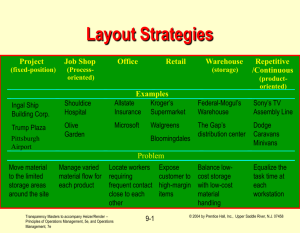
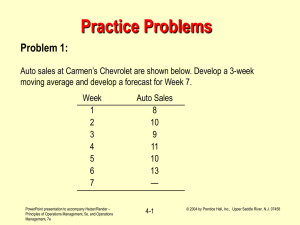
Chapter 1, Heizer/Render, 5th edition
advertisement

Operations Management Forecasting Chapter 4 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-1 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 SATIŞ TAHMİNLEMESİ PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-2 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 BİR İŞLETLETMENİN BAŞARISI İLERİYİ NE KADAR İYİ GÖREBİLMESİNE VE UYGUN STRATEJİLER GELİŞTİRMESİNE BAĞLIDIR PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-3 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 YÖNETİCİLERİN EN TEMEL GÖREVİ: PLAN YAPMAKTIR PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-4 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 PLANLAR GELECEĞE YÖNELİKTİR PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-5 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 ÖYLEYSE GELEÇEĞİ TAHMİNLEMEK ZORUNDAYIZ PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-6 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 YÖNETİÇİLERİN ALDIĞI KARARLARIN BİR ÇOĞUNDA AZ YADA ÇOK BİR TÜR TAHMİN YER ALIR PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-7 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 ÖRNEK BİR BÜRO ŞEFİNİN CUMA GÜNÜ BAZI MEMURLARINA İZİN VEREBİLMEK İÇİN CUMA GÜNÜN İŞ YÜKÜNÜ TAHMİN ETMESİ PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-8 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-9 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 ASLINDA GÜNLÜK HAYATIMIZIN BİR ÇOK KESİTİNDE DE TAHMİN YAPIYORUZ ÖRNEK; PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-10 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 ANCAK BU TAHMİNLERİN BİR KISMI OLDUKÇA KOLAYKEN TAHMİNLENMESİ ÇOK ZOR OLAN KONULARDA VARDIR PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-11 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 ÖRNEĞİN BİR OTOMOTİV ENDÜSTRİSİNİN FİNANS MÜDÜRÜNÜN GELEÇEK YILKI MEVSİMLİK FİNANS İHTİYACINI TAHMİNLEMESİ PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-12 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecasting and optimization are complex Come on! It can‘t go wrong every time... PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-13 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Select significant attributes for your forecaster Which one Is mine? PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-14 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 What is Forecasting? Process of predicting a future event Sales will be $200 Million! Underlying basis of all business decisions Production Inventory Personnel Facilities PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-15 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 TAHMİNLEME NEDİR? EDMUND BURK’YE GÖRE: geçmişe bakarak geleceği hiçbir zaman planlayamassınız. PATRICK HENRY İSE; geçmiş olmadan geleceği hiçbir şekilde yargılayacak bir yol bilmiyorum der. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-16 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 tanımlar “ Tahmin;geleçekteki muhtemel olayların belirli bir zamanda saptanması,hesaplanması ya da kestirimidir. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-17 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 TAHMİNLEME SİSTEMİ ÇİZİM PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-18 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 TAHMİNLEME SİSTEMİ GİRDİLER *PAZAR DURUMLAR *GEÇMİŞ SATIŞLAR *İŞLETME STRATEJİLERİ *ENDÜSTRİNİN DURUMU *EKONOMİNİN DURUMU *TİÇARİ REKABET DURUMU *ÜRETİM KAPASİTESİ *IHUKUKİ VE POLİTİK FAKTÖRLER *DİĞER FAKTÖRLER ÇIKTILAR TAHMİNLEME TEKNİKLERİ VEYA MODELLERİ SATIŞ TAHMİNİ HER MAL İÇİN HER ZAMAN DÖNEMİNDE TALEP TAHMİNİ KARAR VERİCİ PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-19 •HER MAL İÇİN HER ZAMAN DÖNEMİNDE BEKLENEN TALEP *DİGER FAKTÖRLER BAŞKALARININ ÖNERİLERİ RİSK DURUMU TECRÜBE İNSİYATİF VE HİS KİŞİSEL DEĞERLER VE GÜDÜLER SOSYAL VE KÜLTÜREL DEGERLER ÖTEKİ FAKTÖRLER © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Types of Forecasts by Time Horizon Short-range forecast Up to 1 year; usually less than 3 months Job scheduling, worker assignments Medium-range forecast 3 months to 3 years Sales & production planning, budgeting Long-range forecast 3+ years New product planning, facility location PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-20 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Short-term vs. Longer-term Forecasting Medium/long range forecasts deal with more comprehensive issues and support management decisions regarding planning and products, plants and processes. Short-term forecasting usually employs different methodologies than longer-term forecasting Short-term forecasts tend to be more accurate than longer-term forecasts. