lowest to highest notes
– Shape: upward/downward movement
1) Structure of Melody
• Melodic structure is analyzed much like a sentence
• phrase
- unit of meaning within a larger structure
• Combination of phrases make up most music; like sentences in a paragraph
2) Rhythm: Musical Time
• Rhythm refers how long or short notes are.
– The quality which causes people to move in response
– Metergroupings of notes/beats
• Beat
- the basic unit of length
• Measure – how many beats are grouped together
3) Harmony: Musical Space
• Harmony is two or more notes occurring simultaneously
•
Melody is horizontal aspect and harmony is vertical aspect
– Chord - combination of two or more tones that constitute a single block of harmony
– Harmony implies movement and progression of chords in music
3) Tonality: Character of Harmony
• Tonality
- the principle of organization around a central tone, called tonic
– Major
- has brighter sound; used for triumphal marches and grand finales, etc.
– Minor
- has darker sound; used for dirges, laments, etc.
4) Musical Texture
• Types of Texture
– Monophonic
- single-voice texture
– Polyphonic
- combination of two or more melodic lines
– The instruments/voices present is also a part of texture.
• Thin
: few voices
• Thick : many voices
5) Musical Form
• What is
Form ?
– That quality in a work which presents to the mind of the listener an impression of conscious choice and arrangement
– relationship of the parts to the whole
– Binary Form
- two part or A-B form;
– Ternary Form
- three part or A-B-A form
–
Can you recall the form of a typical pop song?
• Verse
•
Chorus
• Verse
•
Chorus
•
Bridge
•
Chorus
5) Form: Pop Song
5) Components of Form
• Theme - most basic element of form which provides unity and from which the idea develops
– Repetition
- fixes material in the mind; familiarity
– Contrast
- sustains interest by introducing change
– Variation
- falls between repetition and contrast where aspects are altered but recognizable
6) Tempo and Dynamics
• Tempo – how fast or slow
– Adagio ……………… Slow
– Moderato …………… Moderate
– Vivace ……………… Lively
• Dynamics – how loud or soft
– piano (p) ……………....
Soft
– mezzo piano (mp)
……Medium soft
– mezzo forte (mf) ……… Medium loud
– forte (f) ........................Loud
6) Tempo and Dynamics
• Markings for tempo and dynamics contribute to the expressive content of music
– Ex. Slow= ballad, Fast= exciting, Soft= gentle, Loud= powerful