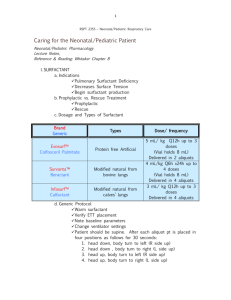
Carbonate rock Study
advertisement

Comparative study of oil recovery efficiency enhanced by surfactants, microemulsion, and nanoemulsion 1,2 Tereza Neuma de Castro Dantas * , 2 Tamyris Thaise Costa de Souza, 2 Afonso Avelino Dantas Neto e 2 Eduardo Lins de Barros Neto 1I N S T I T U T E O F C H E M I S T R Y, P O S T - G R A D U AT I O N P R O G R A M , F E D E R A L U N I V E R S I T Y O F R I O G R A N D E D O NORTE, UFRN, BRAZIL 2 D E PA R T M E N T O F C H E M I C A L E N G I N E E R I N G , P O S T - G R A D U AT I O N P R O G R A M , F E D E R A L U N I V E R S I T Y O F RIO GRANDE DO NORTE, UFRN, BRAZIL * terezaneuma1011@yahoo.com.br ; tereza@eq.ufrn.br Introduction As the reservoir natural energy starts to exhaust, it is necessary to provide additional energy in order to improve the recovery rate. These techniques are called enhanced recovery methods (EOR). In the conventional methods, water or gas are injected in order to keep the reservoir’s energy up. The method’s limitations, such as the viscosity of the retained oil and the high interface tension (fluid/oil), compromises the operations efficiency. The enhanced recovery methods were created to act when the conventional methods are no longer efficient. The main objective of these methods is the interaction between the injected fluid and the oil retained inside the reservoir pores. There are three major categories of EOR: thermal, miscible, and chemical methods. Introduction The oil industry, despite the high levels of technology, still needs help on recovering oil from reservoirs. UFRN – Science and Technology in Surfactants Research Group has developed studies on the use of: These solutions act directly in the rock/oil interface, changing the following properties: - Surfactant solutions; - Microemulsions; - Nanoemulsions. - Interface tension; Wettability; Miscibility; Viscosity. Objective This presentation has, as its main objective, to show the results obtained with the development of new technologies of enhanced oil recovery using surfactant nanoemulsions as injection fluids. solutions, microemulsions, and SURFACTANT Natural or synthetic substances that have a water soluble (polar head group - hydrophilic) and a water insoluble component (tail group hydrophobic), responsible for its adsorption in the liquid-liquid, liquidgas or solid-solid interfaces of a given system. Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions Microemulsions and nanoemulsions are liquid dispersions containing surfactant aggregates. Nanoemulsion Microemulsion oThermodynamically unstable oThermodynamically stable o Transparent aspect X o Transparent aspect o Requires low energy to prepare it – low costs o Requires more energy to be prepared o Greater amount of surfactant o Lower amount of surfactant o Very low interface tension o Low interface tension Methodology Confining pressure apparatus for hydrostatic tests in porous media Experiments using cores of sandstone and carbonate rocks 1st – Brine saturation – injection of KCL 2% at a constant rate of 0.5mL/min; 2nd – Oil saturation – injection of oil (Ubarana Oilfield) at a constant rate of 0.5mL/min; 3rd – Brine injection – conventional recovery 4th – Injection of chemical fluid – enhanced oil recovery Results Sandstone rock study Micromulsion 12.5% - Surfactant 2% - Oil Phase 73% - Aqueous phase Obtained nanoemulsion: 2.5% of Surfactant Ternary phase diagram Nanoemulsion obtaining – Low Energy Results Sandstone rock study Microemulsion x Nanoemulsion 12.5% 2.5% Results Sandstone rock study MICROEMULSION NANOEMULSION Polymer solution % POLYMER 0 0.1 0.5 0 0.1 0.5 0.5 % Conventional Efficiency 71.3 62.5 68.0 57.5 56.7 57.0 53.2 % Advanced Efficiency 56.9 61.3 87.5 39.4 52.6 85.0 30.1 % Total efficiency 87.6 85.50 96.0 74.4 79.4 93.5 67.5 Microemulsion 12.5% - Surfactant Nanoemulsion 2.5% - Surfactant Results Carbonate rock study Micromulsion 12.5% - Surfactant 2% - Oil Phase 73% - Aqueous phase Results Carbonate rock study Conventional efficiency (%) Advanced efficiency (%) Total efficiency (%) ST 54.0 12.5 60.0 ST (KCl 2wt%) 62.0 27.5 72.0 Micro 64.0 59.0 85.0 Micro (KCl 2wt%) 68.0 52.0 84.0 ST – Surfactant solution Micro - Microemulsion Results Carbonate rock Study Study of nanoemulsion systems that were obtained by infinite dilution of microemulsiom systems. Results Carbonate rock study Nanoemulsion 1% - Surfactant Conventional efficiency(%) 59.0 Advanced efficiency (%) 28.0 Total efficiency (%) 70.0 Conclusions o The presented results show the overall potential for surfactant solution, microemulsions, and nanoemulsions application in enhanced oil recovery; o The methods using the developed systems present some extra advantages when compared with other methods, considering that they interact directly with the oil and, consequently, promote the displacement by miscibility and/or reduction of the interface tension between the fluid and the oil, increasing oil production after the conventional treatment; o The nanoemulsion application presents as advantage the use of small amounts of surfactant in its composition.