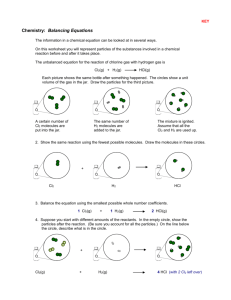
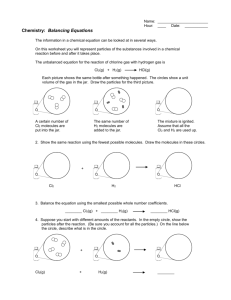
16.1, 16.2: Reaction rate p. 568-572 1. List 6 factors that affect the
advertisement

16.1, 16.2: Reaction rate p. 568-572 1. List 6 factors that affect the rate at which a reaction will occur. 2. Explain how each factor affects reaction rate: a. ________________________: b. ________________________: c. ________________________: d. ________________________: e. ________________________: f. ________________________: p. 560-562 3. What does reaction rate refer to? 4. What is average rate equal to? 5. What is the average reaction rate equation? 6. How does the concentration of reactants change over time during the course of a chemical reaction?(figure 16.2) 7. How does the concentration of products change over time during the course of a chemical reaction?(figure 16.2) 8. How are reaction rates determined? Can they be determined from a balanced chemical reaction? Example: In a reaction between CO and NO2, CO2 and NO are formed. At the start of the reaction, time = 0.00s, the concentration of NO = 0.000M. 2 seconds later (time = 2.00s), the concentration of NO is 0.010M. What is the average rate of the reaction? Average reaction rate = 0.010M – 0.000M = 0.0050 mol/L s 2.00s – 0.00s Practice problems: 1. In the reaction A 2B, suppose that [A] changes from 1.20 M at time = 0 to 0.60 M at time = 3.00 min and that [B] = 0.00 M at time = 0. What is the average rate at which A is consumed in mol/L min? 2. For the reaction H2 + Cl2 2HCl, the following data was collected: Time [H2] [Cl2] 0.00 s 0.030 M 0.050 M 4.00 s 0.020 M 0.040 M a. [HCl] 0.000 M What is the average rate of the reaction? b. What would the [Cl2] be after 4 seconds? Did it increase or decrease? Explain. c. What would the [HCl] be at 4 seconds? Did it increase or decrease? Explain.