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-21 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Influence of Product Life Cycle Stages of introduction and growth require longer forecasts than maturity and decline Forecasts useful in projecting staffing levels, inventory levels, and factory capacity as product passes through life cycle stages PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-22 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Strategy and Issues During a Product’s Life Introduction Company Strategy/Issues Best period to increase market share R&D product engineering critical Growth Maturity Practical to change price or quality image Poor time to change image, price, or quality Competitive costs become critical Strengthen niche Fax machines CD-ROM Color copiers Cost control critical Defend market position Drive-thru restaurants Sales Decline 3 1/2” Floppy disks Station wagons Internet HDTV OM Strategy/Issues Product design and development critical Frequent product and process design changes Short production runs High production costs Forecasting critical Standardization Product and process reliability Less rapid product changes - more minor changes Competitive product improvements and options Increase capacity Limited models Shift toward product focused Attention to quality Enhance distribution PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) Optimum capacity Increasing stability of process Long production runs Product improvement and cost cutting 4-23 Little product differentiation Cost minimization Over capacity in the industry Prune line to eliminate items not returning good margin Reduce capacity © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Types of Forecasts Economic forecasts Address business cycle, e.g., inflation rate, money supply etc. Technological forecasts Predict technological change Predict new product sales Demand forecasts Predict existing product sales PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-24 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Seven Steps in Forecasting Determine the use of the forecast Select the items to be forecast Determine the time horizon of the forecast Select the forecasting model(s) Gather the data Make the forecast Validate and implement results PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-25 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Product Demand Charted over 4 Years with Trend and Seasonality Demand for product or service Seasonal peaks Trend component Actual demand line Random variation Year 1 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) Year 2 4-26 Average demand over four years Year 3 Year 4 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Jury of Executive Opinion Involves small group of high-level managers Group estimates demand by working together Combines managerial experience with statistical models Relatively quick ‘Group-think’ disadvantage PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-27 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 © 1995 Corel Corp. Sales Force Composite Each salesperson projects their sales Combined at district & national levels Sales rep’s know customers’ wants Tends to be overly optimistic Sales © 1995 Corel Corp. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-28 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Delphi Method Iterative group process 3 types of people Decision makers Staff Respondents Decision Makers Staff (What will sales be? survey) Reduces ‘groupthink’ PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) (Sales?) (Sales will be 50!) Respondents (Sales will be 45, 50, 55) 4-29 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Consumer Market Survey Ask customers about purchasing plans What consumers say, and what they actually do are often different Sometimes difficult to answer PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) How many hours will you use the Internet next week? © 1995 Corel Corp. 4-30 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Overview of Quantitative Approaches Naïve approach Moving averages Exponential smoothing Trend projection Time-series Models Linear regression Associative models PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-31 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Quantitative Forecasting Methods (Non-Naive) Quantitative Forecasting Associative Models Time Series Models Moving Average Exponential Smoothing PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) Trend Projection 4-32 Linear Regression © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 What is a Time Series? Set of evenly spaced numerical data Obtained by observing response variable at regular time periods Forecast based only on past values Assumes that factors influencing past and present will continue influence in future Example Year: Sales: 1993 78.7 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 1994 63.5 4-33 1995 89.7 1996 93.2 1997 92.1 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Time Series Components Trend Cyclical Seasonal Random PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-34 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Trend Component Persistent, overall upward or downward pattern Due to population, technology etc. Several years duration Response Mo., Qtr., Yr. