Capital - CUSTOMER SERVICE
advertisement
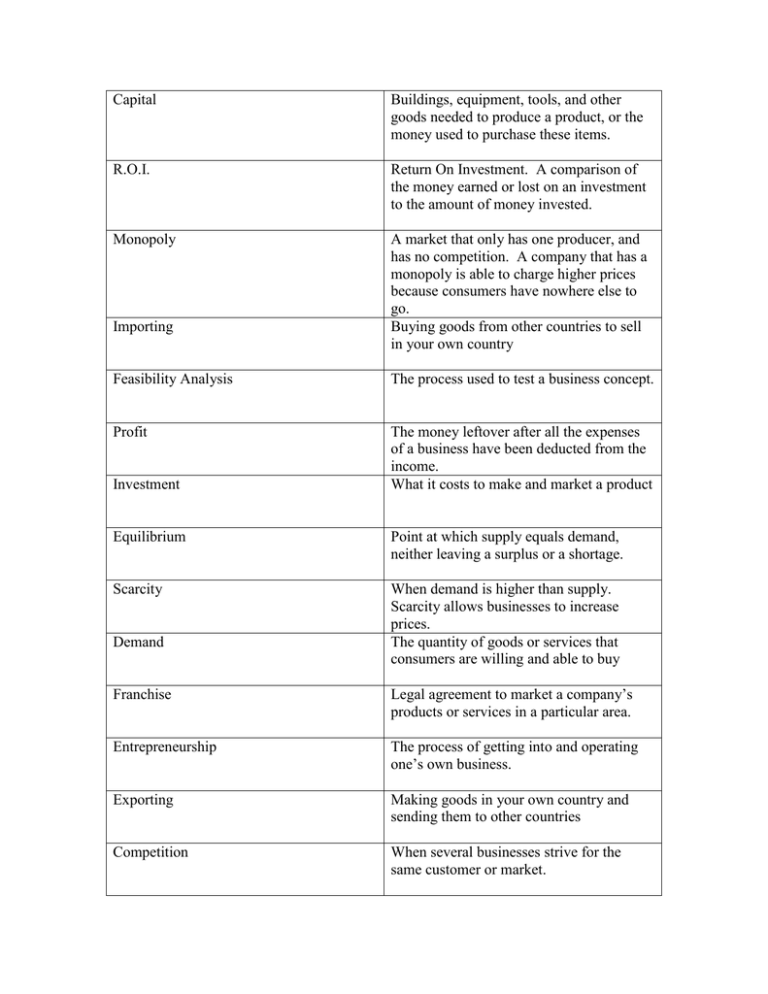
Capital Buildings, equipment, tools, and other goods needed to produce a product, or the money used to purchase these items. R.O.I. Return On Investment. A comparison of the money earned or lost on an investment to the amount of money invested. Monopoly A market that only has one producer, and has no competition. A company that has a monopoly is able to charge higher prices because consumers have nowhere else to go. Buying goods from other countries to sell in your own country Importing Feasibility Analysis The process used to test a business concept. Profit The money leftover after all the expenses of a business have been deducted from the income. What it costs to make and market a product Investment Equilibrium Point at which supply equals demand, neither leaving a surplus or a shortage. Scarcity When demand is higher than supply. Scarcity allows businesses to increase prices. The quantity of goods or services that consumers are willing and able to buy Demand Franchise Legal agreement to market a company’s products or services in a particular area. Entrepreneurship The process of getting into and operating one’s own business. Exporting Making goods in your own country and sending them to other countries Competition When several businesses strive for the same customer or market. Consumer Product Safety Commission Watchdog for consumers over products that may be hazardous. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission Protects the rights of employees age, race, color or national origin, religion, gender or physical challenge. Minimum wage and maximum working hours are identified. Children under 16 cannot work full-time except if employed by parents. Ensures safe and healthy working conditions for employees. Fair Labors Standard Act Occupational Safety & Health Act Fair Packaging and Labeling Act The Supply Curve Requires manufacturers truthfully label products, showing all raw materials used in the production process. The Demand Curve Graph of Equilibrium Target Market The specific market segment toward all of a business’s activities are directed. Demographics Statistical data that describes a given market by criteria such as age, gender, and income. Psychographics Statistical data that describes a given market by criteria such as personality, opinions, and lifestyle. Geographics Study of the market based on where customers live by region, state, city, and/or area. Buying Characteristics Customers will purchase products or services from companies they know or have experience with. Customers have knowledge of and personal experiences with the actual goods or services. Group of people whose opinions are studied to determine the opinions/buying preferences of a larger population. Process of grouping a market into smaller subgroups defined by specific characteristics. Business that offers similar products as your business. Market Segmentation Competitive Analysis Market Research Mission Statement Expresses specific goals for the company. Channels of Distribution The path a product takes from producer to final user (consumer.) Includes transportation, storage & product handling. A graphic representation of the company’s organizational structure. Organizational Chart Marketing Mix The 4 P’s. Product, Price, Place, Promotion Partnership A business with two or more owners who share ideas, abilities, or financial obligations. Partners do not have to share equally. Division of partnership interests spelled-out in Partnership Agreement. Allows customers to obtain products or services with the promise to pay later. Credit Corporation This legal form of ownership operates apart from its owners, and lives-on after the owner dies. Registered by state operated apart from its