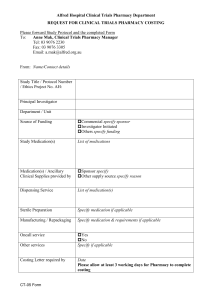
Day 1 slides Module 1 (ppt)

HEALTHCARE
QUALITY
CONCEPTS
Chapter 1
Changing Perspectives in Quality
•
• “Quality in a product or behavior. service is not what the supplier puts in.
It is what the customer conversations in healthcare that if avoided can gets out and is willing to pay for.”
• Participants can identify 2 skills that are essential to effective communication.
2
3
QUALITY, COST,
AND RISK INTEGRATION
Value =
Quality of Care/Services + Outcomes
Cost
4
NON-INTEGRATED
PERSPECTIVE
Governance
Clinical Mgmt
Support
5
Integrated Perspective
Clinical
Support
Management
Governance
6
QUALITY MANAGEMENT:
BASIC PRINCIPLES
• Productive Work is Accomplished Through
Processes.
• Sound Customer-Supplier Relationships are
Absolutely Necessary for Sound Quality
Management.
• The Main Source of Quality Defects is
Problems in the Process.
• Poor Quality is Costly.
7 QUALITY MANAGEMENT:
BASIC PRINCIPLES
• Understanding the Variability of Processes is
Key to Improving Quality.
• Quality Control Should Focus on the Most
Vital Processes.
• The Modern Approach to Quality is
Thoroughly Grounded in Scientific and
Statistical Thinking.
8
QUALITY MANAGEMENT:
BASIC PRINCIPLES
• Total Employee Involvement is Critical.
• New Organizational Structures Can Help Achieve
Quality Improvement.
• Quality Management Employs:
– Quality planning
– Quality control (measurement)
– Quality Improvement
9
TOTAL QUALITY
MANAGEMENT
• An Organizational Management Philosophy and
Top-Level Commitment to Foster a Belief in the
Value of:
Customers
Employees/staff
Management
Teamwork
Deming’s 14 points
10
CONTINUOUS QUALITY
IMPROVEMENT
CQI is a Management Approach of Study and Improving Processes
It is a Management Method for Creating
TQM
At CQI’s Core is a Quality Culture/Patient
Safety Culture
11
CONTINUOUS QUALITY
IMPROVEMENT
Organizational Commitment
Quality Culture
Customer Focus
Team Emphasis on Improving Systems and
Processes
Constant Learning and Improving
12
RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE QUALITY
PROFESSIONAL
Understand Principles of TQM and CQI
Develop a Healthcare Quality Strategy
Participate in Preparation for External Awards
Articulate to Leadership How to Use
TQM and CQI
Data Measurement
Assessment
Improvement
Lead and facilitate change within the organization
13
SYSTEMS THINKING
System:
Perceived whole whose elements hang together effecting each other
Systems Thinking:
A body of principles, methods, and tools focused on the interrelatedness of forces in a system
14
PROCESSES IN SYSTEMS THINKING
Systemic Structure Key
Components:
Process flows,
Attitudes & perceptions,
Ways decisions are made,
Hierarchy
The system working with all its parts
15
PROCESSES IN SYSTEMS THINKING
Four Levels in Systems:
Events (occurrences)
Patterns of Behavior (trends over time)
System Structure (decisions, relationships, efforts, targets, incentives, etc.)
Mental Models (beliefs, assumptions, mind sets about ways work gets done)
16
SYSTEMS THINKING -PROCESS
TOOLS
• Cause and Effect Relationships
A affects B affects C
• Process Diagrams Show a Flow or Sequence of
Activities
A then B then C
Systems Thinking
• Who are the various owners of the process?
• What group of people have some stake or ownership of different parts of the process?
• You can address the symptoms, but until you address the problem you can not resolve it
• Addressing the symptoms is call the Band-Aid approach
17
Medication Process
• MD writes order
• Sent to Pharmacy by Nursing
• Pharmacy fills the order
• Pharmacy sends the medication up to the Nursing
Unit
• Nurses give the medication
• Nurses & MD monitors the patient’s condition
18
Medication Process
• What if the doctor’s handwriting can not be read and doctor is not available?