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-35 © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Seasonal Component Regular pattern of up & down fluctuations Due to weather, customs etc. Occurs within 1 year Summer Response © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. Mo., Qtr. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-36 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Cyclical Component Repeating up & down movements Due to interactions of factors influencing economy Usually 2-10 years duration Cycle Response Mo., Qtr., Yr. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-37 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Random Component Erratic, unsystematic, ‘residual’ fluctuations Due to random variation or unforeseen events © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. Union strike Tornado Short duration & nonrepeating PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-38 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 General Time Series Models Any observed value in a time series is the product (or sum) of time series components Multiplicative model Yi = Ti · Si · Ci · Ri (if quarterly or mo. data) Additive model Yi = Ti + Si + Ci + Ri PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) (if quarterly or mo. data) 4-39 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Naive Approach Assumes demand in next period is the same as demand in most recent period e.g., If May sales were 48, then June sales will be 48 Sometimes cost effective & efficient © 1995 Corel Corp. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-40 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Moving Average Method MA is a series of arithmetic means Used if little or no trend Used often for smoothing Provides overall impression of data over time Equation Demand in Previous n Periods MA n PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-41 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Moving Average Example You’re manager of a museum store that sells historical replicas. You want to forecast sales (000) for 1998 using a 3-period moving average. 1993 4 1994 6 1995 5 1996 3 1997 7 © 1995 Corel Corp. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-42 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Moving Average Solution Time 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Response Yi 4 6 5 3 7 Moving Total (n=3) NA NA NA 4+6+5=15 Moving Average (n=3) NA NA NA 15/3 = 5 NA PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-43 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Moving Average Solution Time 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Response Yi 4 6 5 3 7 Moving Total (n=3) NA NA NA 4+6+5=15 6+5+3=14 Moving Average (n=3) NA NA NA 15/3 = 5 14/3=4 2/3 NA PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-44 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Moving Average Solution Time 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 Response Yi 4 6 5 3 7 NA PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) Moving Total (n=3) NA NA NA 4+6+5=15 6+5+3=14 5+3+7=15 4-45 Moving Average (n=3) NA NA NA 15/3=5.0 14/3=4.7 15/3=5.0 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Moving Average Graph Sales 8 Actual 6 Forecast 4 2 95 96 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 97 98 Year 4-46 99 00 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Weighted Moving Average Method Used when trend is present Older data usually less important Weights based on intuition Often lay between 0 & 1, & sum to 1.0 Equation WMA = Σ(Weight for period n) (Demand in period n) PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) ΣWeights 4-47 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Actual Demand, Moving Average, Weighted Moving Average 35 Sales Demand 30 25 Weighted moving average Actual sales 20 15 10 Moving average 5 0 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Month PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-48 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Disadvantages of Moving Average Methods Increasing n makes forecast less sensitive to changes Do not forecast trend well Require much historical data © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-49 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Method Form of weighted moving average Weights decline exponentially Most recent data weighted most Requires smoothing constant () Ranges from 0 to 1 Subjectively chosen Involves little record keeping of past data PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-50 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Equations Ft = At - 1 + (1-)At - 2 + (1- )2·At - 3 + (1- )3At - 4 + ... + (1- )t-1·A0 Ft = Forecast value At = Actual value = Smoothing constant Ft = Ft-1 + (At-1 - Ft-1) Use for computing forecast PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-51 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Example You’re organizing a Kwanza meeting. You want to forecast attendance for 2000 using exponential smoothing ( = .10). The1995 forecast was 175. 