owners. Ownership represented by shares of stock – public or private. Promotional Mix Includes advertising, publicity, personal selling, and sales promotions. Price Lining Pricing strategy that is used to offer products in the same line and several different prices; low, medium & high. Promotional Pricing Pricing method that lowers prices for a limited time to stimulate demand. Perpetual Inventory Inventory system that us updated on a daily basis. Quantity Discounts Pricing method that is often used when ordering t-shirts for the school – the larger the order, the cheaper the per-unit price. Summary of a company’s profit or loss during any one given period of time Also known as a Profit & Loss Statement. The one-time expenses paid to establish a business. Income Statement Start-up Costs COGS Cost of Goods Sold – the cost of inventory to be sold in a business Net Income Gross income minus operating expenses. Break-Even Point The volume of sales that must be made to cover all expenses of the business Equity Capital Cash invested in a business in exchange for an ownership stake in the business. Collateral Security in the form of assets you pledge to a lender. Fixed Expenses Lease payment, salaries, insurance, advertising. Expenses that do not change with the number of units sold. Expenses that do change with the number of units sold or produced. Variable Expenses Gross Income Total income minus COGS sold. Focus Group Capacity Code of Ethics Global Company A group of people whose opinions are studied to determine the opinions/buying preferences of a larger population. Your ability to repay a loan based on incoming and outgoing cash flow. Behavior guidelines that describes appropriate conduct for a business or organization. A business that sells products in its own country. Domestic A business that sells product in more than one country. Web-based business A business that generates their revenue directly from their website. Primary Data Research collected for the first time and relates directly to the collector’s study. Secondary Data Information collected by someone else for their own purpose. Five Steps of Market Research 1. Identify Your Information Needs 2. Obtain Secondary Resources 3. Collect Primary Data 4. Organize the Data 5. Analyze the Data A small, specialized segment of the market based on customer’s needs. Niche Direct Competitors Offer similar products Indirect Competitors Offer close substitutes that meet the same basic need. Industrial Markets Group of customers who buy products or services for business to use; (not consumerbased) Critical factor in the success of a business, especially for retail stores. Owned and operated by one person. Easy to create. Owner receives all profits, incurs any losses, and is liable for the debts of the business. Location Sole Proprietorship Advertising Paid non-personal presentation of ideas directed toward a mass audience. Publicity Free placement of newsworthy items about company, etc. in the media. Personal Selling Giving an oral presentation to one or more potential buyers. Promotions Use of incentives or interest-building activities to create demand. Competition-Based Pricing Lower or raise of products/services based on what the competition is doing. Odd/Even Pricing Odd numbers suggest bargains ($19.99). Even numbers suggest higher quality ($20.00) Assets Represent things of value that person or company owns and has in its possession or something that will be received and can be measured objectively. What a person or company owes to others—creditors, suppliers, tax authorities, employees, etc.. They are obligations that must be paid under certain conditions and time frames. Ownership in a business. Liabilities Equity The 5 C’s of Credit to Qualify for a Loan Character Capacity Capital Collateral Conditions



