File
advertisement

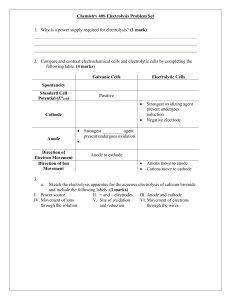
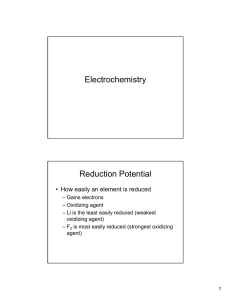
Electrochemistry: Basic Concepts Sometimes, you must find a balanced reaction of cells from only reduction half-reactions. We will go through steps to follow and examples Electrochemistry: Basic Concepts Equations of Cells • Standard Reduction Potentials: lists which are more likely to reduce (take electrons) reduced Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu Cu2+ | Cu • When comparing standard reduction potentials in a cell, the ½ reaction that is… • more (+) is reduction • more (-) is oxidation Electrochemistry: Basic Concepts Equations of Cells • So… which is more likely to reduce? 1) Li+|Li or Be2+|Ba 2) Ga3+|Ga or Cr2+|Cr 3) Cr3+|Cr2+ or Cr2+|Cr 4) Cl2|2Cl- or Cu+|Cu 5) Ag+|Ag or Rb+|Rb 6) Mn2+|Mn or Au+|Au To write equations of Cells 1) Identify which reaction is oxidation and which is reduction, 2) write the balanced equation Silver in a solution of Ag+ and Nickel in a solution of Ni2+ Ag+(aq) + e- → Ag(s) EºAg+|Ag = +0.800 V reduction Ni2+ + 2e- → Ni(s) EºNi2+|Ni = -0.257 V Ni(s) → Ni2+ + 2e2 Ag+(aq) + 2 e- → 2 Ag(s) Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Ni2+ + 2Ag(s) oxidation 1) Identify which reaction is oxidation and which is reduction, 2) write the balanced equation Magnesium in a solution of Mg2+ and Lead in a solution of Pb2+ Mg2+(aq) + 2e- → Mg(s) EºMg2+|Mg = -2.372 V ox Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) EºPb2+|Pb = -0.126 V red Mg(s) → Mg2+(aq) + 2ePb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) Mg(s) + Pb2+ → Mg2+(aq) + Pb(s) 1) Identify which reaction is oxidation and which is reduction, 2) write the balanced equation Beryllium in a Be2+ solution and Iridium in a Ir3+ solution Be2+(aq) + 2e- → Be(s) EºBe2+|Be = -1.847 V ox Ir3+(aq) + 3e- → Ir(s) EºIr3+|Ir = +1.156 V red 3 Be(s) → 3 Be2+(aq) + 2e 6e-2 Ir3+(aq) + 6e 3e-- → 2 Ir(s) 3Be(s) + 2Ir3+(aq) → 3Br2+(aq) + 2Ir(s) Then, how would you find the cell potential? Eºcell = Eºred - Eºox Reminders: • Ch 21 Practice Problems o You know how to do the entire worksheet o SHOW ALL WORK! No work, no credit. o The entire thing is due Monday at the beginning of class • WA ch 21: due Monday night o Use my website and the book for hints Fin jour 3 Table of Contents Chapter 21: Electrochemistry 21.2 – Types of Batteries 21.3 – Electrolysis In class we will cover only what you need to know for the test. Please use your book to answer questions for WebAssign. Electrochemistry: Basic Concepts 21.2: Batteries • Alessandro Volta: • If one cell generates a current, several cells should make a larger current • He piled several cells together to make the first battery • Battery: one or more electrochemical cells in a single package 21.3: Electrolysis • Electrolysis: using electric energy to cause a chemical reaction. • Electrolytic cell: An electrochemical cell in which electrolysis occurs. • Electrolysis forces a current in the reverse direction (a nonspontaneous reaction) by passing an electric current through it (recharging) Electrochemistry: Basic Concepts Voltaic Cell e- e- Electrolytic Cell e- Voltage source e- An electrolytic cell is just the opposite of a voltaic cell Electroplating Reduction of silver ions onto cheaper metals forms silverplate.