• What if the Pharmacy decides not to fill it until later?
Or if the Pharmacy has no medication
• What if it does not get to the unit until after the time it was needed?
• What if the nurses are too busy to be able to give the medication on time?
19
Medication Process
• What if Nursing decides to change the times they administer the medications and does not tell the
Pharmacy?
• What if the Pharmacy does not have a medication and does not contact the doctor until after clinic hours and the MD is not on call?
• What if Pharmacy decides to send the medication in 2 pouches instead of just one?
20
Systems Thinking
• You need to examine the players and determine who will be affected by any actions that you take
• You want to expand your clinic?
– How many more practitioners ?
– Nursing staff to run the clinic & move patients around?
– Lab work increase of workload?
– Radiology increase of workload?
– Pharmacy have needed medications?
• CAN NOT DO IT BY YOURSELF when you want to do something like this
21
THE CONCEPT
OF CUSTOMER
• “Customer” – One Who Receives
Goods or Services
• External Customer – Those Outside the Organization Receiving Services
• Internal Customer – Those
Performing Work, but Dependent
On Others Within the Organization
Performing Work
• Customer Supplier Relationships
22
CUSTOMER FOCUS
• Listen To & Communicate With Customers;
• Identify and Address True Needs;
• Optimize Treatment Patterns and Outcomes:
• Enhance Performance of Internal Processes;
• Respond to Requests For Information;
• Build Trust, Respect, and Loyalty in
Relationships
• Patient Centered Care
• Coordination of Care
23
Keeping the Customer in Mind
• Dissemination of cultural transformation and performance improvement information
within the organization and
to our customers!
24
IDENTIFYING CUSTOMERS AND THEIR
NEEDS
• Identifying Customer Needs & expectations:
Surveys and interviews
Focus groups
Research
Brainstorming
Teams
25
ORGANIZATIONAL
CULTURE
• Culture – Basic Set of Assumptions
About People, How People Work
Together and How Work Gets Done.
26
IMPACT OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
Organizational Ethics
Patient Safety
Corporate Compliance
Organizational Change
Performance and Productivity
Internal and External Customers
27
Quality & Patient Safety Culture
• Most organizations have different organizational cultures, including different healthcare organizations
• Healthcare must change into a Quality and Patient
Safety culture if we are to survive
• There must be a Patient Centered culture
• Care must be Evidence-Based
• Teamwork is essential
28
CULTURAL
TRANSFORMATION
Just Culture – Blame Free
Adoption of “Quality / Patient Safety Culture”
Commitment to Excellence
Long-range Strategic Planning
Flexible Management Styles
Systems Thinking
Delegation and Empowerment
Team Building
Increase Communication
29
CULTURAL
TRANSFORMATION
Visionary Leadership
Systems
Thinking
Inspiration
Management’s Commitment
Employee
Involvement Team Building
Calculated Risk
Taking
Implementation Engagement
Innovation
30
So, How Do We Get There?
• Need to start with defining quality at an organization
• Assess where the organization is in terms of the organizational culture
• Develop and design what the new Quality /
Patient Safety Culture will look like and how to get there
31
REDESIGNING
THE ORGANIZATION
Sustained Approach
Downsizing
Restructuring/Rightsizing
Organizational Structure
Reengineering
32
REEINGINEERING
Work
Redesign
Customer
Focus
Service
Integration
Management
Restructuring
Cross Training
33
INTEGRATED DELIVERY SYSTEMS
• Types:
– Horizontal
Hospital
A
Hospital
D
– Vertical
Hospital
B
Hospital
Hospital C
Rehab
LTC
Clinic
• Degrees of Integration
34
EVALUATING CLINICAL
INTEGRATION
Coordination of Clinical
Processes and Services
Appropriate Sharing of Facilities and
Services
Cost
Effective
Care
Avoid
Unnecessary
Duplication
35
Other Leadership Topics
• Awareness of Statutory & Regulatory
Requirements
– OSHA
– HIPAA
– PPACA
• Quality & Reimbursement
– Capitation
– Pay for Performance