(2). Informal group
advertisement

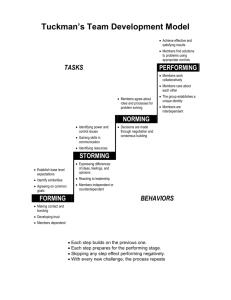
GROUPS AND TEAMS. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 1 Groups Definition Two or more individuals, interacting and interdependent, who come together to achieve particular objectives. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 2 Formal and informal groups (1). Formal groups ……..are those defined by organizational structure with designated work assignments and establishing tasks. For example: the six members making up an airline flight crew are a formal group. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 3 Formal and informal groups (2). Informal groups …….are those neither formally structured nor organizationally determined. These groups are natural formations in the work environment that appear in response to the need for social contact. For example : three employees from different departments who regularly eat their lunch together is an informal group. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 4 Classifying Groups (1).Formal group (2).Informal Command Groups Task Groups group Interest Groups Friendship Groups 5 ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR Four Types of Groups Command group. – determined by the organization chart. It is composed of individuals who directly report to a given manager. An elementary school principal and her 18 teachers form a command group. or the area sales manager along with his sales force. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 6 Four Types of Groups Task group – it is also organizationally determined represent those working together to complete a job task, however a task group’s boundaries are not limited to its immediate hierarchical superior. For instance the hiring of new employees can be a task which can involve GM, HR manager and a particular functional manager. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 7 Four Types of Groups Interest group are such groups that affiliate to attain a specific objective of shared interest. for example employees who come together to have their vacations schedules altered, to support a colleague who has been fired or to seek improvement in working conditions is an interest group. Friendship group – members have one or more common characteristics. for example similar age or holding similar political views ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 8 Conti… Security SelfEsteem Status What Makes People Join Groups? Power ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR Affiliation Goal Achievement 9 Why People Join Groups ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 10 Stages of Group Development Stage II Storming Stage I Forming Stage III Norming Stage IV Performing ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR Stage V Adjourning 11 Stages of Group Development Groups generally pass through a standardized sequence in their evolution. we call this sequence the five stage model of group. Forming, storming, Norming performing and adjourning. The first stage forming is characterized by a great deal of uncertainty about the group purpose, structure and leadership. members are uncertain about what type of behavior is acceptable. This stage is complete when members have begun to think themselves as part of a group. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 12 Stages of Group Development 2.The storming stage is one of the intragroup conflict. members accept the existence of the group, but there is a resistance to the constraints that the group imposes on individuals. Furthermore there is conflict over who will control the group. When this stage is complete, there will be a relatively clear hierarchy of leadership within the group. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 13 Stages of Group Development 3.The Norming stage The Norming stage completes when close relationships have been developed and the group demonstrates cooperation. Cooperation further develops common set of expectations from the group members which defines their behavior. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 14 Stages of Group Development The fourth stage is performing. The group structure becomes fully functional and group energy moves from getting to know and understand each other to performing a task at hand. For permanent work groups performing is the last stage of their development, however for temporary committees, task forces or other similar groups that have a limited task to perform, there is an adjourning stage. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 15 Stages of Group Development 5. Adjourning stage. In this stage the group prepares for its disbandment, where high task performance is no longer the group’s priority, instead attention is directed toward wrapping up activities. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 16 Identity Expectations Group Roles Conflict 17 ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR Perception Roles According to Shakespeare all the world is a stage and all the men and women are players. similarly all the group members are actors. Role is defined as……to engage in a set of expected behavior that are related to occupying a given position in a social unit. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 18 Role identity Role Identity – the ability to recognize attitudes and behaviors consistent with a role. When workers are promoted to supervisory positions vital changes are observed in their behavior with other workers. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 19 Role perception and role expectation Role Perception – our view of how we’re supposed to act in a given situation is called role perception. Role Expectations – how others believe you should act in a given situation is called role expectation. ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 20 Cohesiveness The degree to which members of the group are attracted to each other and motivated to stay in the group Related to the group’s productivity ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 21 Group Decision Making Advantages Disadvantages More Diversity of Views Dominant Individuals Increased information Unclear Responsibility Higher-quality decisions Time and money costs Improved Commitment Increased acceptance 22 ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR Conformity pressures Group Decision Making Groupthink 23 ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR Group shift Symptoms of Groupthink Group members decrease any resistance to their assumptions Members pressure any doubters to support the alternative favored by the majority Group interprets members’ silence as a “yes” vote for the majority ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 24 Groupshift Decision of the group reflects the dominant decision- making norm that develops during the group’s discussion Exaggerates the initial position of the members and more often to greater risk ORGANIZATION BEHAVIOR 25