1995 180 1996 168 1997 159 1996 175 1999 190 © 1995 Corel Corp. PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-52 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, F t (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 1997 159 1998 175 1999 190 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) 175.00 + PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-53 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, F t (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 1997 159 1998 175 1999 190 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) 175.00 + .10( PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-54 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, Ft (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 1997 159 1998 175 1999 190 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) 175.00 + .10(180 - PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-55 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, Ft (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 1997 159 1998 175 1999 190 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) 175.00 + .10(180 - 175.00) PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-56 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, Ft (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 1997 159 1998 175 1999 190 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) 175.00 + .10(180 - 175.00) = 175.50 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-57 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, F t (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1994 168 175.00 + .10(180 - 175.00) = 175.50 1995 159 175.50 + .10(168 - 175.50) = 174.75 1996 175 1997 190 1998 NA 175.00 (Given) PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-58 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, F t (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 175.00 + .10(180 - 175.00) = 175.50 1997 159 175.50 + .10(168 - 175.50) = 174.75 1998 175 174.75 + .10(159 - 174.75)= 173.18 1999 190 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-59 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, F t (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 175.00 + .10(180 - 175.00) = 175.50 1997 1998 159 175.50 + .10(168 - 175.50) = 174.75 175 174.75 + .10(159 - 174.75) = 173.18 1999 190 173.18 + .10(175 - 173.18) = 173.36 2000 NA 175.00 (Given) PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-60 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Solution Ft = Ft-1 + · (At-1 - Ft-1) Forecast, F t (α = .10) Time Actual 1995 180 1996 168 175.00 + .10(180 - 175.00) = 175.50 1997 159 175.50 + .10(168 - 175.50) = 174.75 1998 175 174.75 + .10(159 - 174.75) = 173.18 1999 190 173.18 + .10(175 - 173.18) = 173.36 2000 NA 173.36 + .10(190 - 173.36) = 175.02 175.00 (Given) PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-61 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Exponential Smoothing Graph Sales 190 180 170 160 150 140 93 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) Actual Forecast 94 95 96 Year 4-62 97 98 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecast Effects of Smoothing Constant Ft = At - 1 + (1- )At - 2 + (1- )2At - 3 + ... Weights = Prior Period 2 periods ago 3 periods ago = 0.10 (1 - ) (1 - )2 10% = 0.90 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-63 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecast Effects of Smoothing Constant Ft = At - 1 + (1- ) At - 2 + (1- )2At - 3 + ... Weights = Prior Period = 0.10 2 periods ago 3 periods ago (1 - ) 10% 9% (1 - )2 = 0.90 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-64 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecast Effects of Smoothing Constant Ft = At - 1 + (1- )At - 2 + (1- )2At - 3 + ... Weights = Prior Period = 0.10 2 periods ago 3 periods ago (1 - ) (1 - )2 10% 9% 8.1% = 0.90 PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-65 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecast Effects of Smoothing Constant Ft = At - 1 + (1- )At - 2 + (1- )2At - 3 + ... Weights = Prior Period 2 periods ago 3 periods ago (1 - ) (1 - )2 = 0.10 10% 9% 8.1% = 0.90 90% PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-66 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecast Effects of Smoothing Constant Ft = At - 1 + (1- ) At - 2 + (1- )2At - 3 + ... Weights = Prior Period 2 periods ago 3 periods ago (1 - ) (1 - )2 = 0.10 10% 9% 8.1% = 0.90 90% 9% PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-67 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Forecast Effects of Smoothing Constant Ft = At - 1 + (1- ) At - 2 + (1- )2At - 3 + ... Weights = Prior Period 2 periods ago 3 periods ago (1 - ) (1 - )2 = 0.10 10% 9% 8.1% = 0.90 90% 9% 0.9% PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) 4-68 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458 Choosing Seek to minimize the Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) If: Then: Forecast error = demand - forecast MAD PowerPoint presentation to accompany Operations Management, 6E (Heizer & Render) forecast errors n 4-69 © 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, N.J. 07458